万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
100
- 供应商:
上海酶研生物科技有限公司
- 英文名:
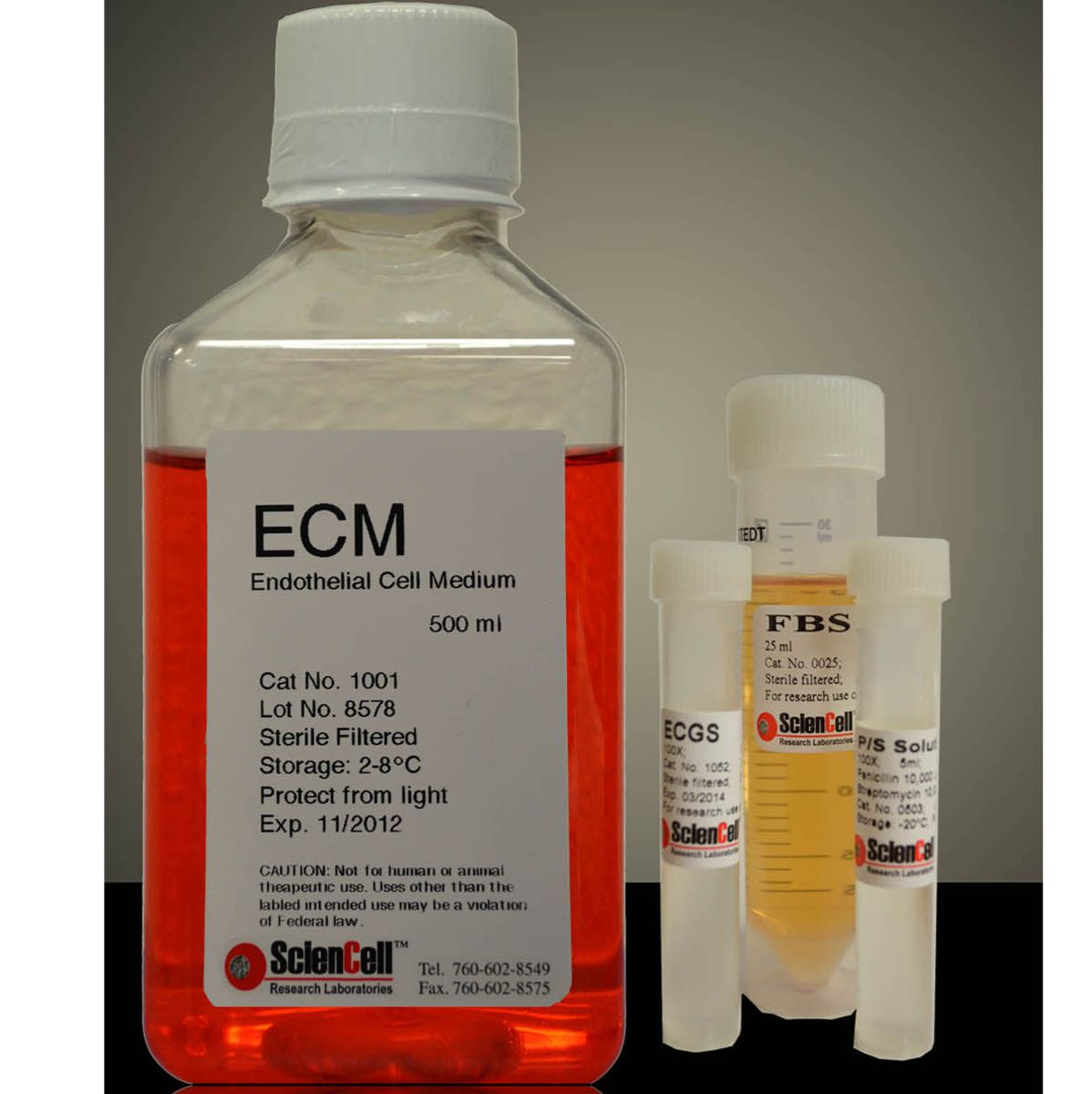
PEpiCM (Prostate Epithelial Cells Medium)
- 规格:
500ml/T
|
货号 |
4411 |
|
产地 |
美国 |
|
缩写 |
PEpiCM |
|
规格 |
500ml |
|
用途 |
科研 |
|
储存 |
4度,-20度 |
|
运输 |
胶冰 |
前列腺上皮细胞培养基是为正常人类前列腺上皮细胞体外培养设计的适于其生长的培养基。培养基是无菌的、液体培养基,包含必需和非必需氨基、维生素、有机和无机化合物、激素、生长因子、微量矿物质。该培养基不含血清。该培养基含HEPES和碳酸氢盐缓冲体系,在5%二氧化碳/95%空气培养箱中平衡时PH值为7.4。该培养基在数量上和质量上都保证理想的营养平衡状态,选择性促进体外正常人类前列腺上皮细胞的生长。
前列腺上皮细胞培养基包含500 ml基础培养基,5 ml前列腺上皮细胞生长添加物,(PEpiCGS,目录编号4452)和5 ml青霉素/链霉素溶液(P/S,目录编号0503)
1. Zhang, M., Lin, D., Luo, C., Wei, P., Cui, K., Chen, K., & Chen, Z. (2023). SAKLK1-374 is more difficult to induce KLK1 expression in normal prostate cell lines than that in prostate cancer cell lines: Rethinking the universality of RNA activation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 643, 157–168.
RNA activation, as a method of regulating gene expression at the transcriptional level, is far less widely used than RNA interference because of the insufficient understanding of the mechanism and the unstable success rate. It is necessary to analyze the failure cases of RNA activation to promote the application of RNA activation. When we validated the saRNAs designed to induce KLK1 expression, we found that saKLK1-374 can upregulate KLK1 expression in prostate tumor cell lines, but failed in normal prostate cell lines. To determine whether the RNA activation of normal cells is difficult only when the target gene is KLK1, we tested p21WAF1/CIP1 as the target gene in RNA activation experiments of normal and cancer prostate cells. Next, to determine whether the above phenomenon exists in other tissues, we used normal and cancerous bladder cells to perform