相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
上海联迈生物工程有限公司
- 库存:
大量
- 靶点:
详见说明书
- 级别:
1
- 目录编号:
LM-10484R-FITC
- 克隆性:
多克隆
- 抗原来源:
Rabbit
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
Anti-Heparanase/FITC
- 抗体名:
Anti-Heparanase/FITC
- 标记物:
FITC标记
- 宿主:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit,
- 适应物种:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit,
- 免疫原:
详见说明书
- 亚型:
IGg
- 形态:
粉末、液体、冻干粉
- 应用范围:
详见说明书
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °C
- 规格:
100ul
| 英文名称 | Anti-Heparanase/FITC |
| 中文名称 | FITC标记的乙酰肝素酶抗体 |
| 别 名 | Heparanase 50 kDa subunit; heparanase; heparanase1; heparanase-1; heparanase 1; Endo glucoronidase; Endo glucoronidase; Endo-glucoronidase; HPSE_HUMAN; Heparanase1; Heparanase 1; HEP; Hpa 1; HPA; Hpa1; HPR 1; HPR1; HPSE 1; HPSE; HPSE1; HSE 1; HSE1. |
| 规格价格 | 100ul/2980元 购买 大包装/询价 |
| 说 明 书 | 100ul |
| 研究领域 | 肿瘤 细胞生物 免疫学 细胞类型标志物 |
| 抗体来源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆类型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反应 | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit, |
| 产品应用 | not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 43kDa |
| 性 状 | Lyophilized or Liquid |
| 浓 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Heparanase |
| 亚 型 | IgG |
| 纯化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存条件 | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
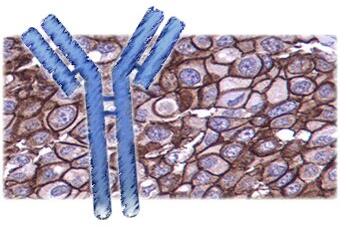
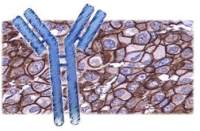
| 产品介绍 | background: Heparanase is an endo-beta-D-glucuronidase, which degrades heparan sulfate side chains of heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) in the extracellular matrix. Heparanase plays an important role in ECM degradation, facilitating the migration and extravasations of tumor cells and inflammatory leukocytes. Upon degradation, heparanase releases growth factors and cytokines that stimulate cell proliferation and chemotaxis. Heparanase is a heterodimer comprised of a 50 kDa subunit harboring the active site and an 8 kDa subunit. It is produced as a latent 65 kDa precursor and proteolytically processed to its active form. Heparanase is highly expressed in myeloid leukocytes (i.e. neutrophils) in platelets and in human placenta. Human heparanase was found to be upregulated in various types of primary tumors, correlating in some cases with increased tumor invasiveness and vascularity and with poor prospective survival. Function: Endoglycosidase that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) into heparan sulfate side chains and core proteoglycans. Participates in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and remodeling. Selectively cleaves the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying either a 3-O-sulfo or a 6-O-sulfo group. Can also cleave the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying a 2-O-sulfo group, but not linkages between a glucuronic acid unit and a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid moiety. It is essentially inactive at neutral pH but becomes active under acidic conditions such as during tumor invasion and in inflammatory processes. Facilitates cell migration associated with metastasis, wound healing and inflammation. Enhances shedding of syndecans, and increases endothelial invasion and angiogenesis in myelomas. Acts as procoagulant by increasing the generation of activation factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activation factor VII. Increases cell adhesion to the extacellular matrix (ECM), independent of its enzymatic activity. Induces AKT1/PKB phosphorylation via lipid rafts increasing cell mobility and invasion. Heparin increases this AKT1/PKB activation. Regulates osteogenesis. Enhances angiogenesis through up-regulation of SRC-mediated activation of VEGF. Implicated in hair follicle inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis. Subunit: Heterodimer; heterodimer formation between the 8 kDa and the 50 kDa subunits is required for enzyme activity. Interacts with TF; the interaction, inhibited by heparin, enhances the generation of activated factor X and activates coagulation. Interacts with HRG; the interaction is enhanced at acidic pH, partially inhibits binding of HPSE to cell surface receptors and modulates its enzymatic activity. Interacts with SDC1; the interaction enhances the shedding of SDC1. Subcellular Location: Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Secreted. Nucleus. Note=Proheparanase is secreted via vesicles of the Golgi. Interacts with cell membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs). Endocytosed and accumulates in endosomes. Transferred to lysosomes where it is proteolytically cleaved to produce the active enzyme. Under certain stimuli, transferred to the cell surface. Associates with lipid rafts. Colocalizes with SDC1 in endosomal/lysosomal vesicles. Accumulates in perinuclear lysosomal vesicles. Heparin retains proheparanase in the extracellular medium. Tissue Specificity: Highly expressed in placenta and spleen and weakly expressed in lymph node, thymus, peripheral blood leukocytes, bone marrow, endothelial cells, fetal liver and tumor tissues. Also expressed in hair follicles, specifically in both Henle's and Huxley's layers of inner the root sheath (IRS) at anagen phase. Post-translational modifications: Proteolytically processed. The cleavage of the 65 kDa form leads to the generation of a linker peptide, and 8 kDa and 50 kDa products. The active form, the 8/50 kDa heterodimer, is resistant to degradation. Complete removal of the linker peptide appears to be a prerequisite to the complete activation of the enzyme. N-glycosylated. Glycosylation of the 50 kDa subunit appears to be essential for its solubility. Similarity: Belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 79 family. Database links: Entrez Gene: 10855 Human Entrez Gene: 15442 Mouse Entrez Gene: 64537 Rat Omim: 604724 Human SwissProt: Q9Y251 Human SwissProt: Q6YGZ1 Mouse SwissProt: Q71RP1 Rat Unigene: 44227 Human Unigene: 265786 Mouse Unigene: 6392 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验当FITC在碱性溶液中与抗体蛋白反应时,主要是蛋白质上赖氨酸的r氨基与荧光素的硫碳胺键(thiocarbmide)结合,形成FITC-蛋白质结合物,即荧光抗体或荧光结合物。一个IgG分子中有86个赖氨酸残基,一般最多能结合15~20个,一个IgG分子可结合2~8个分子的FITC,其反应式如下FITC-N=C=S + N-H2-蛋白质 → FITC-NS-C-N-H2-蛋白质常用Marsshall(1958)法标记荧光抗体,也可以根据条件采用Chadwick等标记法或Clark
ml三蒸水中即成; 方法与步骤: 根据Marshall氏法高效价的抗人球蛋白兔免疫血清,分离球蛋白。 1. 用0.15 mol/L NaCl的盐水及0.15 mol/L pH9.0的NaHCO3-Na2CO3缓冲液稀释使每毫升内含抗体10mg,缓冲液为总量的10%; 2. 将以上溶液降温至4℃,按蛋白:荧光素=50—80mg:1mg的比例加入异硫氰酸荧光素,在0—4℃下电磁搅拌12—14h; 3.用半饱和硫酸铵将标记球蛋白
5. 过柱。取透析过夜的标记物,过葡萄糖凝胶G-25或G-50柱,分离出游离荧光素,收集标记的荧光抗体进行鉴定。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料