相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 技术资料
- 抗体名:
Zenocutuzumab(泽妥珠单抗)
- 靶点:
Human HER2xHER3
- 供应商:
苏州艾洛蒙
- 级别:
研究级
- 目录编号:
CAS:1969309-56-5
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保存条件:
store at -20°C
- 形态:
液体
- 亚型:
Human IgG1, κ
- 规格:
1mg/5mg
| 规格: | 1mg | 产品价格: | ¥4500.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 5mg | 产品价格: | ¥12000.0 |
Zenocutuzumab (MCLA-128) 是一种靶向 HER2 和 HER3 的细胞外结构域的人源化抗体,可用于研究由 NRG1 基因重排驱动的肿瘤。
Zenocutuzumab (MCLA-128) is a humanized antibody targeting the extracellular domains of HER2 and HER3. It can be used for research on tumors driven by NRG1 gene rearrangement.
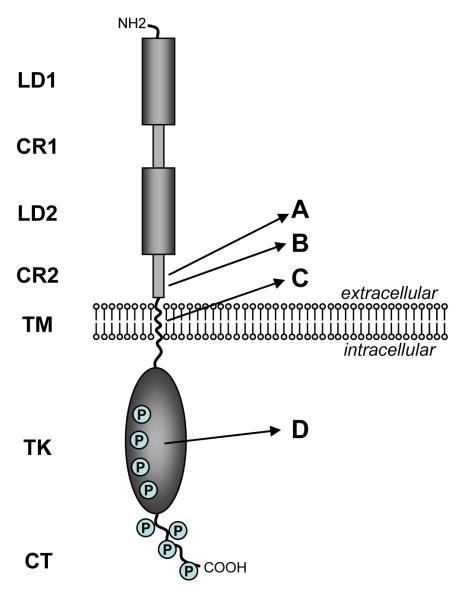
Structure of the HER2 and Neu proteins. The domain structure is shown on the left consisting of two ligand binding regions (LD1 & LD2), two cysteine-rich regions (CR1 & CR2), a short transmembrane domain (TM), a catalytic tyrosine kinase domain (TK), and a carboxy terminal tail (CT). Numerous sites of tyrosine phosphorylation wiithin the TK and CT domains are indicated by circled P.The letters on the right point to specific areas that are altered or mutated in certain naturally occuring or experimentally induced cancers discussed in the text. A) site of somatic mutations found in tumors arising in MMTV-neu mice. B) site of the 48bp deletion in the naturally occuring human ΔHER2 isoform. C) site of the mutation in the neuT oncogene initially discovered in a rat carcinogen induced tumor model and subsequently used in numerous in vitro and transgenic experimental models. D) site of mutations found in rare cases of human lung cancers.
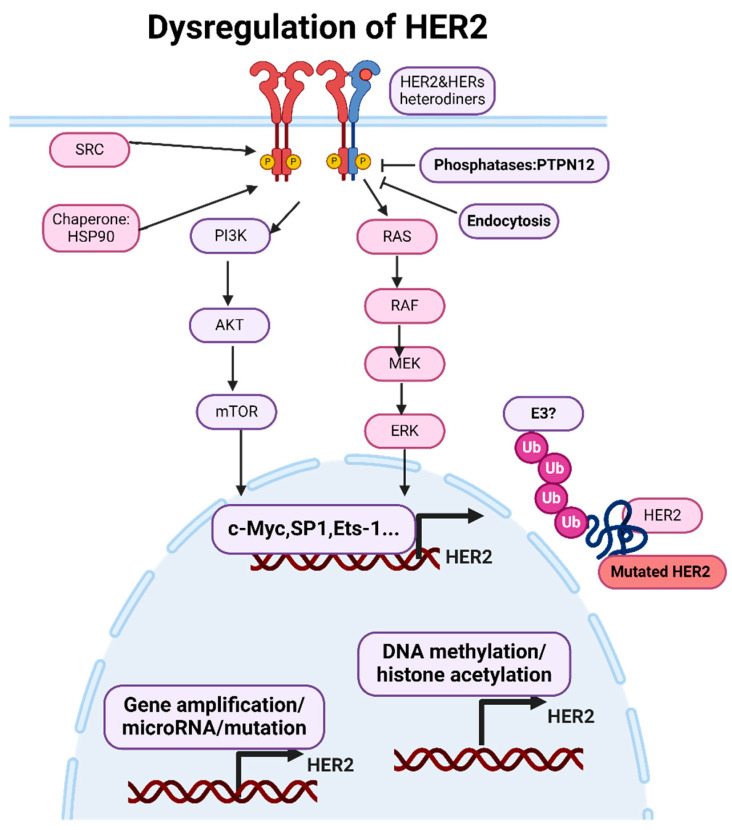
The HER2 receptor has no known ligand that directly binds to it. Instead, HER2 is the preferred partner for forming heterodimers (pairing) with other EGFR family members . HER2 dimerization is a crucial aspect of its signaling mechanism and plays a significant role in the biology of various cancers. The formation of dimers—either homodimers or heterodimers—is a key step in the activation of HER2 signaling pathways . The nature and consequences of HER2 dimerization can vary significantly across different cancer types. In breast cancer, HER2 frequently forms heterodimers with HER3 . The HER2/HER3 heterodimer is highly potent in activating downstream signaling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and MAPK, promoting cell proliferation and survival. HER2 expression in gastric cancer can be more heterogeneous than in breast cancer, with variable patterns of expression within and between tumors. HER2 in gastric cancer also dimerizes with HER3 and potentially dimerizes with other EGFR family members, contributing to aggressive tumor behavior . HER2 mutations, such as insertions in exon 20, can promote constitutive heterodimerization and the activation of HER2 without ligand binding in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) . HER2 can dimerize with EGFR in colorectal cancer, influencing responsiveness to EGFR-targeted therapies such as cetuximab . HER2 is overexpressed in a subset of ovarian cancers, often forming dimers with other EGFR family members .
