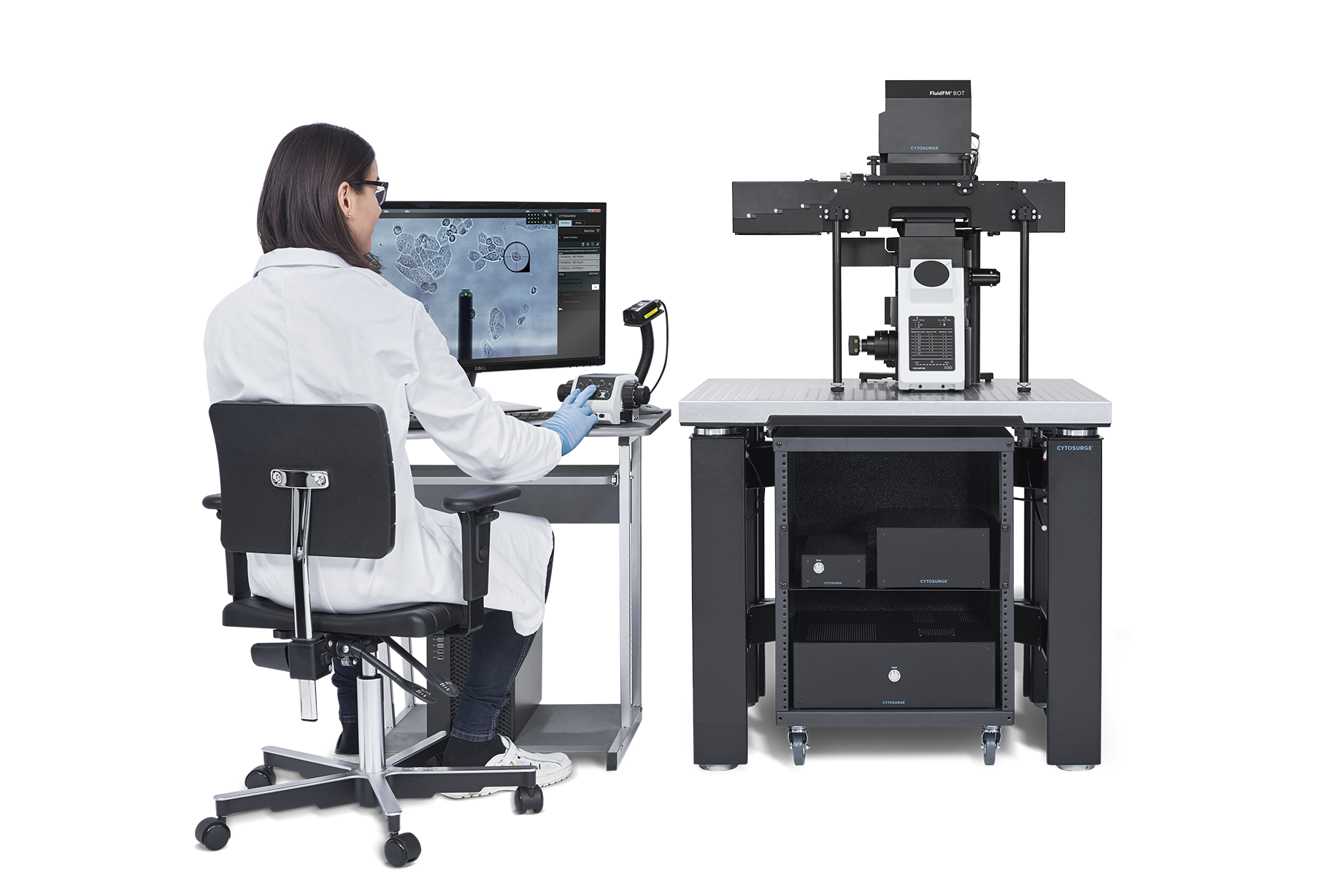
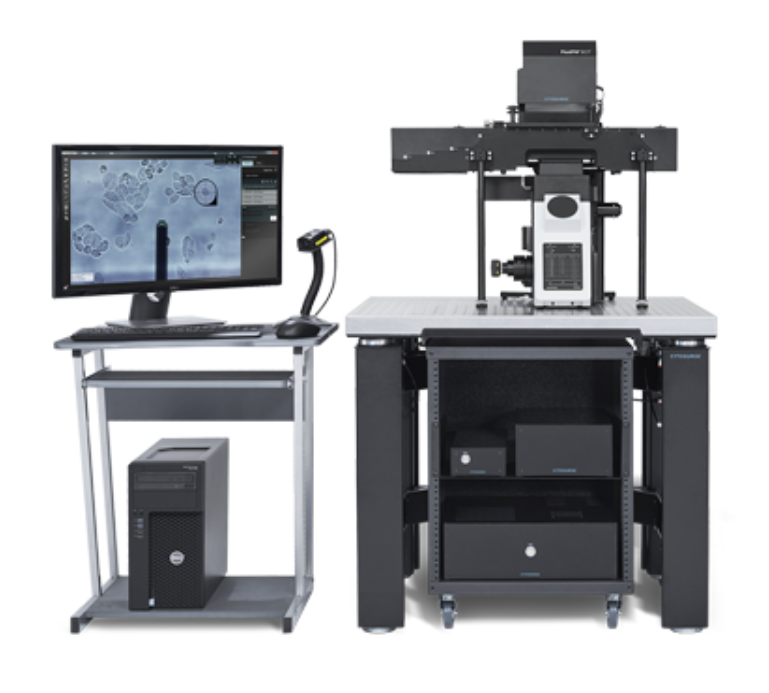
多功能单细胞显微操作系统-FluidFM OMNIUM
研选同类产品更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 用户评价
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
QUANTUM量子科学仪器贸易(北京)有限公司
多功能单细胞显微操作系统- FluidFM OMNIUM
瑞士Cytosurge公司多功能单细胞显微操作系统—FluidFM OMNIUM,是将原子力系统、微流控系统、细胞培养系统为一体的单细胞操作系统。主要功能包括单细胞注射、单细胞提取、单细胞分离、单细胞粘附力的测定、生物3D打印等。
FluidFM OMNIUM打开了传统单细胞实验手段无法触及领域的大门。突破了单细胞研究、药物开发、细胞系开发中的障碍,让细胞膜不再成为阻碍单细胞研究的壁垒。
多功能单细胞显微操作系统FluidFM OMNIUM浓缩了FluidFM技术的全部精华,尤其是在自动化程度和操作速度上的提高。它不仅保留了产品在生物学上的能力,更能够将这些功能进行组合来创造更加高效、便捷全新的试验方法。

应用领域:
FluidFM OMNIUM方便了单细胞水平的研究,尤其适合应用于医疗、单细胞生物学、单细胞质谱、单细胞基因编辑、药物研发等领域。
基本参数:
- 单细胞水平的显微注射、提取、分离以及细胞粘附力测定,全过程通过软件设置自动化完成;