RNA activation experiments with KLK1 and p21WAF1/CIP1 as targets. We have also extended the time from transfection to detection to evaluate whether a longer incubation time can make saRNA upregulate the target genes in normal cells. Fluorescently labeled dsRNA was transfected to evaluate the transfection efficiency, and the expression of Ago2 and IPO8 necessary for RNA activation was also detected. The p21WAF1/CIP1 could be significantly upregulated by saRNA in prostate cancer cells, but not in normal prostate cells. The expression of KLK1 in bladder-derived cell lines was extremely low and could not be induced by saRNA. The p21WAF1/CIP1 was upregulated by saRNA to a higher extent in bladder cancer cells but to a lower extent in normal bladder cells. Prolonging incubation time could not make saRNA induce the expression of target genes in normal cells. Compared with tumor cells used in this study, normal cells had lower transfection efficiency or lower expression of Ago2 and IPO8. Although it has been currently found that normal cell lines in the prostate and bladder might be more difficult to be successfully induced target gene expression by exogenous saRNA than tumor cells due to low transfection efficiency or Ago2 and IPO8 expression, it is not certain that this phenomenon occurs in other types of tissue. However, researchers still need to pay attention to the transfection efficiency and/or the expression levels of Ago2 and IPO8 when conducting RNA activation experiments in normal cells. Less
2. Oh JH, Gertych A, Tajbakhsh J. (2013) "Nuclear DNA Methylation and Chromatin Condensation Phenotypes Are Distinct Between Normally Proliferating/Aging, Rapidly Growing/Immortal, and Senescent Cells." Oncotarget. 4: 474-93.
