相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 技术资料
- 库存:
10
- 供应商:
广东固康生物科技有限公司
- 检测范围:
0.1-2.0mol/l
- 检测方法:
酶联免疫法
- 应用:
——
- 适应物种:
大/小鼠
- 标记物:
——
- 样本:
血清/血浆
- 规格:
96人份(复孔检测样本:40个)/盒
【产品名称】
通用名称:阿狄科®大/小鼠非对称二甲基精氨酸检测试剂盒(酶联免疫法)
【预期用途】
本产品用于定量测定啮齿动物EDTA血浆或血清中以及细胞培养基中的非对称二甲基精氨酸 。仅供科研使用。不用于临床诊断。
【包装规格】
规格:96人份(复孔检测样本:40个)/盒
测试次数:96(40份样本一式两份)
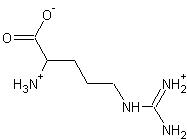
【背景知识】
通用名称:阿狄科®大/小鼠非对称二甲基精氨酸检测试剂盒(酶联免疫法)
【预期用途】
本产品用于定量测定啮齿动物EDTA血浆或血清中以及细胞培养基中的非对称二甲基精氨酸 。仅供科研使用。不用于临床诊断。
【包装规格】
规格:96人份(复孔检测样本:40个)/盒
测试次数:96(40份样本一式两份)

【背景知识】
非对称二甲基精氨酸是NOS内源性抑制剂。它是在甲基化蛋白的蛋白水解过程中形成的,通过DDAH被肾脏排泄或代谢降解去除。包括人内皮细胞和肾小管细胞在内的几种细胞类型能够合成和代谢非对称二甲基精氨酸。许多与内皮功能障碍有关的疾病都发现血液中非对称二甲基精氨酸浓度升高。例如,透析患者血液中非对称二甲基精氨酸水平的升高与动脉硬化程度和心血管风险显著相关。此外,在高胆固醇血症、高血压、动脉硬化、慢性肾功能衰竭和慢性心力衰竭的患者中发现非对称二甲基精氨酸水平升高,与内皮血管扩张受限有关。 在过去的几年中,已证明了NO调节血管张力和结构的重要临床相关性。此外,有报道称,人内皮细胞产生非对称二甲基精氨酸以及NO,这表明非对称二甲基精氨酸对内源性NO的调节。因此,假设慢性肾功能衰竭患者的高血压、动脉硬化和免疫功能障碍与L-精氨酸/NO代谢功能障碍和非对称二甲基精氨酸蓄积有关。L-精氨酸/NO代谢失调的原因只能部分阐明。当然,L-精氨酸/NO代谢调节涉及多个因素,如游离超氧自由基(O2)、非对称二甲基精氨酸积累和NO合酶活性降低。 过去几年的前瞻性临床研究表明,非对称二甲基精氨酸作为新型心血管危险因素的重要性日益提高。
样本要求:啮齿类动物的EDTA血浆和血清及细胞培养基。
储存条件:本产品在2-8℃下保存,可稳定至标签所示日期。
参考文献:
1. Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM, Szuba A, Tangphao O, Tsao PS, Chan JR, Blaschke TF, Cooke JP. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: a novel risk factor for endothelial dysfunction. Its role in hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 1998; 98: 1842 – 1847.
2. Böger RH. The emerging role of asymmetric dimethylarginine as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. Cardiovasc Res. 2003; 59: 824-833.
3. Kielstein JT, Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM, et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: Relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10: 594 – 600.
4. Lu TM, Ding YA, Lin SJ, Lee WS, Tai HC. Plasma levels of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and adverse cardiovascular events after percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J. 2003; 24: 1912-1919.
5. Nijveldt RJ, Teerlink T, Van der Hoven B, Siroen MP, Kuik DJ, Rauwerda JA, van Leeuwen PA. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine in critically ill patients: high plasma concentration is an independent risk factor of ICU mortality. Clin Nutr. 2003; 22: 23-30.
6. Savvidou MD, Hingorani AD, Tsikas D, Frolich JC, Vallance P, Nicolaides KH. Endothelial dysfunction and raised plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine in pregnant women who subsequently develop preeclampsia. Lancet. 2003; 361: 1511-1517.