- 全自动进行细胞核、细胞质定位注射;
- 软件自动更换探针更换,无需手动加载;
- 样品台移动精度:XY轴不大于1 nm;Z轴不大于0.2nm;
- 探针力学控制:提供探针当前压力值并绘制曲线;
- 配置高灵敏度液体微流控系统,流体压力控制精度:±0.5 mbar;
设备特点:
先进:深度自动化设计
一体:无需购买额外设备
简易:操作只需要轻点鼠标
可控:所有变量均可通过软件操纵
|
|
单细胞注射 无损注入的将不同类型的物质准确注入到细胞质或者细胞核。 每小时可注射>100个细胞。
|
|
|
单细胞提取 提取后细胞仍可存活。
|
|
|
细胞分离 无论悬浮或者贴壁细胞均可分离或者分选。整个过程对细胞无损伤。
|
|
|
点打印 纳米精度的高密度点打印能够快速建立使用诸如蛋白、DNA等物质 构成生物感应列阵。
|
|
|
纳米光刻技术 打印纳米精度的各种生物分子所构成的复杂图案。 |
单细胞注射——快速、准确、低损伤
|
|
更优的CRISPR-Cas转染方式: 能够进行高速、高效地将CRISPR-Cas复合物注入细胞,帮助您克服对于传统方式难转染的细胞基因编辑问题。 |
|
|
|
提高质粒的转染效率: 相比于传统的转染方式,FluidFM更加温和、快速,对细胞的损伤更小。 |
|
|
|
贴壁细胞均可注射: 对于注射细胞的种类,本产品并没有太多的限制,即使像心肌细胞这样的注射难度很高的细胞也能够胜任。 |
|
|
|
准确注入体积计算: 通过比对注入荧光分子物质的荧光强度准确计算注入荧光分子的体积。 |
单细胞提取——微量、低创、准确
|
|
活细胞提取 从活细胞中直接提取内容物,并且提取后细胞仍可存活。 |