HER2 can form homodimers or heterodimers with other EGFR family members in a ligand-independent manner. HER2 homodimers are generally less potent in signaling than heterodimers. However, HER2/HER3 heterodimers are particularly potent, activating robust downstream signaling pathways . HER3, with its six binding sites for the p85 subunit of PI3K, plays a critical role in PI3K/AKT pathway activation when dimerized with HER2
Dysregulation of HER2. The expression of HER2 is primarily regulated at the level of gene transcription. Transcription factors and epigenetic modifications can regulate HER2 gene expression by modulating the chromatin structure and accessibility to transcriptional machinery. Endocytosed receptors can undergo lysosomal degradation, leading to the attenuation of HER2-mediated signaling pathways. Figure was made using BioRender.
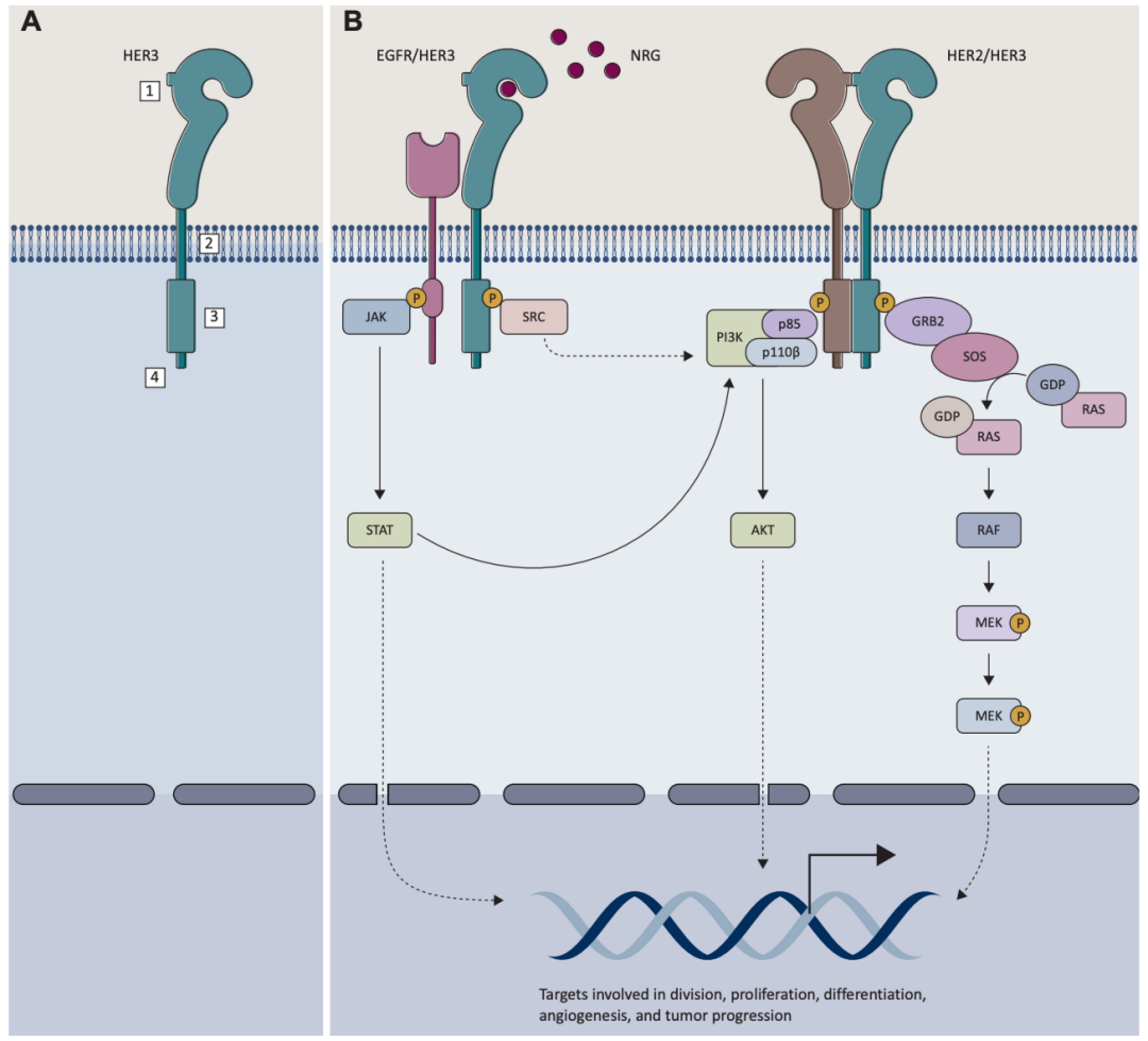
HER3 is a unique EGFR family member with no or little intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. Compared with the other EGFR family members, HER3 diverges at critical residues in the kinase domain locking it in an inactive-like conformation . Although HER3 has been reported to have some kinase activity, it is suggested to be 1000-fold weaker than the kinase activity of the fully activated EGFR . Since HER3 is unable to form homodimers, its activation depends on heterodimerization with another receptor in order to induce the downstream C-terminal phosphorylation events .
The HER3 gene localizes in the long arm of chromosome 12 (12q13.2), encoding a 180 kDa protein . The extracellular domain of HER3 is divided into four subdomains (I–IV): subdomains I and III are leucine-rich β-helical areas responsible for the ligand binding, whereas subdomains II and IV are cysteine-rich regions. Subdomain II also contains a dimerization arm necessary for the interaction with other receptors. The transmembrane domain is followed by an intracellular domain enclosing a flexible juxtamembrane region, kinase domain, and the C-terminal tail. In absence of a ligand, binding between subdomains II and IV keeps HER3 in an inactive state . Upon ligand binding, the dimerization partner’s kinase domain trans-phosphorylates the tyrosine residues in the C-terminal tail of HER3 .
Upon ligand binding, HER3 preferentially dimerizes with EGFR or HER2 inducing a conformational change in the receptor pair. The conformational change leads into transphosphorylation event in the intracellular kinase tail, where the C-terminal tail of HER3 acts as an acceptor for multiple phosphorylations. This induces activation of signaling cascades promoting cell survival and proliferation. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor, EGF: Epidermal growth factor, HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, HER3: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3, NRG: Neuregulin, p85: 85kDa regulator subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, p110: 110kDa catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, AKT: protein kinase B, SHC: SHC-transforming protein 1, GRB2: growth factor receptor bound protein 2, SOS: Son of sevenless, RAS: RAS GTPase, RAF: Raf kinase, MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
HER3 is a unique EGFR family member with no or little intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. Compared with the other EGFR family members, HER3 diverges at critical residues in the kinase domain locking it in an inactive-like conformation . Although HER3 has been reported to have some kinase activity, it is suggested to be 1000-fold weaker than the kinase activity of the fully activated EGFR . Since HER3 is unable to form homodimers, its activation depends on heterodimerization with another receptor in order to induce the downstream C-terminal phosphorylation events .
The HER3 gene localizes in the long arm of chromosome 12 (12q13.2), encoding a 180 kDa protein . The extracellular domain of HER3 is divided into four subdomains (I–IV): subdomains I and III are leucine-rich β-helical areas responsible for the ligand binding, whereas subdomains II and IV are cysteine-rich regions. Subdomain II also contains a dimerization arm necessary for the interaction with other receptors. The transmembrane domain is followed by an intracellular domain enclosing a flexible juxtamembrane region, kinase domain, and the C-terminal tail. In absence of a ligand, binding between subdomains II and IV keeps HER3 in an inactive state . Upon ligand binding, the dimerization partner’s kinase domain trans-phosphorylates the tyrosine residues in the C-terminal tail of HER3 .
Upon ligand binding, HER3 preferentially dimerizes with EGFR or HER2 inducing a conformational change in the receptor pair. The conformational change leads into transphosphorylation event in the intracellular kinase tail, where the C-terminal tail of HER3 acts as an acceptor for multiple phosphorylations. This induces activation of signaling cascades promoting cell survival and proliferation. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor, EGF: Epidermal growth factor, HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, HER3: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3, NRG: Neuregulin, p85: 85kDa regulator subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, p110: 110kDa catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, AKT: protein kinase B, SHC: SHC-transforming protein 1, GRB2: growth factor receptor bound protein 2, SOS: Son of sevenless, RAS: RAS GTPase, RAF: Raf kinase, MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料





