Affinity Measurements Using Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM)
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐

Agilent安捷伦 5063-6570 石英流通池,10x2mm椭圆形孔,M6,1mm光程,40µL,z=15mmFlow cell quartz 1mm 40uL oval ap. 1/pk
¥17802.02

cry1Ab/cry1Ab蛋白Recombinant Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki Pesticidal crystal protein Cry1Ab (cry1Ab)重组蛋白130KDA crystal protein;Crystaline entomocidal protoxinInsecticidal delta-endotoxin CryIA(b)蛋白
¥2616
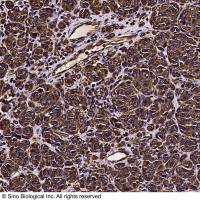
Vimentin Antibody, Rabbit PAb, Antigen Affinity Purified | Vimentin 兔多抗 (抗原亲和纯化)
¥1699

Agilent安捷伦 5063-6571石英流通池,10x2mm椭圆形孔,M6,2mm光程,80µL,z=15mmFlow cell quartz 2mm 80uL oval ap. 1/pk
¥17802.02

Agilent安捷伦 5063-6572石英流通池,10x2mm椭圆形孔,M6,5mm光程,200µL,z=15mmFlow cell quartz 5mm 200uL oval ap. 1/pk
¥17802.02
相关问答