|
|
|
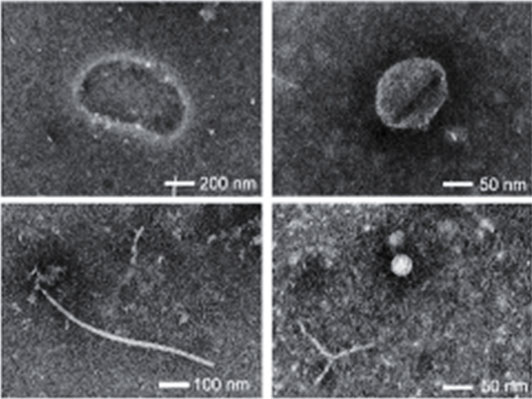
电镜成像 相比于传统的裂解方式,FluidFM OMNIUM提取的样本更为干净,可以得到很好地电镜图像。 |
|
|
|
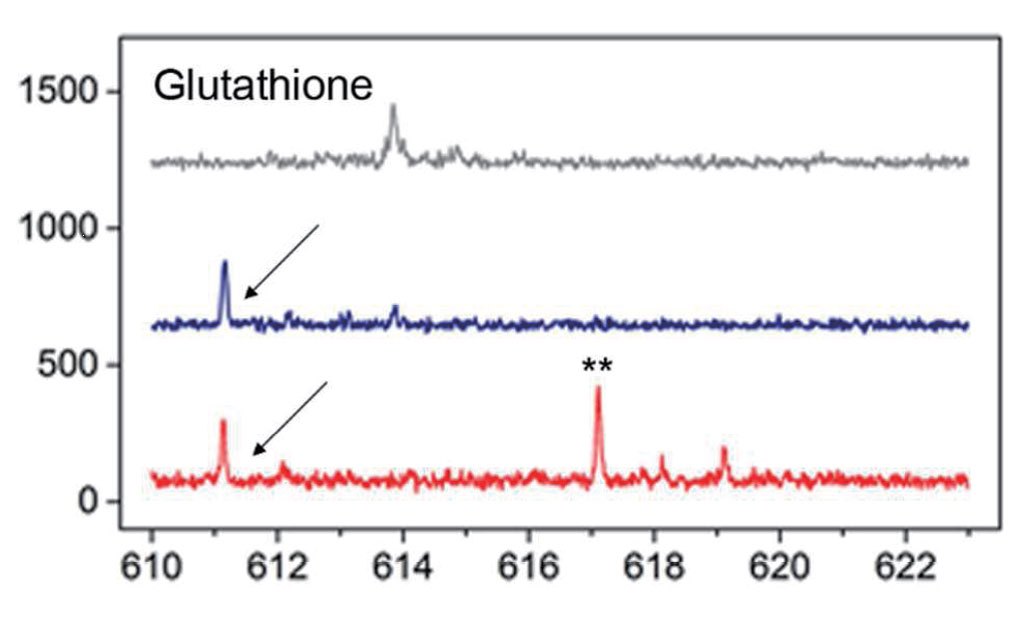
mRNA、酶活力的检测 FluidFM OMNIUM提取的样本也可以直接用于酶活力的测定或mRNA的检测。 |
|
|
|
单细胞质谱分析 FluidFM OMNIUM提取样本也可应用于单细胞代谢组学样本的质谱分析。 |
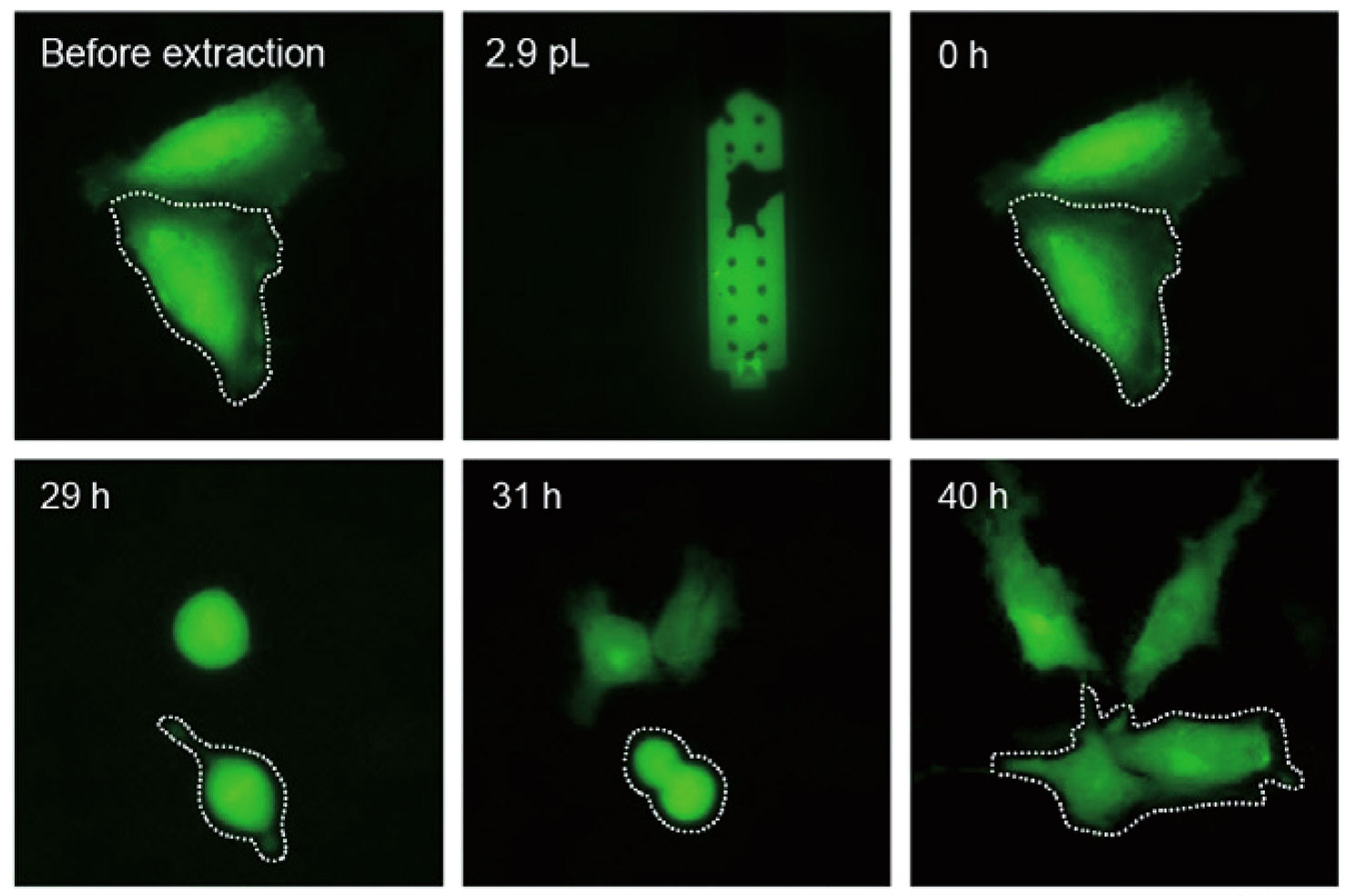
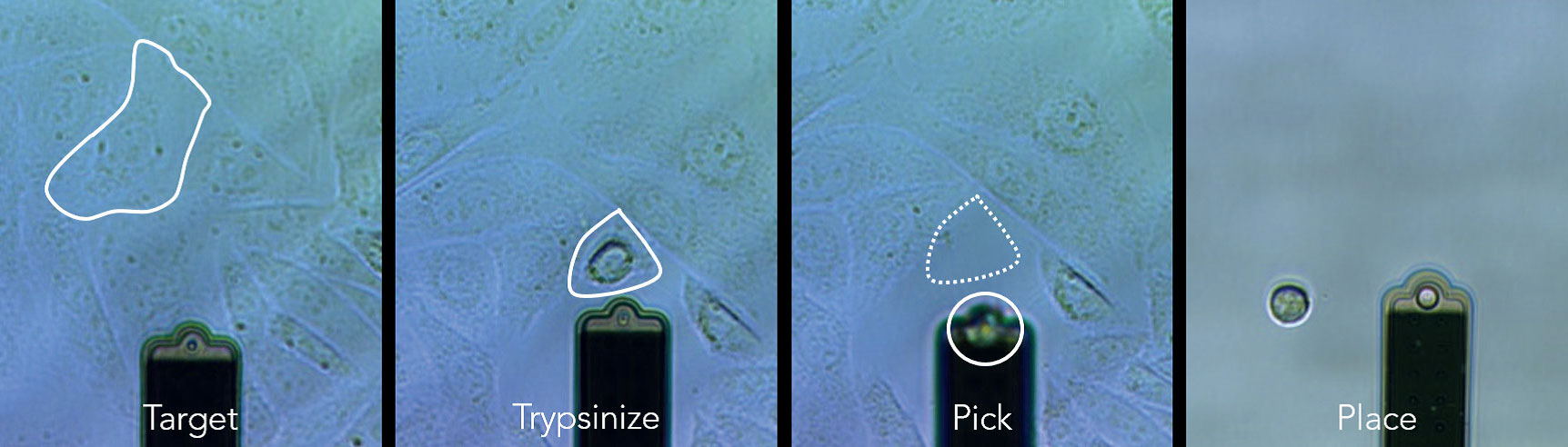
单细胞分离——直观、简单、低损
FluidFM® 一气呵成的细胞分离过程
使用FluidFM OMNIUM分离CHO细胞,仅仅点击几次鼠标,单个细胞便准确的完成了转移。
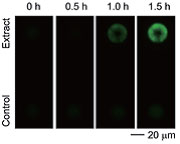
小样本细胞群分离十分友好
对于细胞数不足以使用流式细胞仪分选时,FluidFM OMNIUM很好的这个空白。

测试数据
肝细胞的微量注射

HeLa细胞的微量提取

CHO细胞的单细胞分离

纳米光刻DAPI染料

发表文章
单细胞注射:
1. O.Guillaume-Gentil, E.Potthoff, D.Ossola, et al. Force-controlled fluidic injection into single cell nuclei.(2013)Small,9(11),1904?1907. doi:10.1002/ smll.201202276A.
