相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 询价记录
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 保修期:
一年
- 供应商:
塔望科技
- 规格:
咨询电话:021-51537683/15221725700
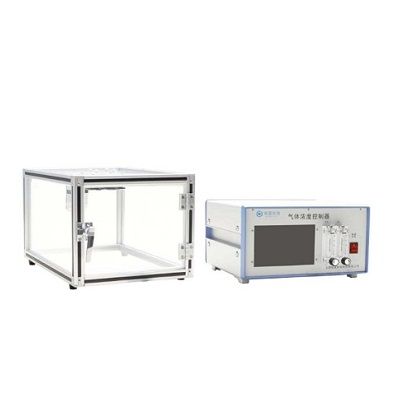
动物低氧高氧实验系统
产品描述
塔望科技提供全系列的动物实验用低/高氧控制产品,包括恒定浓度控制的低氧动物箱、高氧动物箱、可编程的间歇氧浓度控制系统、带缓冲舱的手套低氧箱等。整套低氧/高氧实验箱装置主要由氧气控制器和动物实验箱两部分组成。另可提供多种不同的气体控制器,满足不同实验O2、CO2、NO、CO、O3等气体浓度控制的需求。
Ox-100动物低氧实验系统可以控制动物实验箱内持续低氧的环境,用以制造相关的低氧实验模型。用户可自由设置所需要的浓度和实验持续时间,所有的设置通过控制主机触摸屏完成,人性化设计,操作简便。
Ox-100动物低氧实验系统监测指标全面,动物低氧舱内具有集成化的传感器模块,内置温度、湿度、氧气、二氧化碳传感器。可以实时监测动物低氧舱内的环境。系统通过闭环反馈控制,根据动物低氧舱内的氧浓度实时反馈控制,使动物实验低氧数据更准确,避免了控制型浓度输出和低氧舱内浓度不一致的情况。Ox-100动物低氧实验系统具有优良的控制性能,持续低氧实验时,氧浓度的误差为0.1%。
Ox-100动物低氧实验系统提供不同尺寸的动物低氧箱,默认低氧箱可放置1个大鼠笼(或2个小鼠笼),同时提供大号规格,可容纳2个大鼠笼和4个大鼠笼。如需其它规格,可提供定制。
如需高氧实验,请选择型号Ox-100HE。
产品特点及参数
1. 为动物低氧实验模型的建立提供稳定的低氧环境
2. 按照设定气体浓度自动配比气体,维持恒定的氧气浓度环境。无需在箱体外混合比例气体,实验氧浓度的准确,节省气源
3. 舱体采用全透明PMMA材质,防止由于光线影响动物生物节律
4. 7英寸大屏触摸屏控制,人性化界面,操作简单
5. 监测参数:温度、湿度、氧气O2浓度、二氧化碳浓度
6. 控制精度:±0.1%
7. 非色散红外(NDIR)二氧化碳传感器,测量范围:0~5000ppm
8. 进口电化学氧气O2浓度检测器,测量范围:0-25%vol,线性度好,检测准确、使用寿命长。具有温度补偿机制
9. 温度检测:进口高精度温度传感器
10. 氧气浓度变化动态曲线,直观了解氧气浓度变化的过程
11. 具有定时功能,实验完成,自动恢复常氧状态,并伴有声音提示
12. 氧气浓度自动校准:通过控制器对传感器快速校准
13. 特有的气体混合及循环机制,保证箱体内气体浓度的均一
14. 高性能电磁阀,性能稳定,超长寿命
15. 舱体尺寸有多种选择,可灵活搭配。也可根据实验要求进行定制
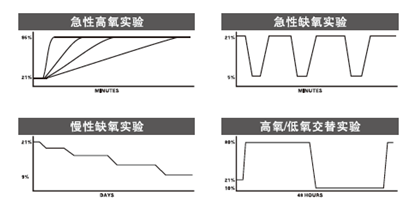
ProOx-100动物间歇低氧实验系统多功能控制
可进行间歇低氧实验(CIH)、急性缺氧实验、慢性缺氧实验、高氧/低氧交替实验
应用领域
肺动脉高压、肾脏疾病研究、肿瘤研究、心血管疾病研究、视网膜病变、运动医学研究、OSAHS、脑发育与神经生物学、干细胞研究、医学研究等
型号说明
|
名称 |
型号 |
说明 |
单位 |
|
动物低氧实验系统 |
Ox-100 |
恒定氧控制,低氧 |
套 |
|
动物氧浓度实验系统 |
Ox-100HE |
恒定氧控制,低氧/高氧 |
套 |
|
动物间歇低氧实验系统 |
ProOx-100 |
恒定氧控制/间歇氧控制,低氧 |
套 |
|
动物间歇氧浓度实验系统 |
ProOx-100HE |
恒定氧控制/间歇氧控制,低氧/高氧 |
套 |
舱体型号(可选择不同尺寸的低氧舱)
|
名称 |
型号 |
说明 |
单位 |
|
动物实验舱体小号 |
OxC-S |
大鼠笼x1 |
台 |
|
动物实验舱体中号 |
OxC-M |
大鼠笼x2 |
台 |
|
动物实验舱体大号 |
OxC-L |
大鼠笼x4 |
台 |
|
动物实验舱体特大号 |
OxC-XL |
大鼠笼x8 |
台 |
|
动物实验舱体-CIH |
OxC-CIH |
36只小鼠 |
台 |
|
手套操作箱 |
Gl-700 |
700L |
台 |
使用客户名单
相关文献
[1]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. "Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia" . [J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[2]Guijuan Chen,Kang Cheng,Yun Niu,Li Zhu,Xueting Wang."Epicatechin gallate prevents inflammatory response in hypoxia-activated microglia and cerebral edema by inhibiting NF-κB signaling" . [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics ,Volume 729, 109393;
[3]Yapeng,LuPanpanChang,WangwangDing,JiangpeiBian,DanWang,XuetingWang,QianqianLuo,XiaomeiWu,LiZhu."Pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial division attenuates simulated high-altitude exposure-induced cerebral edema in mice: Involvement of inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in glial cells". [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Volume 929,2022,175137
[4]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin ."Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner" . [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[5]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,"Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling" . [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[6]Fang Zhao, Yan Meng, Yue Wang, Siqi Fan, Yu Liu,Xiangfeng Zhang, Chenyang Ran, Hongxin Wang and Meili Lu. "Protective effect of Astragaloside IV on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway" .[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,10.3389/fphar.2022.920977
[7]Xu Y, Kong X, Li J, Cui T, Wei Y, Xu J, Zhu Y , Zhu X. “Mild Hypoxia Enhances the Expression of HIF and VEGF and Triggers the Response to Injury in Rat Kidneys.” [J]. Front. Physiol. 12:690496. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.690496
[8]Liang Xie, Qinhan Wu, Weiping Hu, Xu Wu, Guiling Xiang, Shengyu Hao, Han Guo, Shanqun Li. “Impact of histaminergic H3 receptor antagonist on hypoglossal nucleus in chronic intermittent hypoxia conditions.” [J]. Psychopharmacology.
[9]Li Huang, Tianyou Li, Min Zhou, Mengyan Deng, Lidong Zhang, Long Yi, Jundong Zhu, Xiaohui Zhu, Mantian Mi. “Hypoxia Improves Endurance Performance by Enhancing Short Chain Fatty Acids Production via Gut Microbiota Remodeling.” [J]. Front. Microbiol. 12:820691
[10]Yanhong Pei a b, Lifei Huang c, Tong Wang c, Qinhan Yao a, Yanrong Sun a, Yan Zhang a, Xiaomei Yang a, Jiliang Zhai d, Lihua Qin a, Jiajia Xue c, Xing Wang c, Hongquan Zhang a b, Junhao Yan."Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury. materialstoday ADVANCES, Volume 17, March 2023, 100349.
