相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 技术资料
- 抗体名:
Evalstotug
- 抗体英文名:
Anti-Human CTLA4 antibody
- 靶点:
CTLA4, CD152, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, CTLA-4
- 适应物种:
human
- 保质期:
12 months
- 目录编号:
CAS:2460399-39-5
- 级别:
Research Grade
- 供应商:
苏州艾洛蒙
- 标记物:
无
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保存条件:
Store at -20°C for 12 months (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing)
- 形态:
Liquid
- 亚型:
Human IgG1, κ
- 规格:
1mg
Evalstotug 是一种抗 CTLA4 的人源 IgG1 κ 单克隆抗体。
Evalstotug is an anti-CTLA4 human IgG1 κ monoclonal antibody. Recommend Isotype Controls: Human IgG1 kappa, Isotype Control.Evalstotug (BA-3071) is under development for solid tumors, non-small cell lung cancer, uveal melanoma, gastroesophageal (GE) junction carcinomas, renal cell carcinoma, gastric, cervical, transitional cell carcinoma (urothelial cancer). and melanoma. It acts as checkpoint inhibitor by targeting against cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4). It is based on conditionally active biologics (CAB) that optimizes antibodies to be activated and/or inactivated at defined physiological conditions.
CTLA-4又名CD152,是由CTLA-4基因编码的一种跨膜蛋白质,表达于活化的CD4+和CD8+T细胞。CTLA-4于1987年被发现,CTLA-4的发现者詹姆斯·艾利森(James P.Allison)教授和PD-1的发现者本庶佑(Tasuku Honjo)教授在2018年一起获得了诺贝尔生理或医学奖。在T细胞激活的各个阶段,CTLA-4单抗与PD-L1单抗各司其职。其中CTLA-4单抗能够通过解除抑制T细胞活化的信号,从而维持T细胞激活状态。而PD-L1单抗则通过阻断淋巴结中PD-L1与B7-1分子的相互作用,来增强 T细胞启动与活化。在效应阶段,CTLA-4单抗解除肿瘤微环境中调节性T细胞(Treg细胞)的免疫抑制,而PD-L1单抗则阻断PD-L1与PD-1的相互作用,重新激活受抑制的T细胞,使“复活”的效应T细胞迅速杀伤肿瘤细胞。
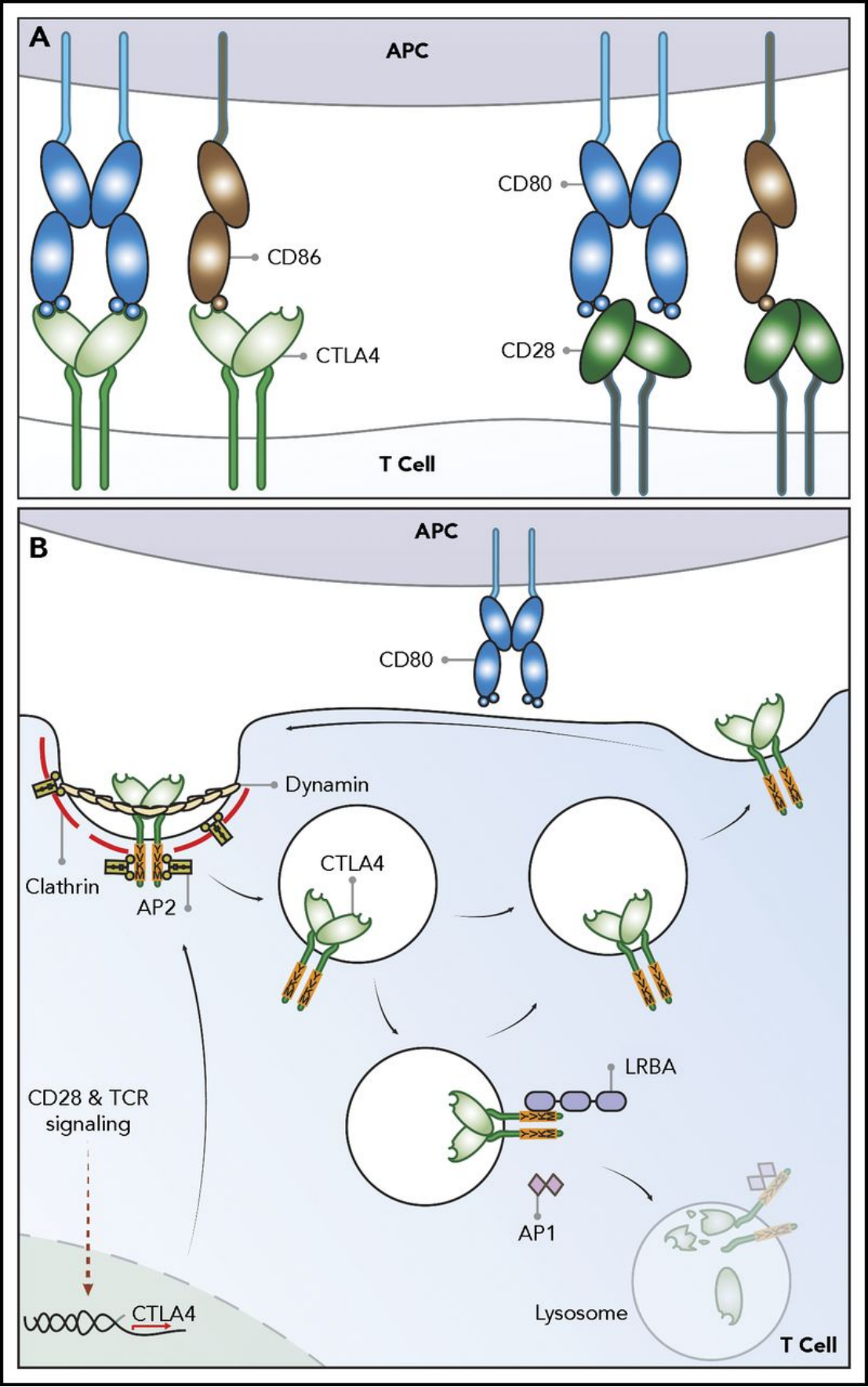
CTLA-4和CD28均为免疫球蛋白超家族成员,二者与相同的配体CD86(B7-2)和CD80(B7-1)结合。CTLA-4的免疫调控功能的关键体现在控制CD4+FoxP3-、CD8+T细胞以及调节性T细胞(Treg)。CTLA-4能够中止激活的T细胞的反应(T cell response)以及介导Treg的抑制功能。
