
MACSima™全自动空间组图谱成像分析系统
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 用户评价
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
1
- 保修期:
1年
- 供应商:
德国美天旎生物技术有限公司
轻松实现同一切片空间多组学成像
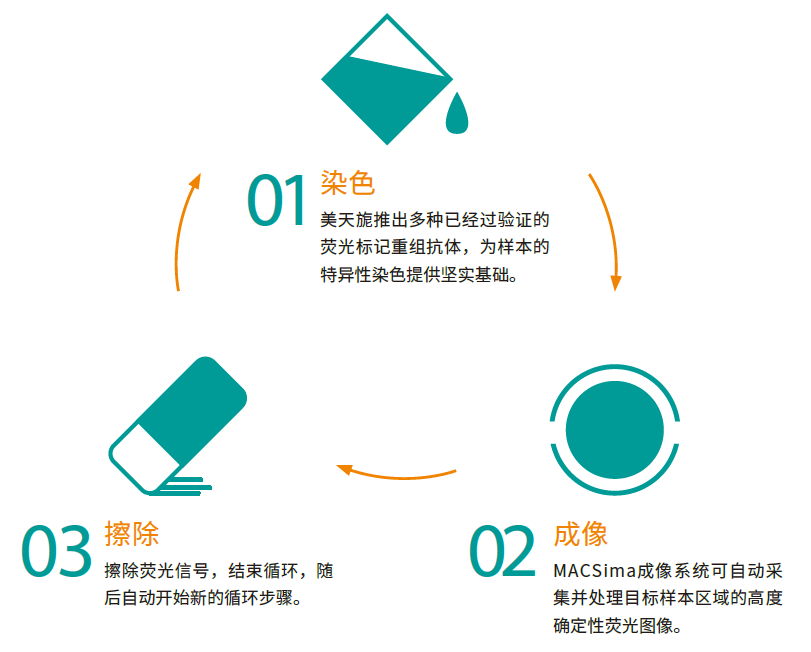
美天旎的MICS技术基于荧光显微术可同时分析单个样本中的数百种标志物。通过不同荧光标记抗体的循环染色,在不损伤样本的情况下,获取多种参数的显微成像数据。循环染色包括三个主要步骤:荧光染色、图像采集和荧光信号擦除,均由MACSima成像系统全自动完成。最终生成的数百种标志物的空间组图谱可帮助科学家以的深度洞察样本的生理学或病理学特性。该系统具有即时处理能力,即便是在循环染色过程中也可随时开始数据分析。
完整的解决方案
MACSima成像系统采用全自动流程和优化的组件,可极大地简化生成复杂的空间组图谱数据的过程,其优点不言而喻。
- 同一个样本分析数百种标志物
获取空间组图谱数据,对单个样本中的数百种蛋白质及其它抗原进行分析。
- 高度自动化的设备
完成实验设计后即可交由MACSima成像系统自动运行。MACSima成像系统是该平台的核心,利用这台仪器可以实现全自动的循环染色和数据处理。
- 已验证的大量抗体组合
基于大量重组工程的荧光素偶联抗体,支持分析您样本上的数百个标记物,这些抗体专门针对MICS进行了验证。
两种信号擦除机制:使用荧光染料偶联抗体染色 (01) 并对染色样本进行图像采集后 (02),可利用下列两种机制之一擦除荧光信号。

- 轻松的实验准备
得益于多种即用型 REAscreen™ 抗体Panel,其中包含来自美天旎生物技术的预定义抗体组,可轻松进行全面的分析。使用我们的 MACSwell™ 样品载样架和各种灵活形式的抗体可分析任何类型的固定样品。
- 化繁为简的分析软件
使用 MACS® iQ View 轻松全面地分析您的超高内涵成像数据。其多功能性和直观的用户界面使这款图像分析软件成为您空间生物学实验的完美伴侣。
MACSwell样本载样架
可分析各种固定样本
要想解决复杂的科学问题,必须突破技术限制。为了能够在MACSima成像系统上不受限制地灵活分析各种固定样本,美天旎开发出MACSwell样本载样架。我们针对组织、贴壁细胞和悬浮细胞设计出三种不同类型的载样架。每种载样架都有明确定义的反应腔室,可以轻松且安全地实现循环染色,确保顺利完成实验。

经过验证的固定方法

一次实验、众多结果

风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 用户评价
用户评价 暂无用户评价
暂无用户评价 文献和实验
文献和实验- Petitpas et al (2025) Injury and inflammation promote cancer progression at the anorectal junction. Cell Reports 44(11):116552.
- Richter et al (2025) Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal mice sequentially recruits neutrophils with dichotomous phenotype and function. Nature Communications 16:9696.
- Sciacco et al (2025) The Role of C/EBP-Homologous Protein in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 29(21):e70919.