[11]Zhang, C., Sun, Y., Guo, Y. et al. “JMJD1C promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating glycolysis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. “[J].Cell Death Discov. 9, 98 (2023).
[12]Fang Zhao, Yan Meng, Yue Wang, Siqi Fan, Yu Liu,Xiangfeng Zhang, Chenyang Ran, Hongxin Wang and Meili Lu. "Protective effect of Astragaloside IV on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway" .[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,10.3389/fphar.2022.920977
[13]Chenyu Xu, Jun Xu, Chunfang Zou, Qian Li, Shan Mao, Ying Shi, Yan Tan, Wei Gu, Liang Ye. "Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Regulates CaMKII-Dependent MAPK Signaling to Promote the Initiation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm." [J]. Hindawi, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity Volume 2021, Article ID 2502324, 15 pages
[14]Jing Zhang, Jian-Zhong Jiang, Jun Xu, Chen-Yu Xu, Shan Mao, Ying Shi, Wei Gu, Chun-Fang Zou, Yue-Ming Zhao, Liang Ye. "Identification of Novel Biomarkers for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Promoted by Obstructive Sleep Apnea." [J]. Elsevier Inc. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license
[15]Zhang Q, Xu L, Bai Y, Chen P, Xing M, Cai F, Wu Y, Song W. “Intermittent hypoxia-induced enhancement of sociability and working memory associates with CNTNAP2 upregulation.” [J]. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 16:1155047.
[16]Chen Zhang, Yue Sun, Yingying Guo, Jingjing Xu, Haiyan Zhao. “JMJD1C promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating glycolysis in pulmonary arterial hypertension.” [J]. Cell Death Discovery (2023) 9:98
动物实验低压氧舱(标准款)
产品描述
动物实验低压氧舱用于模拟低压氧高原环境,压力可以根据需要自行设置,最高可模拟海拔高度12000米,适用于中小型动物如犬、猴、兔、鼠等。
整个实验装置由动物舱体、真空系统、监测及控制系统构成。设备的自动化程度高,无须专人守候,可长期持续一个月运行。
产品特点
多功能
-
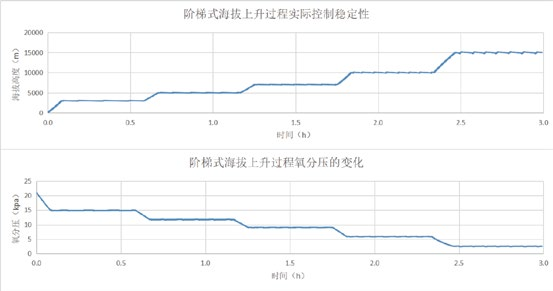
实时显示海拔和氧气浓度动态变化曲线
-
多功能编程控制:可进行阶段式、周期式、循环模式控制
-
实验过程数据可保存至U盘,可在电脑读取分析
-
具备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范
-
提供多方位的报警功能,提醒实验人员异常状态
确保安全
-
从设计开始到最终完成测试和检查,所有实验氧舱都遵循严格的生产过程;
-
具有紧急关闭和自动排气系统,以适应各种情况。
动物舱体
-
主体采用进口亚克力加厚材质,坚固可靠,透明方便观察;
-
铝合金及不锈钢材料支撑;
-
具有脚轮脚刹设计,方便移动。
气体输送控制系统
-
高性能低噪音的真空系统,为系统提供稳定的压力;
-
具有气体缓冲器,减小甚至消除了细股急流气体对小动物的影响;
-
完善的多级空气过滤器,确保动物舱内气体不会污染实验环境。
拓展及特殊定制
-
动物生理指标监测
-
可实现的监测指标:心电图、心率、体温、血压、呼吸、血氧饱和度;
-
呼吸代谢监控功能
-
采血给药功能
-
视频监测功能
-
动物低氧跑台装置
-
低氧强迫游泳装置
-
温控功能
恒温功能,温度可控制,室温-40℃;
低温功能,4℃,温度可控制,室温-4℃;
-
可定制其它功能
应用领域
高原医学研究、肺水肿、脑水肿、肺动脉高压等疾病研究
型号说明
|
名称 |
型号 |
说明 |
|
动物实验低压氧舱 |
ProOx-810 |
舱内尺寸(长×直径):700×560mm |
|
动物实验低压氧舱 |
ProOx-810L |
舱内尺寸(长×直径):1200*800mm |
使用客户名单
相关文献
[1]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia.[J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[2]Guijuan Chen,Kang Cheng,Yun Niu,Li Zhu,Xueting Wang.Epicatechin gallate prevents inflammatory response in hypoxia-activated microglia and cerebral edema by inhibiting NF-κB signaling.[J]Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics ,Volume 729, 109393;
[3]Yapeng,LuPanpanChang,WangwangDing,JiangpeiBian,DanWang,XuetingWang,QianqianLuo,XiaomeiWu,LiZhu.Pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial division attenuates simulated high-altitude exposure-induced cerebral edema in mice: Involvement of inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in glial cells.[J] European Journal of Pharmacology,Volume 929,2022,175137
[4]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin .Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner, [J] European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[5]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling, [J] Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[6]Fang Zhao, Yan Meng, Yue Wang, Siqi Fan, Yu Liu,Xiangfeng Zhang, Chenyang Ran, Hongxin Wang and Meili Lu,Protective effect of Astragaloside IV on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway.[J] Frontiers in Pharmacology,10.3389/fphar.2022.920977
[7]Jing Zhang , Jian-Zhong Jiang , Jun Xu , Chen-Yu Xu , Shan Mao , Ying Shi , Wei Gu , Chun-Fang Zou , Yue-Ming Zhao , Liang Ye.”Identification of Novel Biomarkers for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Promoted by Obstructive Sleep Apnea”[J]Annals of Vascular Surgery, Available online 2 February 2023
[8]Zhang, C., Sun, Y., Guo, Y. et al. “JMJD1C promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating glycolysis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. “[J].Cell Death Discov. 9, 98 (2023).
[9]Zhang, L., Liu, X., Wei, Q. et al. “Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p. “[J]. Mamm Genome 34, 76–89 (2023).
[10]Yanhong Pei a b, Lifei Huang c, Tong Wang c, Qinhan Yao a, Yanrong Sun a, Yan Zhang a, Xiaomei Yang a, Jiliang Zhai d, Lihua Qin a, Jiajia Xue c, Xing Wang c, Hongquan Zhang a b, Junhao Yan."Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury. materialstoday ADVANCES, Volume 17, March 2023, 100349.
[11]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. "Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia" . [J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[12]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin ."Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner" . [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[13]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,"Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling" . [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[14]Yanfei Zhang, Jinyu Fang, Yingyue Dong, Huiru Ding, Quancheng Cheng, Huaicun Liu, Guoheng Xu, Weiguang Zhang“High-Altitude Hypoxia Exposure Induces Iron Overload and Ferroptosis in Adipose Tissue.” [J]. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2367.