目前的研究表明CTLA-4抑制T细胞的反应主要是通过两种途径:
一是通过与CD28竞争性的结合B7或者招募磷酸酶到CTLA-4的胞内结构域部分从而降低TCR(T cell receptor)和CD28的信号。
另一种是降低CD80和CD86在抗原呈递细胞(APC)的表达水平或者通过转胞吞作用(transendocytosis)将它们从APC移除,这样就减少了CD28参与进行T细胞激活。此外,CTLA-4还会介导树突细胞结合CD80/CD86并诱导色氨酸降解酶IDO的表达,从而导致TCR的抑制。CTLA-4抗体通过结合CTLA-4来减少Treg,激活TCR
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) is an inhibitory receptor belonging to the CD28 immunoglobulin subfamily, expressed primarily by T-cells. Its ligands, CD80 and CD86, are typically found on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and can either bind CD28 or CTLA-4, resulting in a costimulatory or a co-inhibitory response, respectively. Because of its dampening effect, CTLA-4 is a crucial regulator of T-cell homeostasis and self-tolerance. The mechanisms by which CTLA-4 exerts its inhibitory function can be categorized as either cell-intrinsic (affects the CTLA-4 expressing T-cell) or cell-extrinsic (affects secondary cells). Research from the last decade has shown that CTLA-4 mainly acts in a cell-extrinsic manner via its competition with CD28, CTLA-4-mediated trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86, and its direct tolerogenic effects on the interacting cell. Nonetheless, intrinsic CTLA-4 signaling has been implicated in T-cell motility and the regulation of CTLA-4 its subcellular localization amongst others. CTLA-4 is well recognized as a key immune checkpoint and has gained significant momentum as a therapeutic target in the field of autoimmunity and cancer. In this chapter, we describe the role of costimulation in immune response induction as well as the main mechanisms by which CTLA-4 can inhibit this process.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料