2. Meister, M. Gabi, P.Behr, et al. FluidFM: Combining atomic force microscopy and nanofluidics in a universal liquid delivery system for single cell applications and beyond.(2009) Nano Letters, 9(6), 2501?2507. doi:10.1021/nl901384x
单细胞提取:
1. O. Guillaume-Gentil, T. Rey, P. Kiefer, A.J. Ibá?ez, R. Steinhoff, R. Br?nnimann, L. Dorwling-Carter, H. Zambelli, R. Zenobi & J.A. Vorholt. Single-Cell Mass Spectrometry of Metabolites Extracted from Live Cells by Fluidic Force Microscopy. (May 2017) Anal Chem., 89(9), 5017-5023. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00367
2. O. Guillaume-Gentil, R.V. Grindberg, R. Kooger, L. Dorwling-Carter, V. Martinez, D. Ossola, M. Pilhofer, T. Zambelli & J.A. Vorholt. Tunable Single-Cell Extraction for Molecular Analyses. (Jul 2016) Cell, 166(2), 506-516. doi: 10.1016/j. cell.2016.06.025.
单细胞分离:
1. O. Guillaume-Gentil, T. Zambelli & J.A. Vorholt.Isolation of single mammalian cells from adherent cultures by fluidic force microscopy. (2014) Lab on a chip, 14(2), 402-414. doi:10.1039/c3lc51174j
2. P. Stiefel, T. Zambelli & J.A. Vorholt. Isolation of optically targeted single bacteria by application of fluidic force microscopy to aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs from the phyllosphere. (2013) Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(16), 4895-4905. doi:10.1128/AEM.01087-13P.