[15]Wan-ping Yang, Mei-qi Li, Jie Ding, Jia-yan Li, Gang Wu, Bao Liu, Yu-qi Gao, Guo-hua Wang, Qian-qian Luo. "High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen.” [J]. bioRxiv preprint, 2023.03.23.533972
参考:
高原疾病介绍
不同的海拔高度大气压和氧分压的变化对比
动物实验低压氧舱(恒温版)
产品描述
动物实验低压氧舱用于模拟低压氧高原环境,压力可以根据需要自行设置,最高可模拟海拔高度12000米,适用于更多的鼠笼或中小型动物如犬、猴、兔、鼠等。
整个实验装置由动物舱体、真空系统、监测及控制系统构成。设备的自动化程度高,无须专人守候,可长期持续一个月运行。
产品特点
人性化操作
-
采用10英寸触摸屏,人性化界面设计,操作简便。
-
两种控制方式:自动、手动,断电可操控;具有传感器组件及机械表双重监测功能。设备自动化程序设计,无须专人守候,可长期持续运转。
-
实时显示海拔和氧分压动态变化曲线。
-
实验过程数据可导出csv格式保存到U盘中,在电脑中读取分析。
-
可根据客户实验需求,订制实验环境及配套其他相关实验设备。
-
配备动物低压专用水瓶,防止在负压环境中,水滴漏速过快。
操作安全放心
-
配备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范。
-
提供多方位报警功能(温度、湿度、压力、氧浓度 上/下限),防止出现安全隐患。配备渐开手轮式舱门,降低因为误操作造成的伤害。
-
舱体采用透明厚亚克力材质,方便研究人员观察实验动物情况。
-
配备气体缓冲器,减小、甚至消除了细股急流气体对小动物的影响。
-
配备多级空气过滤器,确保动物舱内实验环境空气不会收到污染。
-
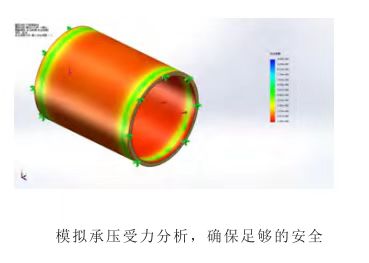
舱体模拟承受力分析,确保这种结构足够安全。
参数显示/功能全
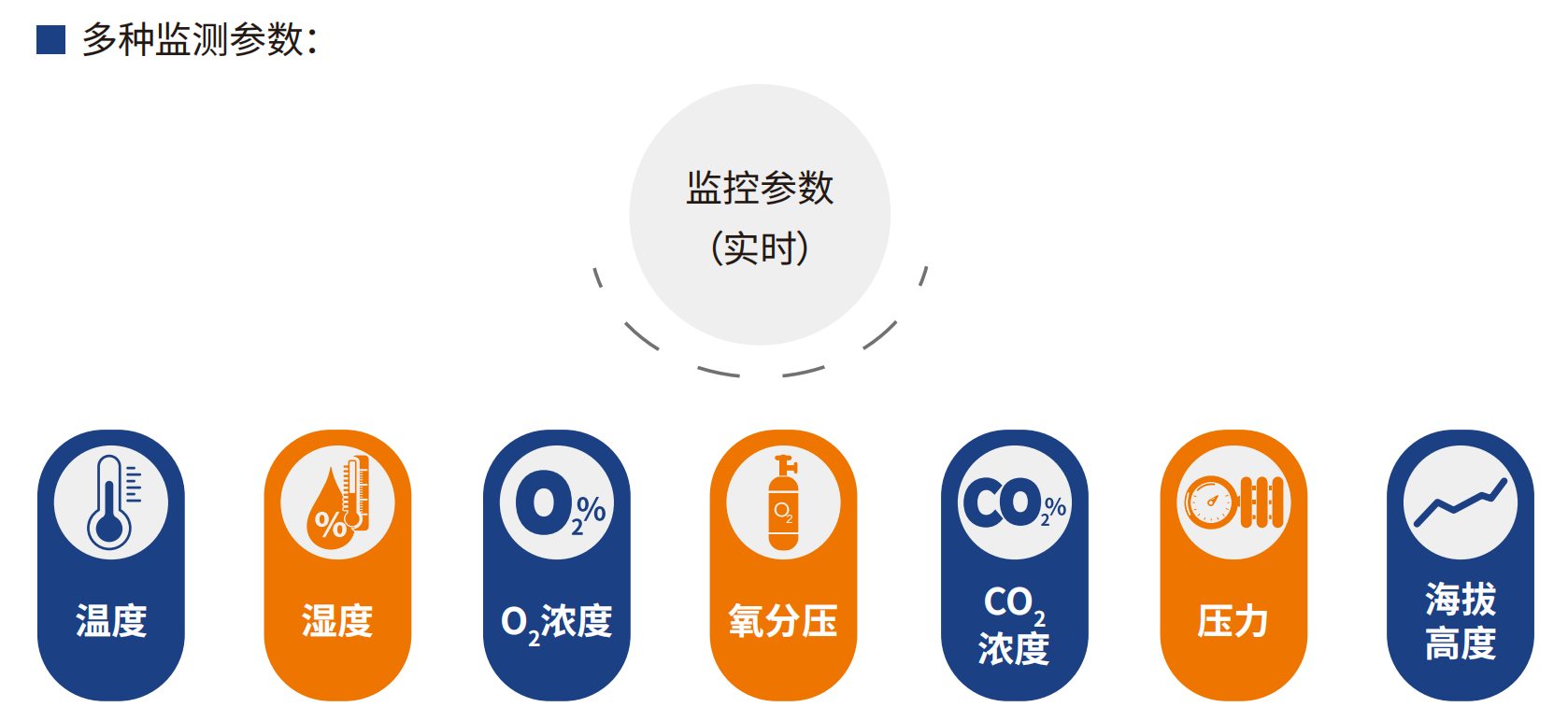

拓展及特殊定制
动物生理指标监测
可实现的监测指标:心电图、心率、体温、血压、呼吸、血氧饱和度;
呼吸代谢监控功能
采血给药功能
视频监测功能
动物低氧跑台装置
低氧强迫游泳装置
温控功能
恒温功能,温度可控制,室温-40℃;
低温功能,4℃,温度可控制,室温-4℃;
可定制其它功能
应用领域
高原医学研究、肺水肿、脑水肿、肺动脉高压等疾病研究
型号说明
|
名称 |
型号 |
说明 |
|
动物低压氧舱 (标准版) |
ProOx-810 |
可以摆放2个大鼠笼/4个小鼠笼 |
|
动物低压氧舱 (恒温版) |
ProOx-811 |
可以摆放2个大鼠笼/4个小鼠笼,同时加上恒温功能 |
|
动物低压氧舱 (大容量版) |
ProOx-810L |
可以摆放4个大鼠笼/8个小鼠笼(可叠加) |
|
动物低压氧舱 (大容量版+恒温) |
ProOx-811L |
可以摆放4个大鼠笼/8个小鼠笼(可叠加),同时加上恒温功能 |
|
动物低压氧舱 基础款 |
ProOx-830 |
可以摆放1个大鼠笼/2个小鼠笼 |
使用客户名单
相关文献
[1]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. "Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia" . [J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[2]Guijuan Chen,Kang Cheng,Yun Niu,Li Zhu,Xueting Wang."Epicatechin gallate prevents inflammatory response in hypoxia-activated microglia and cerebral edema by inhibiting NF-κB signaling" . [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics ,Volume 729, 109393;
[3]Yapeng,LuPanpanChang,WangwangDing,JiangpeiBian,DanWang,XuetingWang,QianqianLuo,XiaomeiWu,LiZhu."Pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial division attenuates simulated high-altitude exposure-induced cerebral edema in mice: Involvement of inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in glial cells". [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Volume 929,2022,175137
[4]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin ."Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner" . [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[5]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,"Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling" . [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[6]Fang Zhao, Yan Meng, Yue Wang, Siqi Fan, Yu Liu,Xiangfeng Zhang, Chenyang Ran, Hongxin Wang and Meili Lu. "Protective effect of Astragaloside IV on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway" .[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,10.3389/fphar.2022.920977
[7]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. "Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia" . [J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[8]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin ."Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner" . [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[9]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,"Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling" . [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[10]Yanfei Zhang, Jinyu Fang, Yingyue Dong, Huiru Ding, Quancheng Cheng, Huaicun Liu, Guoheng Xu, Weiguang Zhang“High-Altitude Hypoxia Exposure Induces Iron Overload and Ferroptosis in Adipose Tissue.” [J]. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2367.
