相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
江西江蓝纯生物试剂有限公司
- 库存:
189
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
phospho-c-Abl (Tyr89)
- 抗体名:
磷酸化非受体酪氨酸激酶c-Abl抗体
- 适应物种:
人/动物/植物
- 应用范围:
WB,ELISA等
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 保存条件:
-20 °
- 规格:
100ul
英文名称 : phospho-c-Abl (Tyr89)
中文名称 : 磷酸化非受体酪氨酸激酶c-Abl抗体
别 名 : c-Abl(phospho Y89); c-Abl(phospho Tyr89); p-c-Abl(Tyr89); tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 isoform b; Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; Abelson murine leukemia viral v abl oncogene homolog 1; Abl 1; ABL; Abl protein; Abl1; Bcr/c abl oncogene protein; JTK 7; JTK7; p150 ; Proto oncogene tyrosine protein kinase ABL1; Transformation gene oncogene ABL; v abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1; v abl; ABL1_HUMAN.
产品类型 : 磷酸化抗体
研究领域 : 肿瘤 细胞生物 信号转导 细胞凋亡 转录调节因子 激酶和磷酸酶
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit,
产品应用 : WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
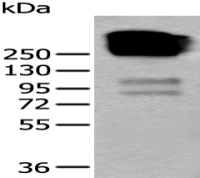
分 子 量 : 124kDa
细胞定位 : 细胞核 细胞浆 细胞膜
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human c-Abl isoform b around the phosphorylation site of Tyr89:AL(p-Y)DF
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : The ABL1 protooncogene encodes a cytoplasmic and nuclear protein tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in processes of cell differentiation, cell division, cell adhesion, and stress response. Activity of c-Abl protein is negatively regulated by its SH3 domain, and deletion of the SH3 domain turns ABL1 into an oncogene. The t(9;22) translocation results in the head-to-tail fusion of the BCR (MIM:151410) and ABL1 genes present in many cases of chronic myelogeneous leukemia. The DNA-binding activity of the ubiquitously expressed ABL1 tyrosine kinase is regulated by CDC2-mediated phosphorylation, suggesting a cell cycle function for ABL1. The ABL1 gene is expressed as either a 6- or 7-kb mRNA transcript, with alternatively spliced first exons spliced to the common exons 2-11. [provided by RefSeq].
Function:
Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays a role in many key processes linked to cell growth and survival such as cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, cell motility and adhesion, receptor endocytosis, autophagy, DNA damage response and apoptosis. Coordinates actin remodeling through tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins controlling cytoskeleton dynamics like WASF3 (involved in branch formation); ANXA1 (involved in membrane anchoring); DBN1, DBNL, CTTN, RAPH1 and ENAH (involved in signaling); or MAPT and PXN (microtubule-binding proteins). Phosphorylation of WASF3 is critical for the stimulation of lamellipodia formation and cell migration. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and motility through phosphorylation of key regulators of these processes such as BCAR1, CRK, CRKL, DOK1, EFS or NEDD9. Phosphorylates multiple receptor tyrosine kinases and more particularly promotes endocytosis of EGFR, facilitates the formation of neuromuscular synapses through MUSK, inhibits PDGFRB-mediated chemotaxis and modulates the endocytosis of activated B-cell receptor complexes. Other substrates which are involved in endocytosis regulation are the caveolin (CAV1) and RIN1. Moreover, ABL1 regulates the CBL family of ubiquitin ligases that drive receptor down-regulation and actin remodeling. Phosphorylation of CBL leads to increased EGFR stability. Involved in late-stage autophagy by regulating positively the trafficking and function of lysosomal components. ABL1 targets to mitochondria in response to oxidative stress and thereby mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. ABL1 is also translocated in the nucleus where it has DNA-binding activity and is involved in DNA-damage response and apoptosis. Many substrates are known mediators of DNA repair: DDB1, DDB2, ERCC3, ERCC6, RAD9A, RAD51, RAD52 or WRN. Activates the proapoptotic pathway when the DNA damage is too severe to be repaired. Phosphorylates TP73, a primary regulator for this type of damage-induced apoptosis. Phosphorylates PSMA7 that leads to an inhibition of proteasomal activity and cell cycle transition blocks. ABL1 acts also as a regulator of multiple pathological signaling cascades during infection. Several known tyrosine-phosphorylated microbial proteins have been identified as ABL1 substrates. This is the case of A36R of Vaccinia virus, Tir (translocated intimin receptor) of pathogenic E.coli and possibly Citrobacter, CagA (cytotoxin-associated gene A) of H.pylori, or AnkA (ankyrin repeat-containing protein A) of A.phagocytophilum. Pathogens can highjack ABL1 kinase signaling to reorganize the host actin cytoskeleton for multiple purposes, like facilitating intracellular movement and host cell exit. Finally, functions as its own regulator through autocatalytic activity as well as through phosphorylation of its inhibitor, ABI1.