3. D?rig, P. Stiefel, P. Behr, et al. Force-controlled spatial manipulation of viable mammalian cells and micro-organisms by means of FluidFM technology.(2010) Applied Physics Letters, 97(2), 023701 1-3. doi:10.1063/1.3462979
2021
1. M. Mathelié-Guinlet, F. Viela, J. Dehullu, S. Filimova, J.M. Rauceo, P.N. Lipke & Y.F. Dufrêne. Single-cell fluidic force microscopy reveals stress-dependent molecular interactions in yeast mating. (2021) Commun Biol. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01498-9
AFM Series: Adhesion of single cells
2020
1. A.G. Nagy, A. Bonyár, I. Székács & R. Horvath. Analysis of single-cell force-spectroscopy data of Vero cells recorded by FluidFM BOT. (2020) IEEE 26th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging (SIITME). doi: 10.1109/SIITME50350.2020.9292265, BIO Series: Adhesion of single cells
2. I. Demir, J. Blockx, E. Dague, P. Guiraud, W. Thielmans, K. Muylaert & C. Formosa-Dague. Nanoscale Evidence Unravels Microalgae Flocculation Mechanism Induced by Chitosan. (2020) ACS Applied Biomaterials. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c007722. AFM Series: Adhesion of single cells
3. P. Saha, T. Duanis-Assaf & M. Reches. Fundamentals and Applications of FluidFM Technology in Single-Cell Studies. (2020) Advanced Materials Interfaces. doi: 10.1002/admi.20001115. AFM Series: REVIEW
4. T. Schlotter, S. Weaver, C. Forró, D. Momotenko, J. Voros, T. Zambelli & M. Aramesh. Force-Controlled formation of dynamic nanopores for single-biomolecule sensing and single-cell secretomics. (2020) ACS Nano. doi: 10.1021/acs.nano.0c04281. AFM Series: SICM, other
5. L. Hofherr, C. Müller-Renno, C. Ziegler. FluidFM as a tool to study adhesion forces of bacteria - Optimization of parameters and comparison to conventional bacterial probe Scanning Force Spectroscopy. (2020). PLOS ONE. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227395. AFM Series: Adhesion of single bacteria
6. T. Schlotter, S. Weaver, T. Zambelli, J. Voros & M. Aramesh. Force-controlled nanopores for single cell measurements using micro-channelled AFM Cantilevers. (2020). Biophysical Journal. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.11.1066. AFM Series: Other
7. J. Zhang, H. Yu, B. Harris, Y. Zheng, U. Celik, L. Na, R. Faller, X. Chen, D. R. Haudenschild, G. Liu. New Means to Control Molecular Assembly (2020) ACS Publications. doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b11377. BIO Series: Nanolithography
8. P. Wysotzki, A. Sancho, J. Gimsa, J. Groll. A comparative analysis of detachment forces and energies in initial and mature cell-material interaction (2020) Science Direct. doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110894. AFM Series: Single Force Spectroscopy
9. M. Sztilkovics, T. Gerecsei, B. Peter, A. Saftics, S. Kurunczi, I. Szekacs, B. Szabo & R. Horvath. Single-cell adhesion force kinetics of cell populations from combined label-free optical biosensor and robotic fluidic force microscopy. (2020) Scientific Reports. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56898-7. BIO Series: Adhesion of single cells
用户单位
国内用户:

国外用户:


风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 用户评价
用户评价 暂无用户评价
暂无用户评价 文献和实验
文献和实验单细胞注射、提取
• W. Chen, O. Guillaume-Gentil, P. Y. Rainer, C. G. Gäbelein, W. Saelens, V. Gardeaux, A. Klaeger, R. Dainese, M. Zachara, T. Zambelli, J. A. Vorholt & B. Deplancke. Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells. (2022) Nature
• Q. Hu, J. Lu, X. Zhang, R. Liu & S-H. Yang. Mitochondria transplantation/transfer between single cells. (2022). Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism.
• C. Gäbelein, Q. Feng, E. Sarajlic, T. Zambelli, O. Guillaume-Gentil, B. Kornmann & J. Vorholt. Mitochondria transplantation between living cells. (2022). PLoS Biology.
• O. Guillaume-Gentil, C. G. Gäbelein, S. Schmieder, V. Martinez, T. Zambelli, M. Künzler & J.A. Vorholt. Injection into and extraction from single fungal cells. (2022). Communications Biology.
