LuMPIS: Luciferase-Based MBP-Pull-Down Protein Interaction Screening System
互联网
互联网
相关产品推荐
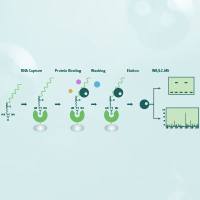
【开学特惠】RNA pull down 技术服务| RNA Pull-down(RNA沉降)实验服务
询价

Recombinant-Mycoplasma-pneumoniae-Oligopeptide-transport-system-permease-protein-oppCoppCOligopeptide transport system permease protein oppC
¥12124

Coronavirus Nucleocapsid重组蛋白|Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid-AVI&His recombinant Protein,Biotinylated
¥4520
sgRNA体外转录和筛选Guide-it™ sgRNA Screening Kit
¥5143

SIRPA/SIRPA蛋白Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SIRPA)重组蛋白Brain Ig-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs蛋白
¥1344