- Stahl et al (2025) CSF1R+ myeloid-monocytic cells drive CAR-T cell resistance in aggressive B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 43(8):1476-1494.
- Durante et al (2025) Precision-cut tumor tissue slices, a novel tool to study the tumor microenvironment interactions with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. PLoS One 20(8):e0327322.
- Münter et al (2025) Multiomic analysis uncovers a continuous spectrum of differentiation and Wnt-MDK-driven immune evasion in hepatoblastoma. Journal of Hepatology 83(2):367-382.
- Cancila et al (2025) Aggressive B cell lymphomas retain ATR-dependent determinants of T cell exclusion from the germinal center dark zone. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 135(18):e187371.
- Vasudevan et al (2025) In vitro integration of a functional vasculature to model endothelial regulation of chemotherapy and T-cell immunotherapy in liver cancer. Biomaterials 320:123175.
- Zheng et al (2025) Protocol for spatial proteomic profiling of tonsil cancer microenvironments using multiplexed imaging-powered deep visual proteomics. STAR Protocols 6(3):103901.
- De Mitri et al (2025) Inhibition of autophagy enhances the antitumor efficacy of T/CAR T cell against neuroblastoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 44(1):185.
- Varano et al (2025) B-cell Receptor Silencing Reveals the Origin and Dependencies of High-Grade B-cell Lymphomas with MYC and BCL2 Rearrangements. Blood Cancer Discovery 6(4):364-393.
- De Faria et al (2025) ETMR stem-like state and chemo-resistance are supported by perivascular cells at single-cell resolution. Nature Communications 16:5394.
- Imle et al (2025) Somatic gene delivery faithfully recapitulates a molecular spectrum of high-risk sarcomas. Nature Communications 16:5283.
- Desantis et al (2025) Spatial imaging unlocks the potential of charting multiple myeloma and extramedullary disease. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 18(1):47.
- Costa-Verdera et al (2025) AAV vectors trigger DNA damage response-dependent pro-inflammatory signalling in human iPSC-derived CNS models and mouse brain. Nature Communications 16:3694.
- Guillaume et al (2025) Lung B cells in ectopic germinal centers undergo affinity maturation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 122(14): e2416855122.
- Harris et al (2025) Human-specific organization of proliferation and stemness in squamous epithelia: A comparative study to elucidate differences in stem cell organization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26(7):3144.
- Spangenberg et al (2025) msiFlow: automated workflows for reproducible and scalable multimodal mass spectrometry imaging and microscopy data analysis. Nature Communications 16:1065.
- Zheng et al (2025) Deciphering functional tumor-immune crosstalk through highly multiplexed imaging and deep visual proteomics. Molecular Cell 85(5):1008-1023.
- Khan et al (2025) β-Glucan reprograms neutrophils to promote disease tolerance against influenza A virus. Nature Immunology 26(2):174-187.
- Yu et al (2024) Therapeutic potential of interleukin-17 neutralization in a novel humanized mst-surgical tumor microenvironment. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 43(1):311.
- Bethke et al (2024) Identification and characterization of fully human FOLR1-targeting CAR T cells for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Cells 13(22):1880.
- Fernández et al (2024) A single-cell atlas of the murine pancreatic ductal tree identifies novel cell populations with potential implications in pancreas regeneration and exocrine pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 167(5):944-960.
- Fischer et al (2024) Lack of SMARCB1 expression characterizes a subset of human and murine peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Nature Communications 15(1):8571.
- Soubéran et al (2024) Brain tumoroids: treatment prediction and drug development for brain tumor with fast, reproducible and easy-to-use personalized models. Neuro-Oncology noae184.
- Agorku et al (2024) Colorectal cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibit effector T cells via NECTIN2 signaling. Cancer Letters 595:216985.
- Watanabe-Kusunoki et al (2024) Gasdermin D drives focal Crystalline Thrombotic Microangiopathy by accelerating Immunothrombosis and Necroinflammation. Blood 144(3):308-322.
- Petta et al (2024) Myeloid A20 is critical for alternative macrophage polarization and type-2 immune-mediated helminth resistance. Frontiers in Immunology 15:1373745.
- Tran et al (2024) Armored TGFβRIIDN ROR1-CAR T cells reject solid tumors and resist suppression by constitutively-expressed and treatment-induced TGFβ1. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 12(4):e008261.
- Herold et al (2024) High-dimensional in situ proteomics imaging to assess γδ T cells in spatial biology. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 115(4):750-759.
- Dirks et al (2024) Disease-specific T cell receptors maintain pathogenic T helper cell responses in postinfectious Lyme arthritis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 134(17):e179391.
- Scheuermann et al (2024) Unveiling spatial complexity in solid tumor immune microenvironments through multiplexed imaging. Frontiers in Immunology 15:1383932.
- Kvedaraite et al (2024) Intestinal stroma guides monocyte differentiation to macrophages through GM-CSF. Nature Communications 15(1):1752.