[11]Wan-ping Yang, Mei-qi Li, Jie Ding, Jia-yan Li, Gang Wu, Bao Liu, Yu-qi Gao, Guo-hua Wang, Qian-qian Luo. "High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen.” [J]. bioRxiv preprint, 2023.03.23.533972
参考研究
高原疾病介绍
不同的海拔高度大气压和氧分压的变化对比
*我公司可提供3Q验证,根据客户的特殊应用、特殊需求提供功能定制服务,也可以提供相关的实验服务,详情请来电咨询。
动物实验高压氧舱
产品描述
动物实验高压氧舱是专门为实验动物设计的一款用于可做高压氧的设备,具有手动和自动两种操作方式,可用于各种缺氧症状的研究。
产品特点
· 采用10英寸触摸屏,操作简单
· 实时显示压力和氧气浓度动态变化曲线
· 工作压力为0-0.3MPa
· 具备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范
· 动物舱体采用进口亚克力加厚耗材,坚固可靠
· 具有抽拉式动物载床,方便去放动物与清洁
· 具有气体缓冲器,减小细股急流气体对动物的影响
· 多级空气过滤器确保气体清洁,同时去除空气供应中的微粒物质、水分、油和油蒸汽
· 提供多方位的报警功能,提醒实验人员异常状态
适用领域
· 迅速纠正机体缺氧状态
· 改善微循环
· 防治各类水肿
· 促使侧枝循环的建立,增加血脑屏障通透性
· 加速病灶修复
· 抑制细菌、微生物
型号说明
| 名称 | 型号 | 说明 |
| 动物实验高压氧舱 | ProOx-820 | 专门为实验动物设计的一款可做高压氧的设备 |
使用客户名单
相关文献
[1] Drekolia M K, Mettner J, Wang D, et al. Cystine import and oxidative catabolism fuel vascular growth and repair via nutrient-responsive histone acetylation[J]. Cell Metabolism (IF 30.9), 2025.
[2] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang C Y, et al. Inactivation of AXL in Cardiac Fibroblasts Alleviates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. Advanced Science (IF 14.1), 2025: e08995.
[3] Lei R, Gu M, Li J, et al. Lipoic acid/trometamol assembled hydrogel as injectable bandage for hypoxic wound healing at high altitude[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 13.4), 2024, 489: 151499.
[4] Li Z, Li H, Qiao W, et al. Multi-omics dissection of high TWAS-active endothelial pathogenesis in pulmonary arterial hypertension: bridging single-cell heterogeneity, machine learning-driven biomarkers, and developmental reprogramming[J]. International Journal of Surgery (IF 10.1), 10.1097.
[5] Pei Y, Huang L, Wang T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury[J]. Materials Today Advances (IF 10), 2023, 17: 100349.
[6] Wang Q, Liu J, Li R, et al. Macrophage κ-opioid receptor inhibits hypoxic pulmonary hypertension progression and right heart dysfunction via an SCD1-dependent anti-inflammatory response[J]. Genes & Diseases (IF 9.4), 2025: 101604.
[7] Wang Y, Zhang R, Chen Q, et al. PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Prevents Hypoxia-induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2024, 20(11): 4297.
[8] Wang Y, Shen P, Wu Z, et al. Plasma Proteomic Profiling Reveals ITGA2B as a key regulator of heart health in high-altitude settlers[J]. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2025: qzaf030.
[9] Lan Y, Zhao S, Song Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of selenized quinoa protein hydrolysate and its regulatory effects on neuroinflammation and gut microbiota in hypoxic mice[J]. Journal of Future Foods, 2025.
[10] Pan Z, Yao Y, Liu X, et al. Nr1d1 inhibition mitigates intermittent hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via Dusp1-mediated Erk1/2 deactivation and mitochondrial fission attenuation[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2024, 10(1): 459.
[11] Zhou Y, Ni Z, Liu J, et al. Gut Microbiota‐Associated Metabolites Affected the Susceptibility to Heart Health Abnormality in Young Migrants at High‐Altitude: Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolites Impart Heart Health in Plateau[C]//Exploration. 2025: 20240332.
[12] Li C, Zhao Z, Jin J, et al. NLRP3-GSDMD-dependent IL-1β Secretion from Microglia Mediates Learning and Memory Impairment in a Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-induced Mouse Model[J]. Neuroscience, 2024, 539: 51-65.
[13] Yang W, Li M, Ding J, et al. High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen[J]. Elife, 2024, 12: RP87496.
[14] You Z, Huang Q, Zeng L, et al. Rab26 promotes hypoxia-induced hyperproliferation of PASMCs by modulating the AT1R-STAT3-YAP axis[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2025, 82(1): 1-16.
[15] Pei C, Shen Z, Wu Y, et al. Eleutheroside B Pretreatment Attenuates Hypobaric Hypoxia‐Induced High‐Altitude Pulmonary Edema by Regulating Autophagic Flux via the AMPK/mTOR Pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2024, 38(12): 5657-5671.
[16] Duan H, Han Y, Zhang H, et al. Eleutheroside B Ameliorates Cardiomyocytes Necroptosis in High-Altitude-Induced Myocardial Injury via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2025, 14(2): 190.
[17] Song J, Zheng J, Li Z, et al. Sulfur dioxide inhibits mast cell degranulation by sulphenylation of galectin-9 at cysteine 74[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15: 1369326.
[18] Jia N, Shen Z, Zhao S, et al. Eleutheroside E from pre-treatment of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. etMaxim.) Harms ameliorates high-altitude-induced heart injury by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2023, 121: 110423.
[19] Huang Q, Han X, Li J, et al. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2025, 17(3): 341.
[20] Wu Y, Tang Z, Du S, et al. Oral quercetin nanoparticles in hydrogel microspheres alleviate high-altitude sleep disturbance based on the gut-brain axis[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2024, 658: 124225.
[21] Zhou Z, Zhao Q, Huang Y, et al. Berberine ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia‐induced cardiac remodelling by preserving mitochondrial function, role of SIRT6 signalling[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2024, 28(12): e18407.
[22] Shang W, Huang Y, Xu Z, et al. The impact of a high-carbohydrate diet on the cognitive behavior of mice in a low-pressure, low-oxygen environment[J]. Food & Function, 2025, 16(3): 1116-1129.
[23] Pei C, Jia N, Wang Y, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 protects against hypobaric hypoxia-induced high-altitude pulmonary edema by inhibiting apoptosis via ERK1/2-P90rsk-BAD ignaling pathway[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2023, 959: 176065.
[24] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[25] Ding Y, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. Bicarbonate-Rich Mineral Water Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced Osteoporosis in Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Pathway Regulation[J]. Nutrients, 2025, 17(6): 998.
[26] Gu N, Shen Y, He Y, et al. Loss of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 alleviates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibiting Cyp1a1 mRNA decay[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2024.
[27] Luan X, Zhu D, Hao Y, et al. Qibai Pingfei Capsule ameliorated inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) via HIF-1 α/glycolysis pathway mediated of BMAL1[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2025, 144: 113636.
