| 出品公司: | ATCC |
|---|---|
| 细胞名称: | ATCC CCL-229细胞, LoVo细胞, 人结肠癌细胞 |
| 细胞又名: | LOVO |
| 细胞来源: | ATCC |
| 产品货号: | CCL-229 |
| 种属来源: | 人 |
| 组织来源: | 结肠 |
| 疾病特征: | Dukes'C型,IV级,结直肠腺癌 |
| 患者年龄: | 56 |
| 患者性别: | 男 |
| 细胞来源: | LoVo细胞ATCC CCL-229于1971年从一个56岁的白人男性患者的左锁骨上区转移性肿瘤结节的分离获得,经组织学证实诊断为结肠腺癌。 |
| 抗原表达: | HLA A11, B15, B17, Cw1, Cw3; 血型B |
| 癌基因: | myc +; myb + ; ras +; fos +; p53 +; sis -; abl -; ros -; src - |
| 基因表达: | 癌胚抗原(CEA)908 ng/106个细胞/10天。CSAp(CSAp-)和结肠抗原3表达为阴性。 |
| 癌细胞诱导: | 能够诱导癌细胞产生 |
| 诱导实验: |
是的,裸鼠
(裸鼠皮下接种10的7次方个细胞后,21天内肿瘤以100%的形成(5/5))
|
| 细胞形态: | 上皮样 |
| 生长特性: | 贴壁生长 |
| 培养基: | F12K培养基,90%;FBS,10%。 |
| 存储人: | M Romsdahl |
| 生长条件: | 气相:空气,95%;二氧化碳,5%; 温度:37 ℃, |
| 传代方法: | 1:2至1:6,每周2次。 |
| 冻存条件: | 95% 完全培养基+5% DMSO,液氮储存 |
| 支原体检测: | 阴性 |
| 安全等级: | 1 |
| 应用: | 该细胞可以作为转染宿主细胞。 |
| STR: |
Amelogenin: XY
CSF1PO: 11,13,14
D13S317: 8, 11
D16S539: 9, 12
D5S818: 11, 12, 13
D7S820: 9.3,10, 11
TH01: 9.3
TPOX: 8,9
vWA: 17,18
|
| 同工酶: |
ES-D, 1
G6PD, B
PGD, A
PGM1, 2
PGM3, 1-2
|
| 参考文献: |
Drewinko B, et al. Further biologic characteristics of a human carcinoembryonic antigen-producing colon carcinoma cell line. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 61: 75-83, 1978. PubMed: 276641
Drewinko B, Yand LY. Restriction of CEA synthesis to the stationary phase of growth of cultured human colon carcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 101: 414-416, 1976. PubMed: 964319
Drewinko B, et al. Establishment of a human carcinoembryonic antigen-producing colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 36: 467-475, 1976. PubMed: 1260746
Trainer DL, et al. Biological characterization and oncogene expression in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 41: 287-296, 1988. PubMed: 3338874
Keesee SK, et al. Nuclear matrix proteins in human colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1913-1916, 1994. PubMed: 8127905
Drewinko B, et al. Response of exponentially growing, stationary-phase, and synchronized cultured human colon carcinoma cells to treatment with nitrosourea derivatives. Cancer Res. 39: 2630-2636, 1979. PubMed: 445465