• M. Li, L. Liu & T. Zambelli. FluidFM for single-cell biophysics. (2021). Nano Research. doi: 10.1007/s12274-021-3573-y FluidFM for single-cell biophysics (2021) Nano Research.
• Y. Cui, X. Lyu, L. Ding, L. Ke, D. Yang, M. Pirouz, Y. Qi, J. Ong, G. Gao, P. Du & R.I. Gregory. Global miRNA dosage control of embryonic germ layer specification. (2021) Nature.
• P. Saha, T. Duanis-Assaf & M. Reches. Fundamentals and Applications of FluidFM Technology in Single-Cell Studies. (2020) Advanced Materials Interfaces.
单细胞分选
• F. Weigl, C. Blum, A. Sancho & J. Groll. Correlative Analysis of Intra- versus Extracellular Cell Detachment Events vis the Alignment of Optical Imaging and Detachment Force Quantification. (2022). Adv. Mater. Technol.
• P.W. Doll, K. Doll, A. Winkel, R. Thelen, R. Ahrens, M. Stiesch & A.E. Guber. Influence of the Available Surface Area and Cell Elasticity on Bacterial Adhesion Forces on Highly Ordered Silicon Nanopillars. (2022). ACS Omega.
• A.G. Nagy, N. Kanyó, A. Vörös, I. Székács, A. Bonyár & R. Horvath. Population distributions of single-cell adhesion parameters during the cell cycle from high-throughput robotic fluidic force microscopy. (2022). Scientific Reports.
• F. Pan, M. Liu, S. Altenried, M. Lei, J. Yang, H. Straub, W.W. Schmal, K. Maniura-Weber, O. Guillaume-Gentil & Q. Ren. Uncoupling bacterial attachment on and detachment from polydimethylsiloxane surfaces though empirical and simulation studies. (2022). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science.
• C. Chien, J. Jiang, B. Gong, T. Li & A. Gaitas. AFM Microfluidic Cantilevers as Weight Sensors for Single Cell Mass Measurements. (2022). BioRxiv.
• A. Sancho, M. B. Taskin, L. Wistlich, P. Stahlhut, K. Wittmann, A. Rossi & J. Groll. Cell Adhesion Assessment Reveals a Higher Force per Contact Area on Fibrous Structures Compared to Flat Surfaces. (2022). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng.
• M. Li, L. Liu & T. Zambelli. FluidFM for single-cell biophysics. (2021). Nano Research. doi: 10.1007/s12274-021-3573-y FluidFM for single-cell biophysics (2021) Nano Research.
• W. Li, A. Sancho, W. Chung, Y. Vinik, J. Groll, Y. Zick, O. Medalia, A.D. Bershadsky & B. Geiger. Differential cellular responses to adhesive interactions with galectin-8- and fibronectin-coated substrates. (2021) Journal of Cell Science.
• A. Garitano-Trojaola, A. Sancho, R. Goetz, P. Eiring, S. Walz, H. Jetani, J. Gil-Pulido, M. DaVia, E. Teufel, N. Rhodes, L. Haertle, E. Arellano-Viera, R. Tibes, A. Rosenwald, L. Rasche, M. Hudecek, M. Sauer, J. Groll, H. Einsele, S. Kraus & M. Kortüm. Actin cytoskeleton deregulaltion confers midostaurin resistance in FLT-3 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. (2021) Communications Biology.
• N. Chala, S. Moimas, C. Giampietro, X. Zhang, T. Zambelli, V. Exarchos, T.Z. Nazari-Shafti, D. Poulikakos & A. Ferrari. Mechanical Fingerprint of Senescence in Endothelial Cells. (2021) Nano Letters.
• Y. Guo, F. Mei, Y. Huang, S. Ma, Y. Wei, X. Zhang, M. Xu, Y. He, B.C. Heng, L. Chen & X. Deng. Matrix stiffness modulates tip cell formation through the p-PXN-Rac1-YAP signaling axis. (2021) Bioactive Materials.
