相关产品推荐更多 >

抗Fas Ligand / FASLG / CD95L 抗体, 抗原亲和纯化, (种属反应: Human), 兔多抗, 101369-T36
¥999
抗Carboxypeptidase A1 / CPA1 抗体, (种属反应: Mouse), 兔单抗, 50448-R003
¥1199
抗CD19 抗体, (种属反应: Mouse), 兔单抗, 50510-R027
¥1699
抗Listeria monocytogenes flagellin / FlaA 抗体, 鼠单抗
¥800
抗SerpinI1 / Neuroserpin 抗体, (种属反应: Mouse), 兔多抗, 50926-RP01
¥999
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
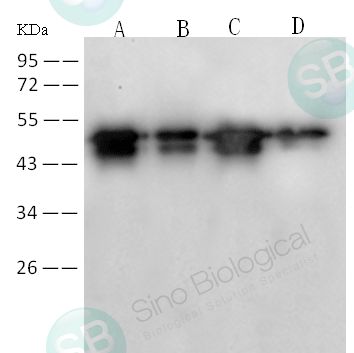
- 免疫原:
Recombinant SARS-CoV Nucleoprotein / NP Protein (Catalog#40143-V08B)
- 亚型:
Rabbit IgG
- 形态:
液体
- 保存条件:
-20℃ to -80℃
- 克隆性:
兔单抗
- 适应物种:
SARS
- 保质期:
12个月
- 抗原来源:
40143-V08B
- 目录编号:
40143-R001
- 级别:
免疫学试剂
- 库存:
99
- 供应商:
北京义翘神州科技股份有限公司
- 宿主:
Rabbit
- 应用范围:
WB,ELISA,IHC-P,ICC/IF
- 浓度:
WB: 1:5000-1:20000
- 靶点:
NP-CoV
- 抗体英文名:
SARS-CoV / SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody, Rabbit MAb
- 抗体名:
新冠病毒核蛋白兔单抗
- 规格:
20.00 µL/50.00 µL/100.00 µL
| 规格: | 20.00 µL | 产品价格: | ¥800.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 规格: | 50.00 µL | 产品价格: | ¥1500.0 |
| 规格: | 100.00 µL | 产品价格: | ¥2500.0 |
抗体种属:SARS
抗体靶点:NP-CoV
抗体应用:WB,ELISA,IHC-P,ICC/IF
抗原货号:40143-V08B
抗原描述:Recombinant SARS-CoV Nucleoprotein / NP Protein (Catalog#40143-V08B)
抗体宿主:Rabbit
抗体Ig类型:Rabbit IgG
抗体纯化方法:Protein A
抗体制备:This product is a recombinant monoclonal antibody expressed from HEK293 cells.
特异性:SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验2, Matschke, J; et al. Neuropathology of patients with COVID-19 in Germany: a post-mortem case series. The Lancet. Neurology, PMID: 33031735
3, Jacob, F; et al. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Cells and Brain Organoids Reveal SARS-CoV-2 Neurotropism Predominates in Choroid Plexus Epithelium. Cell stem cell, PMID: 33010822
4, Szabolcs, M; et al. Identification of Immunohistochemical Reagents for In Situ Protein Expression Analysis of Coronavirus-associated Changes in Human Tissues. Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM, PMID: 33086222
5, Andrews, MG; et al. Tropism of SARS-CoV-2 for Developing Human Cortical Astrocytes. bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, PMID: 33469577
6, Putcharoen, O; et al. Early detection of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients in Thailand. PloS one, PMID: 33577615
7, Xu, X; et al. Dynamics of neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19: an observational study. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, PMID: 34006847
8, Bennett, RS; et al. Scalable, Micro-Neutralization Assay for Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Virus-Neutralizing Antibodies in Human Clinical Samples. Viruses, PMID: 34065987
9, Renuse, S; et al. A mass spectrometry-based targeted assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen from clinical specimens. EBioMedicine, PMID: 34229274
10, Avendaño-Ortiz, J; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Induce Endotoxin Tolerance Hallmarks: A Demonstration in Patients with COVID-19. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), PMID: 34183364
11, Kudose, S; et al. Longitudinal Outcomes of COVID-19-Associated Collapsing Glomerulopathy and Other Podocytopathies. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN, PMID: 34670811
12, Duan, X; et al. An airway organoid-based screen identifies a role for the HIF1α-glycolysis axis in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell reports, PMID: 34731648
13, Bennett, RP; et al. Sangivamycin is highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and has favorable drug properties. JCI insight, PMID: 34807849
14, Maus, A; et al. Targeted Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Sequence Variants by Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Tryptic Peptides. Journal of proteome research, PMID: 34779632
15, Golden, JW; et al. Hamsters Expressing Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Develop Severe Disease following Exposure to SARS-CoV-2. mBio, PMID: 35073750
16, Li, Z; et al. Imatinib and methazolamide ameliorate COVID-19-induced metabolic complications via elevating ACE2 enzymatic activity and inhibiting viral entry. Cell metabolism, PMID: 35150639