Miranda L, et al. Isolation of the human PC6 gene encoding the putative host protease for HIV-1 gp160 processing in CD4+ T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 7695-7700, 1996. PubMed: 8755538
|
| 细胞图片: |
  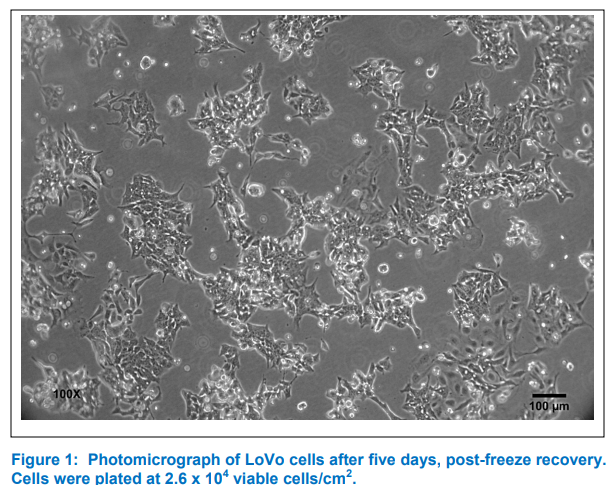  |
| 细胞说明书: |
LoVo细胞ATCC CCL-229说明书 |
LoVo细胞ATCC CCL-229人结肠癌细胞接受后处理
1) 收到细胞后,请检查是否漏液,如果漏液,请 拍照片发给我们。
2) 请先在显微镜下确认细胞生长状态,去掉封口 膜并将T25瓶置于37℃培养约2-3h。
3) 弃去T25瓶中的培养基,添加6ml本公司附带的 完全培养基。
4) 如果细胞密度达80%-90%请及时进行细胞传代, 传代培养用6ml本公司附带的完全培养基。
5) 接到细胞次日,请检查细胞是否污染,若发现 污染或疑似污染,请及时与我们取得联系。
LoVo细胞ATCC CCL-229人结肠癌细胞培养操作
1)复苏细胞:将含有 1mL 细胞悬液的冻存管在 37℃水浴中迅速摇晃解冻,加 入 4mL 培养基混合均匀。在 1000RPM 条件下离心 4 分钟,弃去上清液,补 加 1-2mL 培养基后吹匀。然后将所有细胞悬液加入培养瓶中培养过夜(或将 细胞悬液 加入 10cm 皿中,加入约 8ml 培养基,培养过夜)。第二天换液并 检查细胞密度。
2)细胞传代:如果细胞密度达 80%-90%,即可进行传代培养。
1. 弃去培养上清,用不含钙、镁离子的 PBS 润洗细胞 1-2 次。
2. 加 1ml 消化液(0.25%Trypsin-0.53mM EDTA)于培养瓶中,置于 37℃培 养箱中消化 1-2 分钟,然后在显微镜下观察细胞消化情况,若细胞大部分 变圆并脱落,迅速拿回操作台,轻敲几下培养瓶后加少量培养基终止消 化。
3. 按 6-8ml/瓶补加培养基,轻轻打匀后吸出,在 1000RPM 条件下离心 4 分 钟,弃去上清 液,补加 1-2mL 培养液后吹匀。
4. 将细胞悬液按 1:2 比例分到新的含 8ml 培养基的新皿中或者瓶中。
3)细胞冻存:待细胞生长状态良好时,可进行细胞冻存。下面 T25 瓶为类;
1. 细胞冻存时,弃去培养基后,PBS 清洗一遍后加入 1ml 胰酶,细胞变圆脱 落后,加入 1ml 含血清的培养基终止消化,可使用血球计数板计数。
2. 4 min 1000rpm 离心去掉上清。加 1ml 血清重悬细胞,根据细胞数量加入血 清和 DMSO ,轻轻混匀,DMSO 终浓度为 10%,细胞密度不低于1x106/ml,每支冻存管冻存 1ml 细胞悬液,注意冻存管做好标识。
3. 将冻存管置于程序降温盒中,放入-80 度冰箱,2 个小时以后转入液氮灌储 存。记录冻存 管位置以便下次拿取。
LoVo细胞ATCC CCL-229人结肠癌细胞培养注意事项
1. 收到细胞后首先观察细胞瓶是否完好,培养液是否有漏液、浑浊等现象,若有上述现 象发生请及时和我们联系。
2. 仔细阅读细胞说明书,了解细胞相关信息,如细胞形态、所用培养基、血清比例、所 需细胞因子等,确保细胞培 养条件一致。若由于培养条件不一致而导致细胞出现问 题,责任由客户自行承担。
3. 用 75%酒精擦拭细胞瓶表面,显微镜下观察细胞状态。因运输问题贴壁细胞会有少量 从瓶壁脱落,将细 胞置于培养箱内静置培养 4~6 小时,再取出观察。此时多数细胞均 会贴壁,若细胞仍不能贴壁请用台盼蓝染色测定细胞活力,如果证 实细胞活力正常, 请将细胞离心后用新鲜培养基再次贴壁培养;如果染色结果显示细胞无活力,请拍下 照片及时和我们联系,信息确 认后我们为您再免费寄送一次。
4. 静置细胞贴壁后,请将细胞瓶内的培养基倒出,留 6~8mL 维持细胞正常培养,待细 胞汇合度 80% 左右时正常传代。
5. 请客户用相同条件的培养基用于细胞培养。培养瓶内多余的培养基可收集备用,细胞 传代时可以一定比例和客户 自备的培养基混合,使细胞逐渐适应培养条件。
6. 建议客户收到细胞后前 3 天各拍几张细胞照片,记录细胞状态,便于和 诺安基因 技术 部沟通交流。由 于运输的原因,个别敏感细胞会出现不稳定的情况,请及时和我们联 系,告知细胞的具体情况,以便我们的技术人员跟踪回访直至问 题解决。
7. 该细胞仅供科研使用。