- Chang et al (2024) MHC-I upregulation safeguards neoplastic T cells in the skin against NK cell-mediated eradication in mycosis fungoides. Nature Communications 15(1):752.
- Ng et al (2024) Deterministic reprogramming of neutrophils within tumors. Science 383(6679):eadf6493.
- Daigre et al (2024) Preclinical evaluation of novel folate receptor 1-directed CAR T cells for ovarian cancer. Cancers 16(2):333.
- Budeus et al (2023) Human IgM–expressing memory B cells. Frontiers in Immunology 14:1308378.
- Sigle et al (2023) Translating genomic tools to Raman spectroscopy analysis enables high-dimensional tissue characterization on molecular resolution. Nature Communications 14(1):5799.
- Pfeifei et al (2023) Targeting Stage-Specific Embryonic Antigen 4 (SSEA-4) in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by CAR T Cells Results in Unexpected on Target/off Tumor Toxicities in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24(11):9184.
- Harris et al (2023) Precancerous lesions of the head and neck region and their stromal aberrations: piecemeal data. Cancers 16(2):333.
- Kvedaraite et al (2022) Notch-dependent cooperativity between myeloid lineages promotes Langerhans cell histiocytosis pathology. Science Immunology 7(78):eadd3330.
- Werchau et al (2022) Combined targeting of soluble latent TGF-ß and a solid tumor- associated antigen with adapter CAR T cells. OncoImmunology 11(1):2140534.
- Pfeifei et al (2022) A multimodal imaging workflow for monitoring CAR T cell therapy against solid tumor from whole-body to single-cell level. Theranostics 12(11):4834-4850.
- Kinkhabwala et al (2022) MACSima imaging cyclic staining (MICS) technology reveals combinatorial target pairs for CAR T cell treatment of solid tumors. Scientific Reports 12(1):1911.
- Guilliams et al (2022) Spatial proteogenomics reveals distinct and evolutionarily conserved hepatic macrophage niches. Cell 185(2):379-396.
- Kantari-Mimoun et al (2021) CAR T-cell Entry into Tumor Islets Is a Two-Step Process Dependent on IFNγ and ICAM-1. Cancer Immunology Research 9(12):1425-1438.
- Hinterleitner et al (2021) Platelet PD-L1 reflects collective intratumoral PD-L1 expression and predicts immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Nature Communications 12(1):7005.
- Brinkmann et al (2021) Advanced high dynamic range fluorescence microscopy with Poisson noise modeling and integrated edge-preserving denoising. Journal of Physics Communications 5:075016.
- Schäfer et al (2021) Identification of CD318, TSPAN8 and CD66c as target candidates for CAR T cell based immunotherapy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Nature Communications 12(1):1453.
膜的完美图像。以任一种荧光染料或红外染料染色的凝胶,也能获得漂亮的图像。PXi可容纳的凝胶大小在10cm x 12cm以内。 PXi成像仪还附带GeneTools软件 。它可在数秒钟之内自动生成结果,包括泳道分析、分子量及数量计算,帮您节省宝贵的时间。 此外,Syngene近日还推出了安全且灵敏的UltraSafe Blue™荧光染料,在琼脂 糖和聚丙烯酰胺凝胶染色时可取代EB。与UltraSlim LED蓝光透射仪一起使用,UltraSafe Blue可实现0.5pg
的演变,以及 TME 中细胞间的相互作用和空间分布仍然知之甚少。因此,本研究旨在利用空间多组学技术,深入剖析人源和鼠源 LUAD 前体样本,解析 TME 的空间结构、细胞组成和功能动态,并寻找潜在的早期干预靶点。 研究路线 研究结论 图 4. 成像质谱细胞术技术绘制的空间免疫微环境图 研究团队收集了 114 例人类 LUAD 及其前体样本,利用成像质谱细胞术(IMC)技术,绘制了高分辨率的空间免疫微环境图谱。研究发现,肺腺癌从癌前病变向浸润性癌转变过程中,伴随着巨噬细胞的极化
Nature Cancer I 生物标志物多参数评估mTLS预测实体瘤免疫治疗效果
性,但得益于强大、稳定的 PhenoImager多重免疫荧光整体方案,这项研究可以实现多中心独立实验、大样本量染色、拍摄及分析实现标准化、可双盲评估微环境概况和 TLS 成熟度表征。进而得到新的发现 ,治疗前患者样本中存在成熟 TLS 可被视为患者对免疫治疗反应的预测指标,TLS 没有形成或未成熟组的肿瘤在反应率方面没有区别。mTLS 的预测价值可能不局限于特定肿瘤类型,在大多数肿瘤类型中都观察到具有良好预后的高相关性。 PhenoImager 解决方案,采用特色的 MOTiF™ 快速全组织片扫描
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料







