相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 抗体名:
CD14
- 规格:
1X10^9cells
- 中文介绍:
Cellectra Human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells)是50 nm葡聚糖包被的超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒,专为CD14⁺细胞的分离纯化而设计。产品通过在磁珠表面偶联高亲和力的抗CD14单克隆抗体,可实现对单核细胞与巨噬细胞的高效识别与靶向捕获。产品在无菌制造条件下生产,整个生产过程中不使用动物或人源的成分;经多Donor样本验证,性能稳定可靠;同时支持GMP版本升级,助力临床转化需求;现货发售,保证稳定供应,欢迎咨询选购!
-
产品描述(Product Description)
Cellectra Human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells) are 50 nm dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles which the surface is conjugated with recombinant monoclonal antibodies specific to human CD14 (Isotype: mouse IgG1). They are especially designed for positive selection of CD14+ cells. Cellectra Human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells) are produced under sterile manufacturing conditions (ISO 5), and no animal- or human-derived components are used throughout the production process. It is produced under our rigorous quality control system that includes a comprehensive set of tests including sterility and endotoxin tests.
-
应用说明(Application)
Cellectra Human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells) are designed for the positive selection of monocytes and macrophages from fresh or frozen human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). CD14, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane protein, is predominantly expressed on the surface of human monocytes and macrophages. The magnetic nBeads are conjugated with monoclonal antibodies targeting human CD14 protein, enabling CD14+ cells to be labeled with the specific antibodies and magnetic particles, and separated using the separation columns and magnets.
-
存储(Storage)
This product is stable after storage at: 2-8°C for 36 months in lyophilized state; 2-8°C for 18 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles once reconstituion.
-
无菌(Sterility)
Negative
-
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 0.002 EU per μg by the LAL method / rFC method.
-
注意事项(Important Note)
This product is for research use only and not intended for therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic use.
-
制剂(Formulation)
Please contact us for detailed information.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
-
典型数据-Typical Data
Please refer to DS document for the assay protocol.
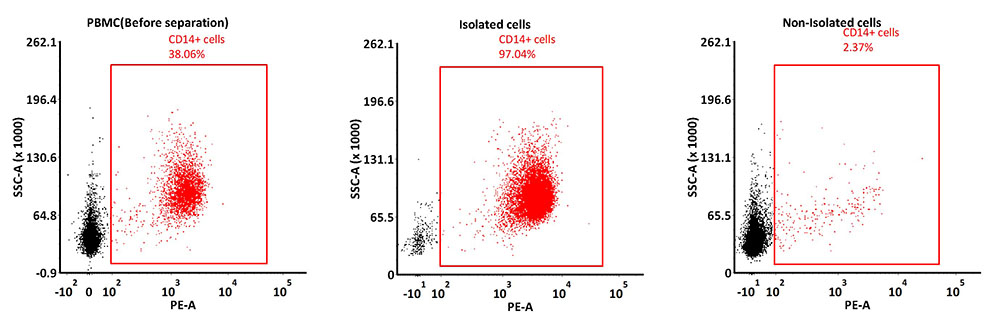
The purity of CD14+ cells isolated by Cellectra human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells) (Cat. No. MBS-S001).
The CD14+ cells were isolated from human PBMCs using Cellectra human CD14 nBeads, premium grade (for cells) (Cat. No. MBS-S001). The isolated cells and non-isolated cells were respectively stained using PE anti-human CD14 antibody, and then analyzed by FCS Express 7 software.
-
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验Lu, You, Hu et al
Clin Exp Rheumatol (2025)
Mataramvura, Ncube, Duri
J Immunol Methods (2025)
Susuki, Shinohara, Murayama et al
Tissue Eng Part C Methods (2025) 31 (7), 261-270
Priest, Schwartz, Wilcox et al
Toxicol Pathol (2025)
血液制品由于包含大量红细胞,给白细胞亚群的分离带来了不小的障碍。常见的实验方法均需要从血液样品中分离 PBMC (外周血单个核细胞)后,进一步获取目的白细胞类群。不仅时间成本巨大,且效率、纯度、得率及细胞活力等核心指标,均对下游研究带来不同影响。下图概述了 PBMC 中各种白细胞的比例。 美天旎StraightFrom®全血磁珠系列基于细胞磁性分选金标准的 MACS 技术, 具备常规 MACS 分选磁珠所有优势的同时,更支持以全血及各种血液制品作为初始样品,快速精准高效分离目的细胞,为临床
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料