Subunit:
Interacts with SORBS1 following insulin stimulation. Found in a trimolecular complex containing CDK5 and CABLES1. Interacts with CABLES1 and PSTPIP1. Interacts with ZDHHC16, ITGB1 and HCK (By similarity). Interacts with INPPL1/SHIP2. Interacts with the 14-3-3 proteins, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, SFN AND YWHAZ; the interaction with 14-3-3 proteins requires phosphorylation on Thr-735 and, sequesters ABL1 into the cytoplasm. Interacts with ABI1, ABI2, BCR, CRK, FGR, FYN, HCK, LYN, PSMA7 RAD9A, RAD51, RAD52, TP73 and WASF3. A complex made of ABL1, CTTN and MYLK regulates cortical actin-based cytoskeletal rearrangement critical to sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-mediated endothelial cell (EC) barrier enhancement.
Subcellular Location:
Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus. Mitochondrion. Note=Shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm depending on environmental signals. Sequestered into the cytoplasm through interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. Localizes to mitochondria in response to oxidative stress. Isoform IB: Nucleus membrane; Lipid-anchor. Note=The myristoylated c-ABL protein is reported to be nuclear.
Tissue Specificity:
Widely expressed.
Post-translational modifications:
Acetylated at Lys-711 by EP300 which promotes the cytoplasmic translocation.
Phosphorylation at Tyr-70 by members of the SRC family of kinases disrupts SH3 domain-based autoinhibitory interactions and intermolecular associations, such as that with ABI1, and also enhances kinase activity. Phosphorylation at Tyr-226 and Tyr-393 correlate with increased activity. DNA damage-induced activation of ABL1 requires the function of ATM and Ser-446 phosphorylation. Phosphorylation at Ser-569 has been attributed to a CDC2-associated kinase and is coupled to cell division. Phosphorylation at Ser-618 and Ser-619 by PAK2 increases binding to CRK and reduces binding to ABI1. Phosphorylation on Thr-735 is required for binding 14-3-3 proteins for cytoplasmic translocation. Phosphorylated by PRKDC.
Polyubiquitinated. Polyubiquitination of ABL1 leads to degradation.
Isoform IB is myristoylated on Gly-2.
DISEASE:
Note=A chromosomal aberration involving ABL1 is a cause of chronic myeloid leukemia. Translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) with BCR. The translocation produces a BCR-ABL found also in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Similarity:
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. ABL subfamily.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Contains 1 SH2 domain.
Contains 1 SH3 domain.
SWISS:
P00519
Gene ID:
25
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
非受体酪氨酸激酶c-Abl广泛表达于各组织细胞中,c-Abl是非受体酪氨酸激酶Src家族的一个成员。在生理状态下,它可以定位于多个亚细胞结构(如细胞核、细胞质、线粒体等)中并呈现不同功能。经研究认为,细胞核内的c-Abl在细胞凋亡调控以及DNA损伤修复过程中起重要作用,而胞质中的c-Abl则与细胞黏附、细胞分化及氧化应激有关联,该蛋白主要用于细胞凋亡的研究。
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验网络 第二节 蛋白酪氨酸激酶 蛋白酷氨酸激酶(protein tyrosine kinase,PTK)是一类催化ATP上γ-磷酸转移到蛋白酪氨酸残基上的激酶,能催化多种底物蛋白质酪氨酸残基磷酸化,在细胞生长、增殖、分化中具有重要作用。迄今发现的蛋白酪氨酸激酶中多数是属于致癌RNA病毒的癌基因产物,也可由脊椎动物的原癌基因产。根据PTK是否存在于细胞膜受体
,能与配体直接结合,对 Hh 信号起负调控作用。受体 Smo 由原癌基因 Smothened 编码,与 G 蛋白偶联受体同源,由 7 个跨膜区的单一肽链构成,N 端位于细胞外,C 端位于细胞内,跨膜区氨基酸序列高度保守,C 末端的丝氨酸与苏氨酸残基为磷酸化部位,蛋白激酶催化时结合磷酸基团。该蛋白家族成员只有当维持全长时才有转录启动子的功能,启动下游靶基因的转录。
、Itk、Tec等,与受体结合或不结合存在,配体结合后被激活; (3)ZAP70家族:ZAP70和Syk,与磷酸化的受体结合后被激活; (4)JAK家族:JAK1、JAK2、JAK3等。 这些PTKs或者直接与受体形成复合物,或者间接地依次被激活,在传递受体信号过程中起着接力棒的作用。 C.核内蛋白酪氨酸激酶 大部分的酪氨酸蛋白激酶位于胞膜上或胞浆内,近年来却发现核内也存在着酪氨酸蛋白激酶,这对于信号在核内的传递有重要意义。重要的核内PTKs有Abl