This study reports on probing the utility of in situ chromatin texture features such as nuclear DNA methylation and chromatin condensation patterns — visualized by fluorescent staining and evaluated by dedicated three-dimensional (3D) quantitative and high-throughput cell-by-cell image analysis — in assessing the proliferative capacity, i.e. growth behavior of cells: to provide a more dynamic picture of a cell population with potential implications in basic science, cancer diagnostics/prognostics and therapeutic drug development. Two types of primary cells and four different cancer cell lines were propagated and subjected to cell-counting, flow cytometry, confocal imaging, and 3D image analysis at various points in culture. Additionally a subset of primary and cancer cells was accelerated into senescence by oxidative stress. DNA methylation and chromatin condensation levels decreased with declining doubling times when primary cells aged in culture with the lowest levels reached at the stage of proliferative senescence. In comparison, immortal cancer cells with constant but higher doubling times mostly displayed lower and constant levels of the two in situ-derived features. However, stress-induced senescent primary and cancer cells showed similar levels of these features compared with primary cells that had reached natural growth arrest. With regards to global DNA methylation and chromatin condensation levels, aggressively growing cancer cells seem to take an intermediate level between normally proliferating and senescent cells. Thus, normal cells apparently reach cancer-cell equivalent stages of the two parameters at some point in aging, which might challenge phenotypic distinction between these two types of cells. Companion high-resolution molecular profiling could provide information on possible underlying differences that would explain benign versus malign cell growth behaviors. Keywords: DNA methylation, chromatin condensation, cell proliferation, aging, senescence, cancer, 3D imaging, cell-by-cell analysis Less
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验
1.) Oh JH, Gertych A, Tajbakhsh J. (2013) "Nuclear DNA Methylation and Chromatin Condensation Phenotypes Are Distinct Between Normally Proliferating/Aging, Rapidly Growing/Immortal, and Senescent Cells." Oncotarget. 4: 474-93.
单细胞测序技术(scRNA-Seq)之 NCB 高分文章解析前列腺癌相关研究
单细胞转录组测序,注释细胞类型主要包括上皮细胞、单核-巨噬细胞系、T细胞、内皮细胞、成纤维细胞、肥大细胞等主要群体。然后分别对每个大群进一步分析。 13 例前列腺癌样本的单细胞研究概况 (1)与肿瘤预后相关的上皮细胞类型 通过拷贝数变异分析、肿瘤细胞的marker基因/ 信号通路相关性分析,将上皮细胞鉴定为 luminal types、cell-cycle 、basal/intermediate 类型;我们主要研究了这些细胞类型与临床预后的关系,发现特异性表达细胞因子 CCL2 的basal
肿瘤分为良性肿瘤和恶性肿瘤,一般所说的癌即指恶性肿瘤而言。恶性肿瘤从组织学上分为上皮性的癌和非上皮性的肉瘤及血液癌。良性恶性的区别常根据临床的预后加以判定。两者的鉴别可见下表,但也有很多例外,常常难以严格的区别。这也由各个肿瘤细胞所处的环境条件来决定。有的学者主张良性肿瘤和恶性肿瘤之间是存在着连续的阶段,可是有的良性、肿瘤例如前列腺腺瘤、乳腺纤维腺瘤、子宫肌瘤、血管球瘤等是和内分泌、神经等机体调节机制有密切关系的组织增生,因而有的学者主张它和恶性肿瘤有本质上的区别
前列腺 增生的病因尚不清楚,但其发生需具备有正常功能的睾丸和老龄两个基本条件。男子随着年龄的逐渐增长,前列腺也随之增大,青春期后(21~31岁),增长较快,为1.6克/年,30~70岁生长缓慢,为0.4克/年,成人的前列腺重约20克。从病理学上看,前列腺增生最早可于25~30岁时发生,而组织学上前列腺增生结节至少要到30~40岁才能出现。但出现前列腺增生结节到临床上出现前列腺增生需要一个比较长的阶段。从组织上看,随着年龄增长,前列腺的基质逐渐增多,上皮组织逐渐减少,而实际上前列腺
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料