相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 国食药监械注册号:
无
- 库存:
100
- 供应商:
上海玉研科学仪器有限公司
- 现货状态:
现货供应MouseOx Plus小动物监护仪
- 保修期:
12个月
- 规格:
敬请来电咨询
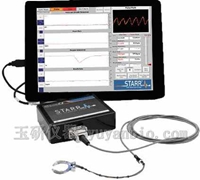
玉研仪器公司作为Mouse Ox Plus 小动物脉搏血氧仪产品的中国区总代理,该仪器适用于小鼠、大鼠、豚鼠、兔子等动物,可以在清醒或麻醉状态下测量动物的脉搏、血氧、呼吸、体温等多种生理参数。
· 小动物脉搏血氧仪可用于多参数数据的采集或手术监护,可拓展多通道大鼠、小鼠的生理信号测量仪;
· 以无创的方式测量小动物(幼鼠,小鼠,大鼠,豚鼠,兔, 等)的血氧饱和度、脉搏频率、呼吸频率、脉搏幅度、呼吸幅度和体温;
· 除体温外,所有测量都是通过一个无创的感应器。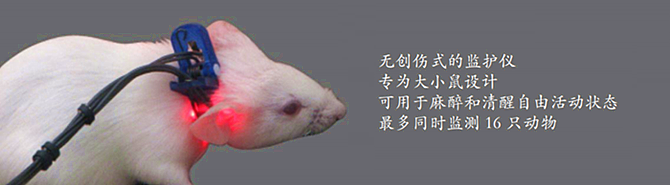
所有测量都是通过一个无创的感应器完成,准确、方便、高效。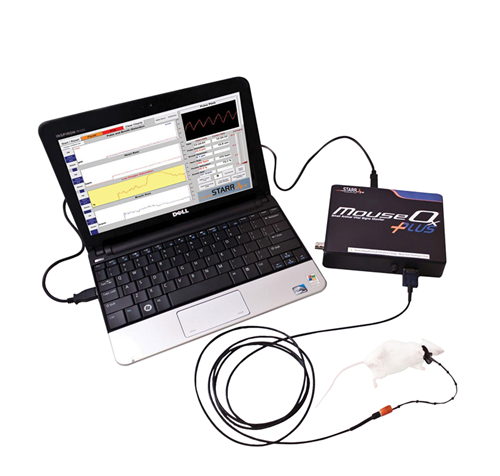
型号:MouseOx 正在对麻醉状态下的小鼠进行测试
有多种探头可供选择:
· 根据实验需求:可选择大鼠型探头、小鼠型探头;
· 根据动物状态:可选择清醒活动状态连续测量和麻醉(或手术)状态测量探头;
· 根据动物数量:有多通道适配器可供选择,同时检测多只动物的生命体征;
· 根据使用环境:可选择核磁环境适用的无磁探头;
主要功能:
· 小动物手术术中监测(保证适当的麻醉深度,防止手术中缺氧)
· 一个无创传感器获得多个生命信号 (动脉血氧饱和度,心率,呼吸频率,脉搏幅度,呼吸幅度)
· 心肺功能参数记录
· 输出模拟数据
经过验证的准确度:
使用有创血气采样测量结果与无创 MouseOx 测量结果的比较, 对比表明, 两者具有很好的线性关系。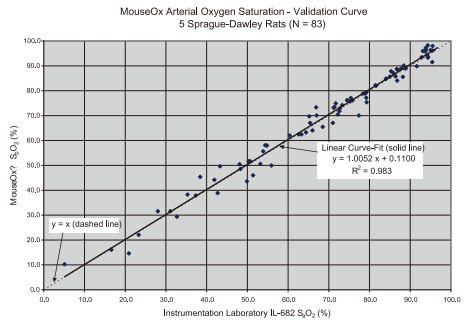
脉搏、血氧、呼吸等心肺监测参数:
· 脉波频率在90到900BPM范围内监测 (每分钟心跳, Beat per minutes, BPM)
· 血氧饱和度监测范围:0% 到100% 动脉血氧饱和度;
· 血氧饱和度监测误差:<1.5% 横跨整个监测范围;
· 血氧饱和度监测反应时间:实时报告动脉血氧饱和度, 在每次心跳以后0.72秒屏幕刷新;
· 呼吸频率监测范围:每分钟 25到450 次;
· 监测反应时间:呼吸率每1.7秒向用户报告, 移动报告的值是10次呼吸的的平均数;
· 无创伤监测脉搏充盈度以估量血流量的变化;
· 脉搏监测范围:内径0到800微米的徽小血管;
· 监测误差:< 2.4%横跨整个监测范围;
· 监测反应时间:脉搏充盈度实时向用户报告, 在每次心跳以后,0.72秒屏幕刷新,刷新屏幕显示被测量的所有脉搏充盈度;
· 无创伤监测动物呼吸幅度的变化;
· 呼吸幅度监测范围:每分钟25到450次;
· 呼吸幅度监测反应时间:呼吸率每1.7秒向用户报告, 移动报告的值是10次呼吸的的平均数;
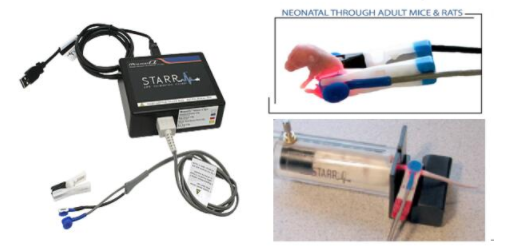
多钟测试探头可选:
根据需要,可选择老鼠清醒状态下使用的颈部探头,麻醉状态下使用的足部探头和大腿探头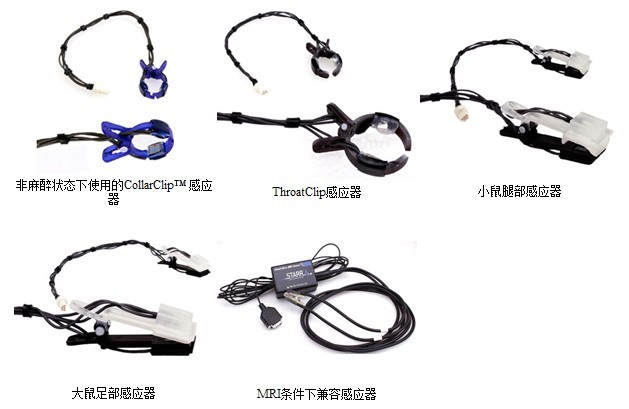
以下是使用有创血气采样测量结果与无创MouseOx测量结果的比较
可实现大鼠、小鼠清醒活动状态下进行测量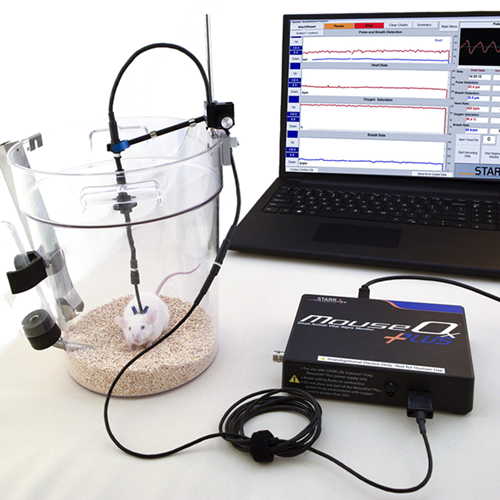
软件界面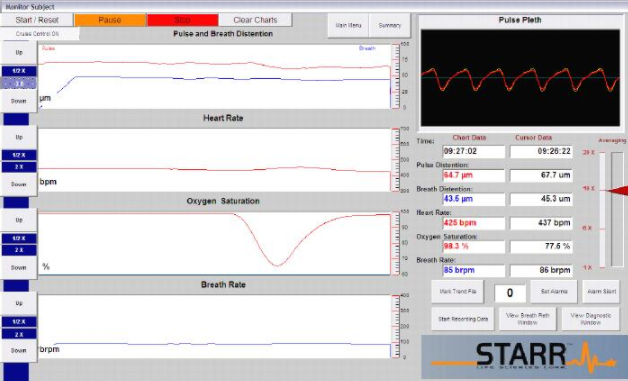
小动物脉搏血氧监护仪的部分参考文献:
1. Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013). The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin modulates the firing 1 properties of the reticular thalamic nucleus bursting neurons. Journal of neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2. Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013). The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein. Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
3. Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013). Enduring Effects of Early Life Stress on Firing Patterns of Hippocampal and Thalamocortical Neurons in Rats: Implications for Limbic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
4. Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic Muscarinic Response Types in Hippocampal CA1 Interneurons Depend on Different Levels of Presynaptic Activity and Different Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes. Neuropharmacology.
5. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
6. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
7. Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013). Effect of BDNF and adipose derived stem cells transplantation on cognitive deficit in Alzheimer model of rats. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
8. Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013). Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
9. Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012). Responsiveness to nicotine of neurons of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract correlates with the neuronal projection target. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
10. Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012). Myelin debris regulates inflammatory responses in an experimental demyelination animal model and multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
11. Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011). Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: A PGE2-independent mechanism.Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
12. Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A27 Expression of the human mutant huntingtin in minipig striatum induced formation of EM48+ inclusions in the neuronal nuclei, cytoplasm and processes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
13. Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29 Frontostriatal pathology in the (C57BL/6J) YAC128 mouse uncovered by the operant delayed alternation task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
14. Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010). A28 Accumulation and aggregation of human mutant huntingtin and neuron atrophy in BAC-HD transgenic rat. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
15. Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9.
敬请关注玉研仪器微信号:
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验小动物脉搏血氧监护仪的部分参考文献:
1. Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013). The calcium-binding protein parvalbumin modulates the firing 1 properties of the reticular thalamic nucleus bursting neurons. Journal of neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2. Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013). The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein. Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
3. Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013). Enduring Effects of Early Life Stress on Firing Patterns of Hippocampal and Thalamocortical Neurons in Rats: Implications for Limbic Epilepsy. PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
4. Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic Muscarinic Response Types in Hippocampal CA1 Interneurons Depend on Different Levels of Presynaptic Activity and Different Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes. Neuropharmacology.
5. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
6. Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013). Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat. The Journal of Physiology.
7. Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013). Effect of BDNF and adipose derived stem cells transplantation on cognitive deficit in Alzheimer model of rats. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
8. Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013). Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
9. Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012). Responsiveness to nicotine of neurons of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract correlates with the neuronal projection target. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
10. Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012). Myelin debris regulates inflammatory responses in an experimental demyelination animal model and multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
11. Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011). Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: A PGE2-independent mechanism.Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
12. Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A27 Expression of the human mutant huntingtin in minipig striatum induced formation of EM48+ inclusions in the neuronal nuclei, cytoplasm and processes. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
13. Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29 Frontostriatal pathology in the (C57BL/6J) YAC128 mouse uncovered by the operant delayed alternation task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
14. Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010). A28 Accumulation and aggregation of human mutant huntingtin and neuron atrophy in BAC-HD transgenic rat. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
15. Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010). A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9.
 技术资料
技术资料