[28] Jiang H, Lu C, Wu H, et al. Decreased cold‐inducible RNA‐binding protein (CIRP) binding to GluRl on neuronal membranes mediates memory impairment resulting from prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2024, 30(9): e70059.
[29] Chang P, Xu M, Zhu J, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Mitochondrial Division Attenuates Simulated High‐Altitude Exposure‐Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: [30] Involvement of Inhibition of Microglia‐Mediated Synapse Elimination[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(6): e70473.
[30] Liu C, Qu D, Li C, et al. miR‐448‐3p/miR‐1264‐3p Participates in Intermittent Hypoxic Response in Hippocampus by Regulating Fam76b/hnRNPA2B1[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(2): e70239.
[31] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang D J, et al. TCF7 enhances pulmonary hypertension by boosting stressed natural killer cells and their interaction with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells[J]. Respiratory Research, 2025, 26(1): 202.
[32] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[33] Cai S, Li Z, Bai J, et al. Optimized oxygen therapy improves sleep deprivation-induced cardiac dysfunction through gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2025, 15: 1522431.
[34] Wang X, Xie Y, Niu Y, et al. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal mediates M1-type microglia and accelerates high-altitude-induced forgetting[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2023, 17: 1189348.
[35] He Y, Wang Y, Duan H, et al. Pharmacological targeting of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema: therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2025, 16: 1644436.
[36] Guo Y, Qin J, Sun R, et al. Molecular hydrogen promotes retinal vascular regeneration and attenuates neovascularization and neuroglial dysfunction in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice[J]. Biological Research, 2024, 57.
[37] Liu L, Zhang J, Song S, et al. Paraventricular nucleus neurons: important regulators of respiratory movement in mice with chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Annals of Medicine, 2025, 57(1): 2588664.
[38] Ma Q, Ma J, Cui J, et al. Oxygen enrichment protects against intestinal damage and gut microbiota disturbance in rats exposed to acute high-altitude hypoxia[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14.
[39] Lan J, Lin J, Guo Y, et al. Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of exosome-derived miRNAs in mouse models of pancreatic injury induced by OSA[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2025, 16: 1712442.
[40] Feng X, Li C, Zhang W, et al. Mechanism of retinal angiogenesis induced by HIF-1α and HIF-2α under hyperoxic conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 36049.
[41] Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y, et al. TGM2 Enhances Hypobaric Hypoxia-mediated Brain Injury Via Regulating NLRP3/GSDMD Signaling[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2025, 50(6): 1-11.
[42] Yang A, Guo L, Zhang Y, et al. MFN2-mediated mitochondrial fusion facilitates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing glucose catabolism and ROS production[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2023: 130413.
[43] Chu H, Jiang W, Zuo N, et al. Astrocyte activation: A key mediator underlying chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive dysfunction[J]. Sleep Medicine, 2025: 106692.
[44] Xu A, Huang F, Chen E, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates heatstroke-induced hippocampal injury by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2024, 41(1): 2382162.
[45] Zhang Z, Zheng X, He Y, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen ameliorates neuroinflammation in heat-stressed BV-2 microglial cells: potential involvement of EAAT2 regulation[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2025, 42(1): 2583133.
[46] Jinyu F, Huaicun L, Yanfei Z, et al. Nogo-A Protein Mediates Oxidative Stress and Synaptic Damage Induced by High-altitude Hypoxia in the Rat Hippocampus[J]. 2024.
[47] Su L, Ni T, Fan R, et al. An attention to the effect of intravitreal injection on the controls of oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model[J]. Experimental Eye Research, 2024, 248: 110094.
[48] Xu Y, Xu J, Li J, et al. Interplay of HIF-1α, SMAD2, and VEGF signaling in hypoxic renal environments: impact on macrophage polarization and renoprotection[J]. Renal Failure, 2025, 47(1): 2561784.
[49] Zhang D, Bian W, Gao Z. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Endometrial Function in Female Rats: Mechanism Exploration[J]. Nature and Science of Sleep, 2025: 2485-2499.
[50] Zhang N, Wei F, Ning S, et al. PPARγ Agonist Rosiglitazone and Antagonist GW9662: Antihypertensive Effects on Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Hypertension in Rats[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 2024: 1-13.
[51] Zhang Y, Zhang A, Yang J, et al. Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosome‐Derived SLC25A3 Ameliorates Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Modulating Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative Stress[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2025, 43(12): e70152.
[52] Lan J, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of m6A-modified circRNAs in the mouse model of myocardial injury induced by obstructive sleep apnea[J]. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 2025, 25(1): 158.
[53] Zhang L, Liu X, Wei Q, et al. Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p[J]. Mammalian Genome, 2023, 34(1): 76-89.
[54] Wei J, Hu M, Chen X, et al. Hypobaric Hypoxia Aggravates Renal Injury by Inducing the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway[J]. Current Medical Science, 2023: 1-9.
[55] Zhang L, Li J, Wan Q, et al. Intestinal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate necrotizing enterocolitis injury[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2025, 79: 101997.
[56] Liao Y, Ke B, Long X, et al. Abnormalities in the SIRT1-SIRT3 axis promote myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ferroptosis caused by silencing the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway[J]. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2023, 23(1): 582.
[57] Wang M, Wen W, Chen Y, et al. TRPC5 channel participates in myocardial injury in chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Clinics, 2024, 79: 100368.
[58] Li J, Ye J. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via postsynaptic mechanisms[J]. Sleep and Breathing, 2024: 1-9.
[59] Binbin L I, Haizhen L I, Houhuang C, et al. Utilizing Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Improve Cognitive Function in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease by Activating Autophagy-Related Signaling Pathways[J]. Physiological Research, 2025, 74(1): 141.
[60] Han J, Wang L, Wang L, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Limits Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Progression by Regulating Th17/Treg Balance[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2025, 48(5): 555-562.
[61] Nan L, Kaisi F, Mengzhen Z, et al. miR-375-3p targets YWHAB to attenuate intestine injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pediatric Surgery International, 2024, 40(1): 63.
[62] Liu B, Zheng W, Tang C, et al. Scutellarein-containing novel formula attenuates hypoxia through inhibiting apoptosis[J]. 2025.
动物实验高低压氧舱
产品描述
动物高低压氧舱是专门为实验动物设计的一款实验氧舱,可同时用于低压氧和高压氧研究。具有手动和自动两种操作方式,可用于模拟高原环境,制作脑水肿、肺动脉高压等动物模型。
产品特点
· 采用10英寸触摸屏,操作简单
· 实时显示压力和氧气浓度动态变化曲线
· 最高可模拟10000米海拔高度,最大压力达0.15MPa
· 具备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范
· 动物舱体采用进口亚克力加厚耗材,坚固可靠
· 具有抽拉式动物载床,方便去放动物与清洁
· 具有气体缓冲器,减小细股急流气体对动物的影响
· 多级空气过滤器确保气体清洁,同时去除空气供应中的微粒物质、水分、油和油蒸汽
· 提供多方位的报警功能,提醒实验人员异常状态
应用领域
高原医学研究、肺水肿、脑水肿、肺动脉高压等疾病研究
型号说明
| 名称 | 型号 | 说明 |
| 动物高低压氧舱 | ProOx-850 | 可同时用于低压氧和高压氧研究 |
使用客户名单
相关文献
[1] Drekolia M K, Mettner J, Wang D, et al. Cystine import and oxidative catabolism fuel vascular growth and repair via nutrient-responsive histone acetylation[J]. Cell Metabolism (IF 30.9), 2025.
[2] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang C Y, et al. Inactivation of AXL in Cardiac Fibroblasts Alleviates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. Advanced Science (IF 14.1), 2025: e08995.
