相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
江西江蓝纯生物试剂有限公司
- 库存:
42
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
Phospho-CHK2 (Ser19)
- 抗体名:
磷酸化细胞周期检测点激酶2抗体
- 适应物种:
人/动物/植物
- 应用范围:
WB,ELISA等
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °
- 规格:
100ul
英文名称 : Phospho-CHK2 (Ser19)
中文名称 : 磷酸化细胞周期检测点激酶2抗体
别 名 : bA444G7; CHK2 checkpoint homolog; CHK2_HUMAN; Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2; CDS 1; CDS1; Checkpoint kinase 2; Checkpoint like protein CHK2; Chek 2; Chek2; Chk 2; CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe); CHK2 checkpoint homolog; HuCds 1; HuCds1; LFS 2; LFS2; PP1425; RAD 53; RAD53; Rad53 homolog; Serine/threonine protein kinase Chk2.
产品类型 : 磷酸化抗体
研究领域 : 肿瘤 染色质和核信号 激酶和磷酸酶 表观遗传学
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human,
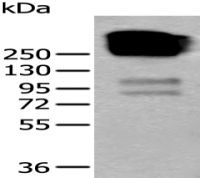
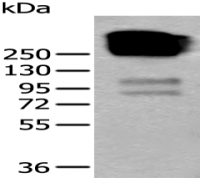
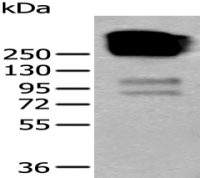
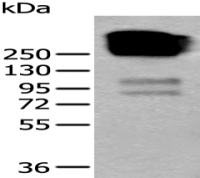
产品应用 : WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
分 子 量 : 61kDa
细胞定位 : 细胞核
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human CHK2 isoform c around the phosphorylation site of ser19:AC(p-S)QP
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : In response to DNA damage and replication blocks, cell cycle progression is halted through the control of critical cell cycle regulators. The protein encoded by this gene is a cell cycle checkpoint regulator and putative tumor suppressor. It contains a forkhead-associated protein interaction domain essential for activation in response to DNA damage and is rapidly phosphorylated in response to replication blocks and DNA damage. When activated, the encoded protein is known to inhibit CDC25C phosphatase, preventing entry into mitosis, and has been shown to stabilize the tumor suppressor protein p53, leading to cell cycle arrest in G1. In addition, this protein interacts with and phosphorylates BRCA1, allowing BRCA1 to restore survival after DNA damage. Mutations in this gene have been linked with Li-Fraumeni syndrome, a highly penetrant familial cancer phenotype usually associated with inherited mutations in TP53. Also, mutations in this gene are thought to confer a predisposition to sarcomas, breast cancer, and brain tumors. This nuclear protein is a member of the CDS1 subfamily of serine/threonine protein kinases. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]
Function:
Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis in response to the presence of DNA double-strand breaks. May also negatively regulate cell cycle progression during unperturbed cell cycles. Following activation, phosphorylates numerous effectors preferentially at the consensus sequence [L-X-R-X-X-S/T]. Regulates cell cycle checkpoint arrest through phosphorylation of CDC25A, CDC25B and CDC25C, inhibiting their activity. Inhibition of CDC25 phosphatase activity leads to increased inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDK-cyclin complexes and blocks cell cycle progression. May also phosphorylate NEK6 which is involved in G2/M cell cycle arrest. Regulates DNA repair through phosphorylation of BRCA2, enhancing the association of RAD51 with chromatin which promotes DNA repair by homologous recombination. Also stimulates the transcription of genes involved in DNA repair (including BRCA2) through the phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor FOXM1. Regulates apoptosis through the phosphorylation of p53/TP53, MDM4 and PML. Phosphorylation of p53/TP53 at 'Ser-20' by CHEK2 may alleviate inhibition by MDM2, leading to accumulation of active p53/TP53. Phosphorylation of MDM4 may also reduce degradation of p53/TP53. Also controls the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes through phosphorylation of the transcription factor E2F1. Tumor suppressor, it may also have a DNA damage-independent function in mitotic spindle assembly by phosphorylating BRCA1. Its absence may be a cause of the chromosomal instability observed in some cancer cells.
Subunit:
Homodimer. Homodimerization is part of the activation process but the dimer may dissociate following activation. Interacts with PML. Interacts with TP53. Interacts with RB1; phosphorylates RB1. Interacts with BRCA1. Interacts (phosphorylated at Thr-68) with MDC1; requires ATM-mediated phosphorylation of CHEK2. Interacts with TP53BP1; modulates CHEK2 phosphorylation at Thr-68 in response to ionizing radiation. Interacts with CDC25A; phosphorylates CDC25A and mediates its degradation in response to ionizing radiation. Interacts with CUL1; mediates CHEK2 ubiquitination and regulation.