17, Mizutani, M; et al. Pathologic and Neuropathologic Study of a Case of COVID-19. JMA journal, PMID: 35224283
18, Tomris, I; et al. Distinct spatial arrangements of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression in Syrian hamster lung lobes dictates SARS-CoV-2 infection patterns. PLoS pathogens, PMID: 35255100
19, Wang, Z; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+ T cells are associated with long-term persistence of neutralizing antibodies. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, PMID: 35461307
20, Chong, Z; et al. Nasally-delivered interferon-λ protects mice against upper and lower respiratory tract infection of SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron. bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, PMID: 35118466
21, Zheng, H; et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal distinct immune response landscapes in lung and intestinal tissues from SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques. Cell reports, PMID: 35594870
22, Chong, Z; et al. Nasally delivered interferon-λ protects mice against infection by SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron. Cell reports, PMID: 35523172
23, Rosendal, E; et al. Serine Protease Inhibitors Restrict Host Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infections. mBio, PMID: 35532162
24, Nicholson, MW; et al. Cardio- and Neurotoxicity of Selected Anti-COVID-19 Drugs. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland), PMID: 35745684
25, Wang, L; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF10 impairs cilia by enhancing CUL2ZYG11B activity. The Journal of cell biology, PMID: 35674692
26, Vanderboom, PM; et al. Machine Learning-Based Fragment Selection Improves the Performance of Qualitative PRM Assays. Journal of proteome research, PMID: 35849720
27, Xue, Y; et al. Cardiopulmonary Injury in the Syrian Hamster Model of COVID-19. Viruses, PMID: 35891384
28, Lee, S; et al. Immunological and Pathological Peculiarity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Beta Variant. Microbiology spectrum, PMID: 36005818
29, Coler, B; et al. Diminished Antiviral Innate Immune Gene Expression in the Placenta Following a Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, PMID: 36126729
30, Khan, M; et al. Anatomical barriers against SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion at vulnerable interfaces visualized in deceased COVID-19 patients. Neuron, PMID: 36446381
31, Lindqvist, R; et al. A Syntenin Inhibitor Blocks Endosomal Entry of SARS-CoV-2 and a Panel of RNA Viruses. Viruses, PMID: 36298757
32, Chen, M; et al. Infection of SARS-CoV-2 causes severe pathological changes in mouse testis. Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao, PMID: 36494057
33, Que, H; et al. Tripterin liposome relieves severe acute respiratory syndrome as a potent COVID-19 treatment. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, PMID: 36566328
34, Wang, Y; et al. Biparatopic antibody BA7208/7125 effectively neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron BA.1-BA.5. Cell discovery, PMID: 36609558
35, Higashi-Kuwata, N; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors containing P1' 4-fluorobenzothiazole moiety highly active against SARS-CoV-2. Nature communications, PMID: 36841831
36, Emmi, A; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins and genomic sequences in human brainstem nuclei. NPJ Parkinson's disease, PMID: 36781876
37, Massimo, M; et al. Haemorrhage of human foetal cortex associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Brain : a journal of neurology, PMID: 36642091
38, Qiu, S; et al. Successful clearance of persistent SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection following a single dose of Ad5-nCoV vaccine. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, PMID: 36922500
39, Nchioua, R; et al. Reduced replication but increased interferon resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1. Life science alliance, PMID: 36977594