[3] Lei R, Gu M, Li J, et al. Lipoic acid/trometamol assembled hydrogel as injectable bandage for hypoxic wound healing at high altitude[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 13.4), 2024, 489: 151499.
[4] Li Z, Li H, Qiao W, et al. Multi-omics dissection of high TWAS-active endothelial pathogenesis in pulmonary arterial hypertension: bridging single-cell heterogeneity, machine learning-driven biomarkers, and developmental reprogramming[J]. International Journal of Surgery (IF 10.1), 10.1097.
[5] Pei Y, Huang L, Wang T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury[J]. Materials Today Advances (IF 10), 2023, 17: 100349.
[6] Wang Q, Liu J, Li R, et al. Macrophage κ-opioid receptor inhibits hypoxic pulmonary hypertension progression and right heart dysfunction via an SCD1-dependent anti-inflammatory response[J]. Genes & Diseases (IF 9.4), 2025: 101604.
[7] Wang Y, Zhang R, Chen Q, et al. PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Prevents Hypoxia-induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2024, 20(11): 4297.
[8] Wang Y, Shen P, Wu Z, et al. Plasma Proteomic Profiling Reveals ITGA2B as a key regulator of heart health in high-altitude settlers[J]. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2025: qzaf030.
[9] Lan Y, Zhao S, Song Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of selenized quinoa protein hydrolysate and its regulatory effects on neuroinflammation and gut microbiota in hypoxic mice[J]. Journal of Future Foods, 2025.
[10] Pan Z, Yao Y, Liu X, et al. Nr1d1 inhibition mitigates intermittent hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via Dusp1-mediated Erk1/2 deactivation and mitochondrial fission attenuation[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2024, 10(1): 459.
[11] Zhou Y, Ni Z, Liu J, et al. Gut Microbiota‐Associated Metabolites Affected the Susceptibility to Heart Health Abnormality in Young Migrants at High‐Altitude: Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolites Impart Heart Health in Plateau[C]//Exploration. 2025: 20240332.
[12] Li C, Zhao Z, Jin J, et al. NLRP3-GSDMD-dependent IL-1β Secretion from Microglia Mediates Learning and Memory Impairment in a Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-induced Mouse Model[J]. Neuroscience, 2024, 539: 51-65.
[13] Yang W, Li M, Ding J, et al. High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen[J]. Elife, 2024, 12: RP87496.
[14] You Z, Huang Q, Zeng L, et al. Rab26 promotes hypoxia-induced hyperproliferation of PASMCs by modulating the AT1R-STAT3-YAP axis[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2025, 82(1): 1-16.
[15] Pei C, Shen Z, Wu Y, et al. Eleutheroside B Pretreatment Attenuates Hypobaric Hypoxia‐Induced High‐Altitude Pulmonary Edema by Regulating Autophagic Flux via the AMPK/mTOR Pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2024, 38(12): 5657-5671.
[16] Duan H, Han Y, Zhang H, et al. Eleutheroside B Ameliorates Cardiomyocytes Necroptosis in High-Altitude-Induced Myocardial Injury via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2025, 14(2): 190.
[17] Song J, Zheng J, Li Z, et al. Sulfur dioxide inhibits mast cell degranulation by sulphenylation of galectin-9 at cysteine 74[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15: 1369326.
[18] Jia N, Shen Z, Zhao S, et al. Eleutheroside E from pre-treatment of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. etMaxim.) Harms ameliorates high-altitude-induced heart injury by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2023, 121: 110423.
[19] Huang Q, Han X, Li J, et al. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2025, 17(3): 341.
[20] Wu Y, Tang Z, Du S, et al. Oral quercetin nanoparticles in hydrogel microspheres alleviate high-altitude sleep disturbance based on the gut-brain axis[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2024, 658: 124225.
[21] Zhou Z, Zhao Q, Huang Y, et al. Berberine ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia‐induced cardiac remodelling by preserving mitochondrial function, role of SIRT6 signalling[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2024, 28(12): e18407.
[22] Shang W, Huang Y, Xu Z, et al. The impact of a high-carbohydrate diet on the cognitive behavior of mice in a low-pressure, low-oxygen environment[J]. Food & Function, 2025, 16(3): 1116-1129.
[23] Pei C, Jia N, Wang Y, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 protects against hypobaric hypoxia-induced high-altitude pulmonary edema by inhibiting apoptosis via ERK1/2-P90rsk-BAD ignaling pathway[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2023, 959: 176065.
[24] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[25] Ding Y, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. Bicarbonate-Rich Mineral Water Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced Osteoporosis in Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Pathway Regulation[J]. Nutrients, 2025, 17(6): 998.
[26] Gu N, Shen Y, He Y, et al. Loss of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 alleviates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibiting Cyp1a1 mRNA decay[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2024.
[27] Luan X, Zhu D, Hao Y, et al. Qibai Pingfei Capsule ameliorated inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) via HIF-1 α/glycolysis pathway mediated of BMAL1[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2025, 144: 113636.
[28] Jiang H, Lu C, Wu H, et al. Decreased cold‐inducible RNA‐binding protein (CIRP) binding to GluRl on neuronal membranes mediates memory impairment resulting from prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2024, 30(9): e70059.
[29] Chang P, Xu M, Zhu J, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Mitochondrial Division Attenuates Simulated High‐Altitude Exposure‐Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: [30] Involvement of Inhibition of Microglia‐Mediated Synapse Elimination[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(6): e70473.
[30] Liu C, Qu D, Li C, et al. miR‐448‐3p/miR‐1264‐3p Participates in Intermittent Hypoxic Response in Hippocampus by Regulating Fam76b/hnRNPA2B1[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(2): e70239.
[31] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang D J, et al. TCF7 enhances pulmonary hypertension by boosting stressed natural killer cells and their interaction with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells[J]. Respiratory Research, 2025, 26(1): 202.
[32] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[33] Cai S, Li Z, Bai J, et al. Optimized oxygen therapy improves sleep deprivation-induced cardiac dysfunction through gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2025, 15: 1522431.
[34] Wang X, Xie Y, Niu Y, et al. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal mediates M1-type microglia and accelerates high-altitude-induced forgetting[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2023, 17: 1189348.
[35] He Y, Wang Y, Duan H, et al. Pharmacological targeting of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema: therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2025, 16: 1644436.
[36] Guo Y, Qin J, Sun R, et al. Molecular hydrogen promotes retinal vascular regeneration and attenuates neovascularization and neuroglial dysfunction in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice[J]. Biological Research, 2024, 57.
[37] Liu L, Zhang J, Song S, et al. Paraventricular nucleus neurons: important regulators of respiratory movement in mice with chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Annals of Medicine, 2025, 57(1): 2588664.
[38] Ma Q, Ma J, Cui J, et al. Oxygen enrichment protects against intestinal damage and gut microbiota disturbance in rats exposed to acute high-altitude hypoxia[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14.
[39] Lan J, Lin J, Guo Y, et al. Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of exosome-derived miRNAs in mouse models of pancreatic injury induced by OSA[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2025, 16: 1712442.
[40] Feng X, Li C, Zhang W, et al. Mechanism of retinal angiogenesis induced by HIF-1α and HIF-2α under hyperoxic conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 36049.
[41] Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y, et al. TGM2 Enhances Hypobaric Hypoxia-mediated Brain Injury Via Regulating NLRP3/GSDMD Signaling[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2025, 50(6): 1-11.
[42] Yang A, Guo L, Zhang Y, et al. MFN2-mediated mitochondrial fusion facilitates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing glucose catabolism and ROS production[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2023: 130413.
