相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
江西江蓝纯生物试剂有限公司
- 库存:
87
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
HLA-DRB4
- 抗体名:
组织相容性抗原DRB4抗体
- 适应物种:
人/动物/植物
- 应用范围:
WB,ELISA等
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °
- 规格:
100ul/200ul
| 规格: | 100ul | 产品价格: | ¥1580.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 200ul | 产品价格: | ¥2480.0 |
英文名称 : HLA-DRB4
中文名称 : 组织相容性抗原DRB4抗体
别 名 : DR 4; DR beta 4 chain; DR4; DRB1 transplantation antigen; DRB4; DRB4_HUMAN; HLA class II histocompatibility antigen; HLA class II histocompatibility antigen DR beta 4 chain; HLA-DRB4; Human leucocyte antigen DRB4; Leukocyte antigen; Major histocompatibility complex class II DR beta 4; MHC class II antigen DRB4; MHC class II antigen HLA DR beta; MHC class2 antigen; MHC HLA DR-beta chain.
研究领域 : 细胞生物 免疫学
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human, Dog, Sheep,
产品应用 : ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
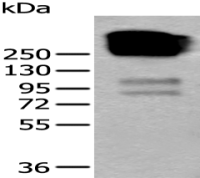
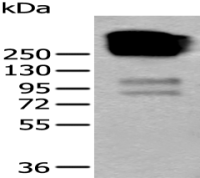
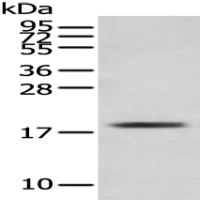
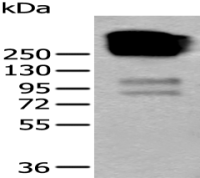
分 子 量 : 27kDa
细胞定位 : 细胞膜
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human HLA-DRB4:21-120/266 <Extracellular>
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : HLA-DRB4 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta (DRB) chain, both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and its gene contains 6 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. DRB1 is expressed at a level five times higher than its paralogues DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. The presence of DRB4 is linked with allelic variants of DRB1, otherwise it is omitted. There are 4 related pseudogenes: DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8 and DRB9. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
Function:
Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accomodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form an heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal miroenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading.
Subcellular Location:
Cell membrane. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Golgi apparatus > trans-Golgi network membrane. Endosome membrane. Lysosome membrane. Late endosome membrane. The MHC class II complex transits through a number of intracellular compartments in the endocytic pathway until it reaches the cell membrane for antigen presentation.
Post-translational modifications:
Ubiquitinated by MARCH1 and MARCH8 at Lys-254 leading to sorting into the endosome system and down-regulation of MHC class II. When associated with ubiquitination of the alpha subunit of HLA-DR: HLA-DRA 'Lys-244', the down-regulation of MHC class II may be highly effective.
Similarity:
Belongs to the MHC class II family.
Contains 1 Ig-like C1-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain.
SWISS:
P13762
Gene ID:
3126
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验(1)主要组织相容性抗原 其免疫原抗性较强,所引起的免疫排斥反应发生得快且强烈,在移植免疫中主要涉及的是主要组织相容性抗原。 (2)次要组织相容性抗原其免疫原性较弱,引起的免疫排斥反应发生得慢而弱。但其重要性也不可忽视,因为由于组织配型技术的进展,可在一定程度上控制主要组织相容性抗原引起的免疫排斥反应,而目前对次要组织相容性抗原了解甚少,尚无法控制。 (3)其他参与排斥反应发生的抗原 如人类ABO血型抗原,组织特异性抗原,内皮细胞抗原,SK抗原,种属特异性糖蛋白抗原。
佚名 本世纪初即已发现,在不同种属或同种不同系的动物个体间进行正常组织或肿瘤移植会出现排斥,它是供者与受者组织不相容的反映。其后证明,排斥反应本质上是一种免疫反应,它是由组织表面的同种异型抗原诱导的。这种代表个体特异性的同种抗原称为组织相容性抗原(histocompatibility antigen)或移植抗原(transplantation antigen
次要组织相容性抗原(mHA)一般仅引起较弱的排斥反应,但某些次要组织相容性抗原的组合能引起强而迅速的排斥反应。 次要组织相容性抗原包括非ABO血型抗原及性染色体相关抗原。例如男性Y染色体上有编码次要组织相容性抗原的基因,称为H-Y基因,女性受者可针对男性供者H-Y抗原产生排斥反应。另外,在不使用免疫抑制剂的情况下,即使主要组织相容性抗原完全相同的同胞兄弟姐妹间进行移植,仍会发生移植排斥,此乃由次要组织相容性抗原所引起,这些抗原可能定位在其他染色体上。由于组织配型技术的改进,在主要
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料