40, Dickey, TH; et al. Design of a stabilized RBD enables potently neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 single-component nanoparticle vaccines. Cell reports, PMID: 36943870
41, Alhammad, YM; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Mac1 is required for IFN antagonism and efficient virus replication in mice. bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology, PMID: 37066301
42, Byström, JW; et al. At-home sampling to meet geographical challenges for serological assessment of SARS-CoV-2 exposure in a rural region of northern Sweden, March to May 2021: a retrospective cohort study. Euro surveillance : bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin, PMID: 36995373
43, Yue, M; et al. Coronaviral ORF6 protein mediates inter-organelle contacts and modulates host cell lipid flux for virus production. The EMBO journal, PMID: 37218505
44, Van Slambrouck, J; et al. Visualising SARS-CoV-2 infection of the lung in deceased COVID-19 patients. EBioMedicine, PMID: 37224768
45, Min, YQ; et al. A new cellular interactome of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its biological implications. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, PMID: 37211047
46, Burnap, SA; et al. Cross-linking Mass Spectrometry Uncovers Interactions Between High-density Lipoproteins and the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, PMID: 37343697
47, Addetia, A; et al. Neutralization, effector function and immune imprinting of Omicron variants. Nature, PMID: 37648855
48, Alhammad, YM; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Mac1 is required for IFN antagonism and efficient virus replication in cell culture and in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, PMID: 37607224
49, Hirata, Y; et al. Genomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in forensic autopsy cases of COVID-19. Journal of medical virology, PMID: 37537838 50, Ford, ES; et al. Repeated mRNA vaccination sequentially boosts SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cells in persons with previous COVID-19. Nature immunology, PMID: 38057617 51, Sasaki, M; et al. Combination therapy with oral antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs improves the efficacy of delayed treatment in a COVID-19 hamster model. EBioMedicine, PMID: 38159532
52, Garvanska, DH; et al. The NSP3 protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds fragile X mental retardation proteins to disrupt UBAP2L interactions. EMBO reports, PMID: 38177924
53, Uraki, R; et al. An mRNA vaccine encoding the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain protects mice from various Omicron variants. NPJ vaccines, PMID: 38167505
54, Yang, L; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection causes dopaminergic neuron senescence. Cell stem cell, PMID: 38237586
55, Nagasawa, S; et al. Changes in SARS-CoV-2 viral load and titers over time in SARS-CoV-2-infected human corpses. PloS one, PMID: 38536820
56, Wang, W; et al. Digital Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Lateral Flow Test Dipstick: Ultrasensitive, Rapid Virus Quantification in Environmental Dust. Environmental science & technology, PMID: 38452107
57, Du, H; et al. Fulminant myocarditis induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection without severe lung involvement: insights into COVID-19 pathogenesis. Journal of genetics and genomics = Yi chuan xue bao, PMID: 38447818
58, Jeong, GU; et al. Generation of a lethal mouse model expressing human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 for SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis. Experimental & molecular medicine, PMID: 38816566
59, Liu, B; et al. An unconventional VH1-2 antibody tolerates escape mutations and shows an antigenic hotspot on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Cell reports, PMID: 38805396 60, Komiya, Y; et al. Necroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells drives lung inflammation and injury caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease, PMID: 39154794 61, Yabu, H; et al. Janus-Type Immunofluorescent Probes and a Quantitative Immunoassay System. Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids, PMID: 39145991