[43] Chu H, Jiang W, Zuo N, et al. Astrocyte activation: A key mediator underlying chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive dysfunction[J]. Sleep Medicine, 2025: 106692.
[44] Xu A, Huang F, Chen E, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates heatstroke-induced hippocampal injury by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2024, 41(1): 2382162.
[45] Zhang Z, Zheng X, He Y, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen ameliorates neuroinflammation in heat-stressed BV-2 microglial cells: potential involvement of EAAT2 regulation[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2025, 42(1): 2583133.
[46] Jinyu F, Huaicun L, Yanfei Z, et al. Nogo-A Protein Mediates Oxidative Stress and Synaptic Damage Induced by High-altitude Hypoxia in the Rat Hippocampus[J]. 2024.
[47] Su L, Ni T, Fan R, et al. An attention to the effect of intravitreal injection on the controls of oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model[J]. Experimental Eye Research, 2024, 248: 110094.
[48] Xu Y, Xu J, Li J, et al. Interplay of HIF-1α, SMAD2, and VEGF signaling in hypoxic renal environments: impact on macrophage polarization and renoprotection[J]. Renal Failure, 2025, 47(1): 2561784.
[49] Zhang D, Bian W, Gao Z. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Endometrial Function in Female Rats: Mechanism Exploration[J]. Nature and Science of Sleep, 2025: 2485-2499.
[50] Zhang N, Wei F, Ning S, et al. PPARγ Agonist Rosiglitazone and Antagonist GW9662: Antihypertensive Effects on Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Hypertension in Rats[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 2024: 1-13.
[51] Zhang Y, Zhang A, Yang J, et al. Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosome‐Derived SLC25A3 Ameliorates Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Modulating Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative Stress[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2025, 43(12): e70152.
[52] Lan J, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of m6A-modified circRNAs in the mouse model of myocardial injury induced by obstructive sleep apnea[J]. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 2025, 25(1): 158.
[53] Zhang L, Liu X, Wei Q, et al. Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p[J]. Mammalian Genome, 2023, 34(1): 76-89.
[54] Wei J, Hu M, Chen X, et al. Hypobaric Hypoxia Aggravates Renal Injury by Inducing the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway[J]. Current Medical Science, 2023: 1-9.
[55] Zhang L, Li J, Wan Q, et al. Intestinal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate necrotizing enterocolitis injury[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2025, 79: 101997.
[56] Liao Y, Ke B, Long X, et al. Abnormalities in the SIRT1-SIRT3 axis promote myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ferroptosis caused by silencing the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway[J]. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2023, 23(1): 582.
[57] Wang M, Wen W, Chen Y, et al. TRPC5 channel participates in myocardial injury in chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Clinics, 2024, 79: 100368.
[58] Li J, Ye J. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via postsynaptic mechanisms[J]. Sleep and Breathing, 2024: 1-9.
[59] Binbin L I, Haizhen L I, Houhuang C, et al. Utilizing Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Improve Cognitive Function in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease by Activating Autophagy-Related Signaling Pathways[J]. Physiological Research, 2025, 74(1): 141.
[60] Han J, Wang L, Wang L, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Limits Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Progression by Regulating Th17/Treg Balance[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2025, 48(5): 555-562.
[61] Nan L, Kaisi F, Mengzhen Z, et al. miR-375-3p targets YWHAB to attenuate intestine injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pediatric Surgery International, 2024, 40(1): 63.
[62] Liu B, Zheng W, Tang C, et al. Scutellarein-containing novel formula attenuates hypoxia through inhibiting apoptosis[J]. 2025.
参考:
高原疾病介绍
不同的海拔高度大气压和氧分压的变化对比
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
- 作者
- 内容
- 询问日期
 文献和实验
文献和实验[1] Drekolia M K, Mettner J, Wang D, et al. Cystine import and oxidative catabolism fuel vascular growth and repair via nutrient-responsive histone acetylation[J]. Cell Metabolism (IF 30.9), 2025.
[2] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang C Y, et al. Inactivation of AXL in Cardiac Fibroblasts Alleviates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. Advanced Science (IF 14.1), 2025: e08995.
[3] Lei R, Gu M, Li J, et al. Lipoic acid/trometamol assembled hydrogel as injectable bandage for hypoxic wound healing at high altitude[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 13.4), 2024, 489: 151499.
[4] Li Z, Li H, Qiao W, et al. Multi-omics dissection of high TWAS-active endothelial pathogenesis in pulmonary arterial hypertension: bridging single-cell heterogeneity, machine learning-driven biomarkers, and developmental reprogramming[J]. International Journal of Surgery (IF 10.1), 10.1097.
[5] Pei Y, Huang L, Wang T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury[J]. Materials Today Advances (IF 10), 2023, 17: 100349.
[6] Wang Q, Liu J, Li R, et al. Macrophage κ-opioid receptor inhibits hypoxic pulmonary hypertension progression and right heart dysfunction via an SCD1-dependent anti-inflammatory response[J]. Genes & Diseases (IF 9.4), 2025: 101604.
[7] Wang Y, Zhang R, Chen Q, et al. PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Prevents Hypoxia-induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2024, 20(11): 4297.
[8] Wang Y, Shen P, Wu Z, et al. Plasma Proteomic Profiling Reveals ITGA2B as a key regulator of heart health in high-altitude settlers[J]. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2025: qzaf030.
[9] Lan Y, Zhao S, Song Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of selenized quinoa protein hydrolysate and its regulatory effects on neuroinflammation and gut microbiota in hypoxic mice[J]. Journal of Future Foods, 2025.
[10] Pan Z, Yao Y, Liu X, et al. Nr1d1 inhibition mitigates intermittent hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via Dusp1-mediated Erk1/2 deactivation and mitochondrial fission attenuation[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2024, 10(1): 459.
[11] Zhou Y, Ni Z, Liu J, et al. Gut Microbiota‐Associated Metabolites Affected the Susceptibility to Heart Health Abnormality in Young Migrants at High‐Altitude: Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolites Impart Heart Health in Plateau[C]//Exploration. 2025: 20240332.
[12] Li C, Zhao Z, Jin J, et al. NLRP3-GSDMD-dependent IL-1β Secretion from Microglia Mediates Learning and Memory Impairment in a Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-induced Mouse Model[J]. Neuroscience, 2024, 539: 51-65.
[13] Yang W, Li M, Ding J, et al. High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen[J]. Elife, 2024, 12: RP87496.
[14] You Z, Huang Q, Zeng L, et al. Rab26 promotes hypoxia-induced hyperproliferation of PASMCs by modulating the AT1R-STAT3-YAP axis[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2025, 82(1): 1-16.
[15] Pei C, Shen Z, Wu Y, et al. Eleutheroside B Pretreatment Attenuates Hypobaric Hypoxia‐Induced High‐Altitude Pulmonary Edema by Regulating Autophagic Flux via the AMPK/mTOR Pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2024, 38(12): 5657-5671.
[16] Duan H, Han Y, Zhang H, et al. Eleutheroside B Ameliorates Cardiomyocytes Necroptosis in High-Altitude-Induced Myocardial Injury via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2025, 14(2): 190.
[17] Song J, Zheng J, Li Z, et al. Sulfur dioxide inhibits mast cell degranulation by sulphenylation of galectin-9 at cysteine 74[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15: 1369326.
[18] Jia N, Shen Z, Zhao S, et al. Eleutheroside E from pre-treatment of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. etMaxim.) Harms ameliorates high-altitude-induced heart injury by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2023, 121: 110423.
[19] Huang Q, Han X, Li J, et al. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2025, 17(3): 341.