Subcellular Location:
Isoform 2: Nucleus. Note=Isoform 10 is present throughout the cell.
Isoform 4: Nucleus.
Isoform 7: Nucleus.
Isoform 9: Nucleus.
Isoform 12: Nucleus.
Nucleus, PML body. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Note=Recruited into PML bodies together with TP53.
Tissue Specificity:
High expression is found in testis, spleen, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes. Low expression is found in other tissues.
Post-translational modifications:
Phosphorylated. Phosphorylated at Ser-73 by PLK3 in response to DNA damage, promoting phosphorylation at Thr-68 by ATM and the G2/M transition checkpoint. Phosphorylation at Thr-68 induces homodimerization. Autophosphorylates at Thr-383 and Thr-387 in the T-loop/activation segment upon dimerization to become fully active and phosphorylate its substrates like for instance CDC25C. DNA damage-induced autophosphorylation at Ser-379 induces CUL1-mediated ubiquitination and regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylation at Ser-456 also regulates ubiquitination. Phosphorylated by PLK4.
Ubiquitinated. CUL1-mediated ubiquitination regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Ubiquitination may also regulate protein stability (PubMed:17715138).
DISEASE:
Defects in CHEK2 are associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2 (LFS2) [MIM:609265]; a highly penetrant familial cancer phenotype usually associated with inherited mutations in p53/TP53.
Defects in CHEK2 may be a cause of susceptibility to prostate cancer (PC) [MIM:176807]. It is a malignancy originating in tissues of the prostate. Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop in the acini of the prostatic ducts. Other rare histopathologic types of prostate cancer that occur in approximately 5% of patients include small cell carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, prostatic ductal carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma (basaloid), signet-ring cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Defects in CHEK2 are found in some patients with osteogenic sarcoma (OSRC) [MIM:259500].
Defects in CHEK2 is a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]. A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. Note=CHEK2 variants are associated with susceptibility to breast cancer and contribute to a substantial fraction of familial breast cancer (PubMed:12094328).
Similarity:
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CHK2 subfamily.
Contains 1 FHA domain.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
SWISS:
O96017
Gene ID:
11200
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
Chk2作为Cdks的调节参与细胞周期调节过程,是生物进化过程中非常保守的蛋白激酶,在DNA损伤引起的细胞周期检测点调节中有着非常重要的作用。
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验3 篇 Nature 连发,解决世纪难题,周期蛋白的毁灭调控蕴含癌症患者的新生
在 cyclin D 上,被泛素化标记的 cyclin D 将会被蛋白酶体降解。此外研究还发现,AMBRA1 缺失会导致 cyclin D 和 MYC 蛋白水平升高。cyclin D 与 CDK4/6 结合,使 RB1 蛋白磷酸化。磷酸化 RB1 释放 E2F 转录因子来驱动细胞周期进程所需基因的表达。在 AMBRA1 缺失的细胞中,cyclin D 也能与 CDK2 激酶形成复合物,使癌细胞能够抵抗 CDK4/6 抑制剂的治疗。高水平的 cyclin D 会促进细胞增殖,从而导致 DNA 损伤、复制应激
【求助】P53的翻译后修饰都有哪些? 怎样验证其修饰后与靶标启动子的结合活性的变化?
酰转移酶p300的结合增强,从而增加了p53的水平和稳定性。Ser15可在IR(电离辐射)或UV(紫外线)作用下发生磷酸化。同时IR 或UV 还可以分别通过活化CHK2(细胞周期关卡激酶2)和CHK1(细胞周期关卡激酶1)引起Ser20的磷酸化。 除常见的72位密码子多态性外,p53肿瘤还可显示一种少见的47位残基上的单核苷酸多态现象,野生型p53在此残基上编码脯氨酸,而在少数人群中编码的则是丝氨酸。此残基临近的Ser46被p38磷酸化后可以显著增强p53诱导凋亡的能力,而Ser-47多态
颠覆认知!为了生存,癌细胞竟主动断裂 DNA,Science 研究揭开背后机制
的。 那么 CAD 和 ICAD 是否嵌入到 DDR 信号机制中呢?研究人员注意到,ATM 和 ATR 激酶活性的抑制或丢失可以限制 CAD/ICAD 的募集,减少相应的 DNA 断裂数量。为了确定 ATR 是否更直接地调控 ICAD,研究人员分析了 ICAD 的序列并确定了两个潜在的 ATM/ATR 磷酸化位点,Ser107 和 Ser257。研究人员发现在细胞暴露于 IR 后,这两个位点都出现了广泛的磷酸化,并且磷酸化依赖于 IR 后 24 小时 ATM 和 ATR 激酶的活性。 这表明 ATR/ATM