62, Rosen, LE; et al. A potent pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody resilient to epitope diversification. Cell, PMID: 39383863
63, Chaopreecha, J; et al. Andrographolide attenuates SARS-CoV-2 infection via an up-regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC). Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology, PMID: 39631298
64, Lee, JH; et al. Dose-dependent serological profiling of AdCLD-CoV19-1 vaccine in adults. mSphere, PMID: 39723823
65, Nakamura, S; et al. Structure-guided engineering of a mutation-tolerant inhibitor peptide against variable SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, PMID: 39854234
66, Xing, L; et al. Early fusion intermediate of ACE2-using coronavirus spike acting as an antiviral target. Cell, PMID: 39889696
67, Han, S; et al. Host specific sphingomyelin is critical for replication of diverse RNA viruses. Cell chemical biology, PMID: 39566509
68, Liu, A; et al. Harnessing 2D and 3D human endometrial cell culture models to investigate SARS-CoV-2 infection in early pregnancy. Clinical science (London, England : 1979), PMID: 39666439
69, Shull, T; et al. Elevated neuroinflammation, autoimmunity, and altered IgG glycosylation profile in the cerebral spinal fluid of severe COVID-19 patients. Brain, behavior, and immunity, PMID: 40157461 70, Oba, S; et al. Iguratimod, a promising therapeutic agent for COVID-19 that attenuates excessive inflammation in mouse models. European journal of pharmacology, PMID: 40147575 71, Kubinski, HC; et al. Variant mutation G215C in SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid enhances viral infection via altered genomic encapsidation. PLoS biology, PMID: 40299982
72, Vacharathit, V; et al. Persistent IP-10/CXCL10 dysregulation following mild omicron breakthrough infection: Immune network signatures across COVID-19 waves and implications for mRNA vaccine outcomes. Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), PMID: 40306350
73, Sadler, CJ; et al. Signal Enhancement in Immunoassays via Coupling to Catalytic Nanoparticles. ACS sensors, PMID: 40390533
74, Wei, X; et al. Immune imprinting blunts omicron pathogenicity fluctuations and highlights the essential role of cellular immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell reports, PMID: 40471788
75, Lam, JY; et al. The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants. International journal of molecular sciences, PMID: 40565240
76, Gu, ZQ; et al. TRPML2 channel modulation by PI(
3,5)P₂ and small-molecule agonists controls endosomal vesicle dynamics. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, PMID: 40664038
77, Parthasarathy, S; et al. PARP14 is an interferon-induced host factor that promotes IFN production and affects the replication of multiple viruses. mBio, PMID: 40937852
78, Chen, L; et al. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea severity and treatment on COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune responses. Journal of thoracic disease, PMID: 40950906
诊断,SARS-CoV-2抗原检测在最近几个月也变得越来越重要,也可以用作即时诊断 (POC ) 。 在这里,必须区分专业使用的测试和非专业测试,例如那些由小学生进行的测试。后者通常基于口腔或鼻粘膜的拭子或唾液样本,用于直接检测病原体。根据最近的研究结果,与鼻咽拭子或患者自己采集的鼻拭子相比,在病原体检测时,唾液尤其具有更高的灵敏度。 此外,唾液也被证明适合作为样本类型,用于在血清学测试中检测SARS-CoV-2 特异性 IgG抗体。因此,由IgA 抗体介导的所谓“粘膜免疫”也很容易测量。这有助于防止免疫
5位院士为代表,超12篇CNS大作,5月新冠研究汇总——全方位围攻新冠病毒,值得收藏
从 8 名 SARS-CoV-2 感染者的单个 B 细胞中分离并鉴定了 206 株 RBD 特异性单克隆抗体,并鉴定出具有抗 SARS-CoV-2 中和活性的抗体,这种中和活性与它们与 ACE2 竞争 RBD 结合的能力有关9。 此外,复旦大学基础医学院应天雷团队在抗新冠抗体药物研发方面也取得了重要的进展,该团队发现了一系列抗新冠全人源纳米抗体,可靶向新冠病毒受体结合区上的五类不同表位。该成果于 5 月 14 日在 Cell Host & Microbe 上发表,题为
盘点 2020 年中国学者的十大免疫学研究成果,有的已经被写进高考题?!
水平上揭示了早期复发肝癌特征性免疫图谱和免疫逃逸机制。 图片来源:Cell 10. 最后的最后,怎么能忘了免疫学在新冠研究中的重要地位!2020 年 5 月 18 日,北京大学谢晓亮团队联合多家单位在 Cell 发表题为 Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients’ B Cells 的研究
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料