相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
100
- 国食药监械注册号:
无
- 保修期:
12个月
- 现货状态:
10天
- 供应商:
玉研仪器公司
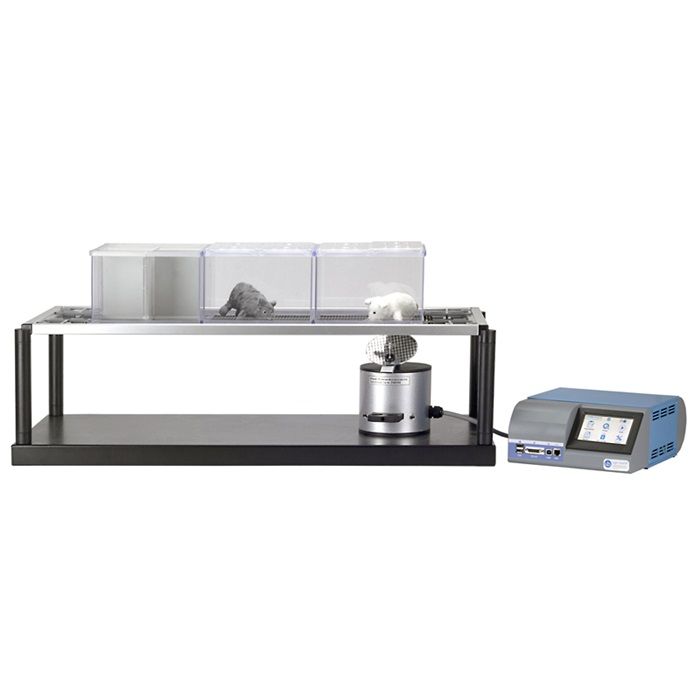
动态足底触觉仪是评估大鼠、小鼠足底对触觉敏感性的测试设备。
动物模型的刺痛测试与分析在药物诊断、神经病理学和机体损伤性研究等多种研究领域有着广泛的应用。

型号:37550
主要特色
· 自动检测动物反应,无需人为判断;
· 可调节施加力的测试速率;
· 带统计和分析软件;
· 可通过U盘进行数据拷贝;
· 可选配打印机对数据进行打印;
· 可选配鼠筒可进行口部、面部刺激

测试主机
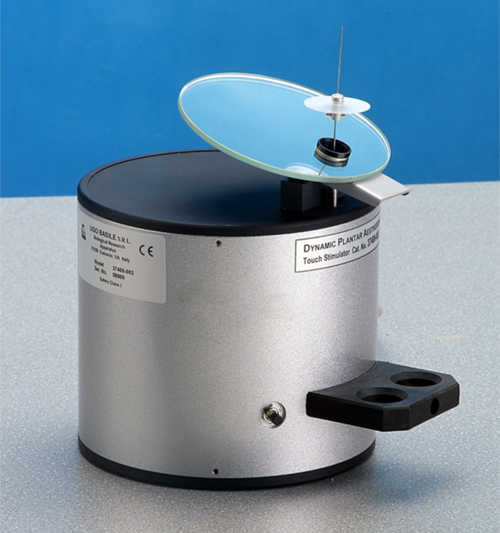

触觉刺激器

测试主机显示面板
主要配置
· 便携和易用移动的触觉刺激器,配有刚性探针和可调节角度的镜子;
· 控制主机,带触控屏,显示直观,操作方便;
· 十字孔板测试平台;
· 模块化动物鼠笼:使用隔板可分配成3个大鼠鼠笼和12个小鼠鼠笼测试单元;

电控型测试探针

测试平台
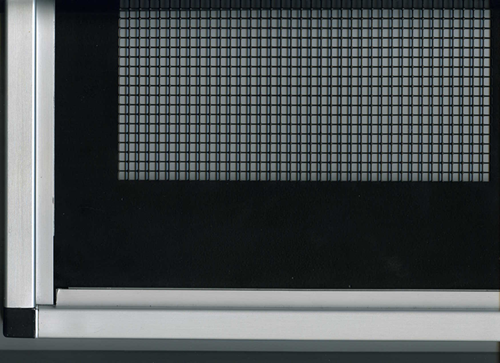
十字测试网格
设备的操作
· 大鼠、小鼠被放置到测试平台上,用测试鼠笼约束;
· 受试动物在鼠笼内科自由活动;
· 给出一定的环境适应时间和老鼠的探索时间;
· 操作人员将触觉刺激器放置在动物爪子正下方,在反光镜的帮助下定位硬丝;
· 启动触觉刺激器的按钮开始测试;
A:刚性探针被自动抬高;
B:探针接触足底后,开始施力;
C:力度以预设施力速率增加,直到动物移除爪子或达到预设力度,自动停止加力;
· 自动记录两个测试指标:缩爪的潜伏期(单位:S)和缩爪时的力度(单位:g)
数据的采集
· 测试主机可直观显示测试数据,并对数据进行存储;
· 数据可导出到电脑,或者使用专用U盾进行数据拷贝;
· 通信由基于CUB Data Acquisition Windows®的专用软件包52050-10管理;
· 能够将实验数据传送到电脑并使用常用软件进行管理;
· 配备了存储键,用于记录回顾实验数据;
· 支持使用远程网络连接测试主机,对实验参数进编辑;

