万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 库存:
99
- 供应商:
BIOCYTO
- 肿瘤类型:
NC
- 细胞类型:
primary
- 品系:
NC
- 组织来源:
KINDY
- 相关疾病:
NC
- 物种来源:
RAT
- 免疫类型:
NC
- 细胞形态:
圆梭形
- 是否是肿瘤细胞:
否
- 器官来源:
Renal
- 运输方式:
常温
- 年限:
NC
- 生长状态:
贴壁
- 规格:
10^6
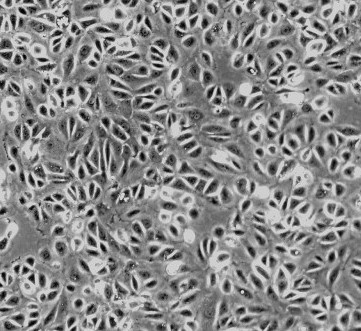
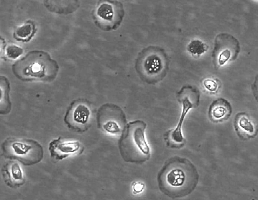
Renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (RPTEpiC) play a crucial role in renal function. They reabsorb nearly all of the glucose and amino acids in the glomerular filtrate, while allowing other substances of no nutritional value to be excreted in the urine. They are also a major site of injury in a variety of congenital, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases. RPTEpiC can produce inflammatory mediators such as cytokines or chemokines and actively participate in acute inflammatory processes by affecting and directing leukocyte chemotaxis via the production of IL-8 [1, 2]. RPTEpiC express IL-2R alpha and MHC class II antigens during inflammation after renal transplantation or in crescentic glomerulonephritis, indicating the capacity to participate in the pathogenesis of immune renal injury [3]. To be able to study the relationship between proximal tubular cells and a variety of renal diseases, the RPTEpiC culture provides a useful in vitro model.
RRPTEpiC from ScienCell Research Laboratories are isolated from neonate day 2 CD® IGS rat kidney tissue. RRPTEpiC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 10^5 cells in 1 ml volume. RRPTEpiC are characterized by immunofluorescent method with antibodies to cytokeratin-18, -19 and vimentin. RRPTEpiC are negative for mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast and fungi. RRPTEpiC are guaranteed to further culture under the conditions provided by ScienCell Research Laboratories; however, RRPTEpiC are not recommended for long-term cultures due to limited expansion capacity and senescence after subculturing.
| Product | Catalog no. | Amount | Storage |
| RPTEpiC | RPT001 | 1X10^6/vial | in liquid nitrogen |
Product Use
For Research Use Only.Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Culture Conditions
Culture Type:Adherent
Temperature Range:36℃ to 38℃
Incubator Atmosphere:Humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2
Passaging Adherent Cells
All solutions and equipment that come in contact with the cells must be sterile.
Always use proper sterile technique and work in a laminar flow hood.
1. Remove and discard the spent cell culture media from the culture vessel.
2. Wash cells using a balanced salt solution without calcium and magnesium (approximately 2 mL per 10 cm2 culture surface area). Gently add washsolution to the side of the vessel opposite the attached cell layer to avoiddisturbing the cell layer,and rock the vessel back and forth several times.
Note: The wash step removes any traces of serum, calcium, and magnesium that would inhibit the action of the dissociation reagent.
3. Remove and discard the wash solution from the culture vessel
4. Add the pre-warmed dissociation reagent such as trypsin or TrypLE™to the side of the flask; use enough reagent to cover the cell layer (approximately0.5 mL per 10 cm2). Gently rock the container to get complete coverage of the cell layer.
5. Incubate the culture vessel at room temperature for approximately 2minutes.
Note: that the actual incubation time varies with the cell line used.
6. Observe the cells under the microscope for detachment. If cells areless than 90% detached, increase the incubation time a few more minutes, checking for dissociation every 30 seconds. You may also tap the vessel to expedite cell Tetachment.
7. When ≥ 90% of the cells have detached, tilt the vessel for a minimallength of time to allow the cells to drain. Add the equivalent of 2 volumes (twice thevolume used for the dissociation reagent) of pre-warmed complete growth medium.Disperse the medium by pipetting over the cell layer surface several times.
8. Transfer the cells to a 15-mL conical tube and centrifuge then at200 × g for 5 to 10 minutes. Note that the centrifuge speed and time vary based on the cell type.
9. Resuspend the cell pellet in a minimal volume of pre-warmed complete growth medium and remove a sample for counting.
10. Determine the total number of cells and percent viability using a hemacytometer, cell counter and Trypan Blue exclusion, or the Countess® Automated CellCounter. If necessary, add growth media to the cells to achieve the desired cellconcentration and recount the cells.
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验Primary Culture of Human Proximal Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
of human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells (PTEC) provides a well-characterized in vitro model, phenotypically representative of PTEC in vivo. This in vitro system allows for investigation of the cellular mechanisms underlying proximal tubular injury
Primary Culture of Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells and Interstitial Fibroblasts
. This chapter outlines methods by which proximal tubular epithelial cells and renal interstitial fibroblasts can be isolated and characterized from human renal nephrectomy tissue.
Primary Kidney Proximal Tubule Cells
Primary rabbit kidney epithelial cell cultures can be obtained that express renal proximal tubule functions. Toward these ends, renal proximal tubules are purified from the rabbit kidney by the method of Brendel and Meezan. To summarize
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料