• M. Koehler, S.J.L. Petitjean, J. Yang, P. Aravamudhan, X. Somoulay, C. Lo Giudice, M. A. Poncin, A.C. Dumitru, T.S. Dermody & D. Alsteens. Reovirus directuly enganges integrin to recruit clathrin for entry into host cells. (2021) Nature communications, 12, 2149.
• M. Mathelié-Guinlet, F. Viela, J. Dehullu, S. Filimova, J.M. Rauceo, P.N. Lipke & Y.F. Dufrêne. Single-cell fluidic force microscopy reveals stress-dependent molecular interactions in yeast mating. (2021) Commun Biol.
其他
• C. Shen, Z. Zhu, D. Zhu, C. van Nisselroy, T. Zambelli & D. Momotenko. Electrochemical 3D printing of Ni-Mn and Ni-Co alloy with FluidFM. (2022). Nanotechnology.
• C. Chien, J. Jiang, B. Gong, T. Li & A. Gaitas. AFM Microfluidic Cantilevers as Weight Sensors for Single Cell Mass Measurements. (2022). BioRxiv.
• I. Demi, I. Lüchtefeld, C. Lemen, E. Dague, P. Guiraud, T. Zambelli & C. Formosa-Dague. Probing the interactions between air bubbles and (bio)interfaces at the nanoscale using FluidFM technology. (2021). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science.
• C. Müller-Renno, D. Remmel, M. Braun, K. Boonrod, G. Krczal & C. Ziegler. Producing plant virus patterns with defined 2D structure. (2021). PSS Applications and materials science.
• S. Wang, S. Liu, A. Sulkanen, J.M. Fox, X. Jia & G. Liu. Controlled Molecular Assembly of Tetrazine Derivatives on Surfaces. (2021). CCS Chem. (2021) CCS Chem.
• A. Saftics, B. Türk, A. Sulyok, N. Nagy, T. Gerecsei, I. Szekacs, S. Kurunczi & R. Horvath. Biomimetic dextran-based hydrogel layers for cell micropatterning over large areas using the FluidFM BOT technology. (2019) Langmuir, ACS.Langmuir.8b03249.
• J. Zhang, H. Yu, B. Harris, Y. Zheng, U. Celik, L. Na, R. Faller, X. Chen, D. R. Haudenschild, G. Liu. New Means to Control Molecular Assembly (2020) ACS Publications.
为了实现这一目标,我们利用 TruAI 技术生成了一个深层神经网络 (DNN) 模型,该模型能够在所有时间点准确地识别多能 ESC 和分化细胞的位置,即使是在荧光强度很弱的情况下。 使用这个技术可以长期对细胞群的 G1、S 和 G2 期进行可靠的监控。 随后,通过应用 scanR 动力学模块,我们可以追踪数以千计的细胞,评估每个细胞的运动轨迹,并获得单细胞水平在细胞周期变化方面的定量动态信息。 为了展示 scanR 系统作为研究工具的多功能性,所有数据的展示(包括直方图、散点图、图库、踪迹和动力
的荧光标记物发光的现象。在生物学领域中,由于分析物质荧光的方法敏感性极高,而且几乎所有的有机分子都能够直接或经过适当的化学处理后发生荧光,故很早就受到重视,并逐渐发展成为生物学和医学中的荧光分析。在生物医学领域应用荧光分析最多的是荧光显微技术,基本工具为荧光显微镜。但一般的荧光显微镜某些情况下荧光的亮度不足,使观察困难随着光电技术和计算机技术的进步,已经发展出的激光共聚焦显微镜,操作更加方便,实验可重复性提高,使受激荧光的应用更加广泛[5]。 2 、发光生物发光 在生物发光领域中最容易
设计,便捷精确的操作系统,使实验室影像分析领域进入了一个全新的时代。 下面以研究干细胞活体移植后的存活率为例,简介一两种内源性荧光色素标记的实验方法,供专业人士参考。 用荧光色素DiD标记 间充质干细胞 1. 先用胰蛋白酶消化待标记材料,使之成为一定密度的悬浮液; 2. 从细胞培养箱中取出间充质干细胞,吸取含原有培养基的细胞悬浮液进行标记; 3. 用10 ml Mg/Ca-free PBS (不含钙镁离子的磷酸缓冲液)清洗细胞,吸去PBS, 钙镁离子会影响胰蛋白
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料