7. Stühlinger M, Abbasi F, Chu JW, Lamendola C, McLaughlin TL, Cooke JP, Reaven GM, Tsao PS. Relationship between insulin resistance and an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. J Am Med Assoc. 2002; 287: 1420- 1426.
8. Vallance P, Leone A, Calver A, Collier J, Moncada S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of NO synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1992; 339: 572 – 575.
9. Zoccali C, Bode-Böger SM, Mallamaci F, Benedetto FA, Tripepi G, Malatino L, Cataliotti A, Bellanuova I, Fermo I, Frölich JC, Böger RH. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: An endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase predicts mortality in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Lancet. 2001; 358: 2113- 2117.
10. Kwiecien S, Ptak-Belowska A, Krzysiek-Maczka G, Targosz A, Jasnos K, Magierowski M, Szczyrk U, Brzozowski B, Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T. Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, interacts with gastric oxidative metabolism and enhances stress-induced gastric lesions. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012, 63 (5): 515- 524.
11. Piecha G, Koleganova N, Ritz E, Müller A, Fedorova OV, Bagrov AY, Lutz D, Schirmacher P, Gross-Weissmann ML. High Salt Intake Causes Adverse Fetal Programming--Vascular Effects beyond Blood Pressure. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation : Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 2012, 27 (9): 3464–76.
样本要求:啮齿类动物的EDTA血浆和血清及细胞培养基。
储存条件:本产品在2-8℃下保存,可稳定至标签所示日期。
参考文献:
1. Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM, Szuba A, Tangphao O, Tsao PS, Chan JR, Blaschke TF, Cooke JP. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: a novel risk factor for endothelial dysfunction. Its role in hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 1998; 98: 1842 – 1847.
2. Böger RH. The emerging role of asymmetric dimethylarginine as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. Cardiovasc Res. 2003; 59: 824-833.
3. Kielstein JT, Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM, et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: Relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10: 594 – 600.
4. Lu TM, Ding YA, Lin SJ, Lee WS, Tai HC. Plasma levels of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and adverse cardiovascular events after percutaneous coronary intervention. Eur Heart J. 2003; 24: 1912-1919.
5. Nijveldt RJ, Teerlink T, Van der Hoven B, Siroen MP, Kuik DJ, Rauwerda JA, van Leeuwen PA. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine in critically ill patients: high plasma concentration is an independent risk factor of ICU mortality. Clin Nutr. 2003; 22: 23-30.
6. Savvidou MD, Hingorani AD, Tsikas D, Frolich JC, Vallance P, Nicolaides KH. Endothelial dysfunction and raised plasma concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine in pregnant women who subsequently develop preeclampsia. Lancet. 2003; 361: 1511-1517.
7. Stühlinger M, Abbasi F, Chu JW, Lamendola C, McLaughlin TL, Cooke JP, Reaven GM, Tsao PS. Relationship between insulin resistance and an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. J Am Med Assoc. 2002; 287: 1420- 1426.
8. Vallance P, Leone A, Calver A, Collier J, Moncada S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of NO synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1992; 339: 572 – 575.
9. Zoccali C, Bode-Böger SM, Mallamaci F, Benedetto FA, Tripepi G, Malatino L, Cataliotti A, Bellanuova I, Fermo I, Frölich JC, Böger RH. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: An endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase predicts mortality in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Lancet. 2001; 358: 2113- 2117.
10. Kwiecien S, Ptak-Belowska A, Krzysiek-Maczka G, Targosz A, Jasnos K, Magierowski M, Szczyrk U, Brzozowski B, Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T. Asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, interacts with gastric oxidative metabolism and enhances stress-induced gastric lesions. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012, 63 (5): 515- 524.
11. Piecha G, Koleganova N, Ritz E, Müller A, Fedorova OV, Bagrov AY, Lutz D, Schirmacher P, Gross-Weissmann ML. High Salt Intake Causes Adverse Fetal Programming--Vascular Effects beyond Blood Pressure. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation : Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association 2012, 27 (9): 3464–76.

风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料
阿狄科®大/小鼠非对称二甲基精氨酸检测试剂盒(酶联免疫法)
¥11000