[20] Wu Y, Tang Z, Du S, et al. Oral quercetin nanoparticles in hydrogel microspheres alleviate high-altitude sleep disturbance based on the gut-brain axis[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2024, 658: 124225.
[21] Zhou Z, Zhao Q, Huang Y, et al. Berberine ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia‐induced cardiac remodelling by preserving mitochondrial function, role of SIRT6 signalling[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2024, 28(12): e18407.
[22] Shang W, Huang Y, Xu Z, et al. The impact of a high-carbohydrate diet on the cognitive behavior of mice in a low-pressure, low-oxygen environment[J]. Food & Function, 2025, 16(3): 1116-1129.
[23] Pei C, Jia N, Wang Y, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 protects against hypobaric hypoxia-induced high-altitude pulmonary edema by inhibiting apoptosis via ERK1/2-P90rsk-BAD ignaling pathway[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2023, 959: 176065.
[24] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[25] Ding Y, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. Bicarbonate-Rich Mineral Water Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced Osteoporosis in Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Pathway Regulation[J]. Nutrients, 2025, 17(6): 998.
[26] Gu N, Shen Y, He Y, et al. Loss of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 alleviates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibiting Cyp1a1 mRNA decay[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2024.
[27] Luan X, Zhu D, Hao Y, et al. Qibai Pingfei Capsule ameliorated inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) via HIF-1 α/glycolysis pathway mediated of BMAL1[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2025, 144: 113636.
[28] Jiang H, Lu C, Wu H, et al. Decreased cold‐inducible RNA‐binding protein (CIRP) binding to GluRl on neuronal membranes mediates memory impairment resulting from prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2024, 30(9): e70059.
[29] Chang P, Xu M, Zhu J, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Mitochondrial Division Attenuates Simulated High‐Altitude Exposure‐Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: [30] Involvement of Inhibition of Microglia‐Mediated Synapse Elimination[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(6): e70473.
[30] Liu C, Qu D, Li C, et al. miR‐448‐3p/miR‐1264‐3p Participates in Intermittent Hypoxic Response in Hippocampus by Regulating Fam76b/hnRNPA2B1[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(2): e70239.
[31] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang D J, et al. TCF7 enhances pulmonary hypertension by boosting stressed natural killer cells and their interaction with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells[J]. Respiratory Research, 2025, 26(1): 202.
[32] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[33] Cai S, Li Z, Bai J, et al. Optimized oxygen therapy improves sleep deprivation-induced cardiac dysfunction through gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2025, 15: 1522431.
[34] Wang X, Xie Y, Niu Y, et al. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal mediates M1-type microglia and accelerates high-altitude-induced forgetting[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2023, 17: 1189348.
[35] He Y, Wang Y, Duan H, et al. Pharmacological targeting of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema: therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2025, 16: 1644436.
[36] Guo Y, Qin J, Sun R, et al. Molecular hydrogen promotes retinal vascular regeneration and attenuates neovascularization and neuroglial dysfunction in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice[J]. Biological Research, 2024, 57.
[37] Liu L, Zhang J, Song S, et al. Paraventricular nucleus neurons: important regulators of respiratory movement in mice with chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Annals of Medicine, 2025, 57(1): 2588664.
[38] Ma Q, Ma J, Cui J, et al. Oxygen enrichment protects against intestinal damage and gut microbiota disturbance in rats exposed to acute high-altitude hypoxia[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14.
[39] Lan J, Lin J, Guo Y, et al. Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of exosome-derived miRNAs in mouse models of pancreatic injury induced by OSA[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2025, 16: 1712442.
[40] Feng X, Li C, Zhang W, et al. Mechanism of retinal angiogenesis induced by HIF-1α and HIF-2α under hyperoxic conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 36049.
[41] Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y, et al. TGM2 Enhances Hypobaric Hypoxia-mediated Brain Injury Via Regulating NLRP3/GSDMD Signaling[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2025, 50(6): 1-11.
[42] Yang A, Guo L, Zhang Y, et al. MFN2-mediated mitochondrial fusion facilitates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing glucose catabolism and ROS production[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2023: 130413.
[43] Chu H, Jiang W, Zuo N, et al. Astrocyte activation: A key mediator underlying chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive dysfunction[J]. Sleep Medicine, 2025: 106692.
[44] Xu A, Huang F, Chen E, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates heatstroke-induced hippocampal injury by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2024, 41(1): 2382162.
[45] Zhang Z, Zheng X, He Y, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen ameliorates neuroinflammation in heat-stressed BV-2 microglial cells: potential involvement of EAAT2 regulation[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2025, 42(1): 2583133.
[46] Jinyu F, Huaicun L, Yanfei Z, et al. Nogo-A Protein Mediates Oxidative Stress and Synaptic Damage Induced by High-altitude Hypoxia in the Rat Hippocampus[J]. 2024.
[47] Su L, Ni T, Fan R, et al. An attention to the effect of intravitreal injection on the controls of oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model[J]. Experimental Eye Research, 2024, 248: 110094.
[48] Xu Y, Xu J, Li J, et al. Interplay of HIF-1α, SMAD2, and VEGF signaling in hypoxic renal environments: impact on macrophage polarization and renoprotection[J]. Renal Failure, 2025, 47(1): 2561784.
[49] Zhang D, Bian W, Gao Z. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Endometrial Function in Female Rats: Mechanism Exploration[J]. Nature and Science of Sleep, 2025: 2485-2499.
[50] Zhang N, Wei F, Ning S, et al. PPARγ Agonist Rosiglitazone and Antagonist GW9662: Antihypertensive Effects on Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Hypertension in Rats[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 2024: 1-13.
[51] Zhang Y, Zhang A, Yang J, et al. Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosome‐Derived SLC25A3 Ameliorates Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Modulating Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative Stress[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2025, 43(12): e70152.
[52] Lan J, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of m6A-modified circRNAs in the mouse model of myocardial injury induced by obstructive sleep apnea[J]. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 2025, 25(1): 158.
[53] Zhang L, Liu X, Wei Q, et al. Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p[J]. Mammalian Genome, 2023, 34(1): 76-89.
[54] Wei J, Hu M, Chen X, et al. Hypobaric Hypoxia Aggravates Renal Injury by Inducing the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway[J]. Current Medical Science, 2023: 1-9.
[55] Zhang L, Li J, Wan Q, et al. Intestinal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate necrotizing enterocolitis injury[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2025, 79: 101997.
[56] Liao Y, Ke B, Long X, et al. Abnormalities in the SIRT1-SIRT3 axis promote myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ferroptosis caused by silencing the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway[J]. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2023, 23(1): 582.
[57] Wang M, Wen W, Chen Y, et al. TRPC5 channel participates in myocardial injury in chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Clinics, 2024, 79: 100368.
[58] Li J, Ye J. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via postsynaptic mechanisms[J]. Sleep and Breathing, 2024: 1-9.
[59] Binbin L I, Haizhen L I, Houhuang C, et al. Utilizing Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Improve Cognitive Function in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease by Activating Autophagy-Related Signaling Pathways[J]. Physiological Research, 2025, 74(1): 141.
[60] Han J, Wang L, Wang L, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Limits Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Progression by Regulating Th17/Treg Balance[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2025, 48(5): 555-562.
[61] Nan L, Kaisi F, Mengzhen Z, et al. miR-375-3p targets YWHAB to attenuate intestine injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pediatric Surgery International, 2024, 40(1): 63.
[62] Liu B, Zheng W, Tang C, et al. Scutellarein-containing novel formula attenuates hypoxia through inhibiting apoptosis[J]. 2025.
 技术资料
技术资料暂无技术资料 索取技术资料