参考文献:
l R. Lu, A. Schmidtko: “Direct Intrathecal Drug Delivery in Mice for Detect-ing In Vivo Effects of cGMP on Pain Processing” Methods in Molecular Biology 1020: 215-221, 2013
l I.Q. Russe et alia: “Activation of the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Reduces Inflammatory Nociception” Journal of Pain 2, 2013
l J. Btesh et alia: “Mapping the Binding Site of TRPV1 on AKAP79: Implications for Inflammatory Hyperalgesia” J. Neuroscience 33 (21): 9184-9193, 2013
l V. Brázda et alia: “Dynamic Response to Peripheral Nerve Injury Detected by In Situ Hybridization of IL-6 and its Receptor mRNAs in the Dorsal Root Ganglia is not Strictly Correlated With Signs of Neuropathic Pain” Molecular Pain 9(42), 2013
l D. Piomelli et alia: ”Anandamide Suppresses Pain Initiation Through a Peripheral Endocannabinoid Mechansmsm” Nature NSC , 2010
l P.J. Austin et alia: “G. Chronic Constriction of the Sciatic Nerve and Pain Hypersensitivity Testing in Rats” JoVE 61, e3393, doi:10.3791/3393, 2012




敬请来电咨询。
敬请关注玉研仪器微信号:

风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验《Science》
1.La Montanara, Paolo, et al. "Cyclin-dependent–like kinase 5 is required for pain signaling in human sensory neurons and mouse models." Science translational medicine 12.551 (2020): eaax4846.doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aax4846
IF 19.32
2.Feng, Jiao, et al. "A new painkiller nanomedicine to bypass the blood-brain barrier and the use of morp*hine." Science advances 5.2 (2019): eaau5148.doi:10.1126/sciadv.aau5148
IF 14.96
3.Hsiao, Hung-Tsung, et al. "The analgesic effect of propofol associated with the inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor and inflammasome in complex regional pain syndrome." Journal of biomedical science 26 (2019): 1-11. doi:10.1186/s12929-019-0576-z
IF 12.77
4.Zhou, Luming, et al. "Reversible CD8 T cell–neuron cross-talk causes aging-dependent neuronal regenerative decline." Science 376.6594 (2022): eabd5926. doi: 10.1126/science.abd5926
IF 63.71
《Nature》
5.Oswald, Manfred J., et al. "Cholinergic basal forebrain nucleus of Meynert regulates chronic pain-like behavior via modulation of the prelimbic cortex." Nature Communications 13.1 (2022): 5014.doi:
IF 17.69
6.Landra-Willm, Arnaud, et al. "A photoswitchable inhibitor of TREK channels controls pain in wild-type intact freely moving animals." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 1160.doi:
IF 17.69
7.Nees, Timo A., et al. "Role of TMEM100 in mechanically insensitive nociceptor un-silencing." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 1899.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36806-4
IF 17.69
8.Zhang, Qiaosheng, et al. "A prototype closed-loop brain–machine interface for the study and treatment of pain." Nature Biomedical Engineering (2021): 1-13. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00736-7
IF 29.23
9.Zhang, Su-Bo, et al. "CircAnks1a in the spinal cord regulates hypersensitivity in a rodent model of neuropathic pain." Nature communications 10.1 (2019): 4119.doi:1
10.IF: 17.69
11.Jiang, Wenhao, et al. "PGE2 activates EP4 in subchondral bone osteoclasts to regulate osteoarthritis." Bone research 10.1 (2022): 27. doi:10.1038/s41413-022-00201-4
13.36
12.Bao, Yi-Ni, et al. "The dopamine D1–D2DR complex in the rat spinal cord promotes neuropathic pain by increasing neuronal excitability after chronic constriction injury." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 53.2 (2021): 235-249.doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00563-5
IF 12.15
13.Takeda, Ikuko, et al. "Controlled activation of cortical astrocytes modulates neuropathic pain-like behaviour." Nature communications 13.1 (2022): 4100.doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31773-8
IF 17.69
14.Liang, Hai-Ying et al. “nNOS-expressing neurons in the vmPFC transform pPVT-derived chronic pain signals into anxiety behaviors.” Nature communications vol. 11,1 2501. 19 May. 2020, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16198-5 doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16198-5
IF 17.69
15.Zhou, Hang, et al. "A sleep-active basalocortical pathway crucial for generation and maintenance of chronic pain." Nature Neuroscience (2023): 1-12. doi: 10.1038/s41593-022-01250-y
IF 28.77
16.Wang, Yan et al. “TRPV1 SUMOylation regulates nociceptive signaling in models of inflammatory pain.” Nature communications vol. 9,1 1529. 18 Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03974-7
IF 17.69
17.Iwasaki, Mai, et al. "An analgesic pathway from parvocellular oxytocin neurons to the periaqueductal gray in rats." Nature Communications 14.1 (2023): 1066. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36641-7
IF 17.69
《Cell》
18.Zhang, Fang-Xiong et al. “BK Potassium Channels Suppress Cavα2δ Subunit Function to Reduce Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain.” Cell reports vol. 22,8 (2018): 1956-1964. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.073
IF 10.00
19.Gui, Xianwei et al. “Botulinum toxin type A promotes microglial M2 polarization and suppresses chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through the P2X7 receptor.” Cell & bioscience vol. 10 45. 23 Mar. 2020, doi:10.1186/s13578-020-00405-3
 技术资料
技术资料