相关产品推荐更多 >
万千商家帮你免费找货
0 人在求购买到急需产品
- 详细信息
- 文献和实验
- 技术资料
- 供应商:
优利科(上海)生命科学有限公司
- 库存:
100
- 靶点:
详询
- 级别:
科研
- 目录编号:
/
- 克隆性:
单克隆
- 抗原来源:
/
- 保质期:
1年
- 抗体英文名:
Anti-Insulin(1D4:)
- 抗体名:
Insulin(1D4:)抗体
- 标记物:
详询
- 宿主:
Mouse
- 适应物种:
/
- 免疫原:
Insulin from porcine pancreas
- 亚型:
IgG
- 形态:
Lyophilized or Liquid
- 应用范围:
ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500
- 保存条件:
-20℃
- 浓度:
1mg/ml
- 规格:
详询

| 英文名称 Anti-Insulin(1D4:) |
| 中文名称 猪胰岛素单克隆抗体 |
| 别 名 ILPR; INS; Insulin A chain; Insulin B chain; Insulin precursor; IRDN; Proinsulin; Proinsulin precursor. |
| 浓 度 1mg/1ml |
| 规 格 0.1ml/100μg 1ml/1mg |
| 抗体来源 Mouse |
| 克隆类型 monoclonal |
| 克 隆 号 1D4 |
| 交叉反应 Human, Pig |
| 产品类型 一抗 |
研究领域 肿瘤 心血管 细胞生物 免疫学 神经生物学 信号转导 生长因子和激素 糖尿病 内分泌病 新陈代谢 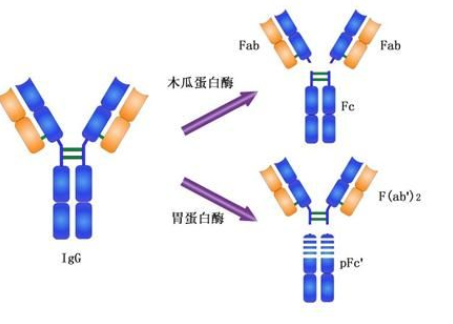 |
| 蛋白分子量 predicted molecular weight: 5.8/12kDa |
| 性 状 Lyophilized or Liquid |
| 免 疫 原 Insulin from porcine pancreas |
| 亚 型 IgG |
| 纯化方法 affinity purified by Protein A |
| 储 存 液 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 with 10 mg/ml BSA and 0.1% Sodium azide |
| 产品应用 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 |
| (石蜡切片需做抗原修复) |
| not yet tested in other applications. |
| optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
保存条件 Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.  |
| Important Note This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| 产品介绍 Insulin is a pancreatic hormone that regulates glucose and is involved in the synthesis of protein and fat. It increases cell permeability to monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids. It accelerates glycolysis, the pentose phosphate cycle, and glycogen synthesis in liver. Heterodimer of a B chain and an A chain linked by two disulfide bonds.Belongs to the insulin family. The insulin-link growth factors, IGF-I and IGF-II (also desinated somatomedin C and multiplication stimulating activator, respectvely), share approximatly 76% sequence identity and are 50% related to pro-insulin.IGF-I and IGF-II are nonglycosylated, single chain proteins of 70 and 76 amino acids in length, respectivelly. IGF-I functions as an autocrine regulator of growth in vaious, whereas the function of IGF-II is less well defined. |
| Function : Insulin decreases blood glucose concentration. It increases cell permeability to monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids. It accelerates glycolysis, the pentose phosphate cycle, and glycogen synthesis in liver. |
| Subunit : Heterodimer of a B chain and an A chain linked by two disulfide bonds. |
| Subcellular Location : Secreted. |
| DISEASE : Hyperproinsulinemia, familial (FHPRI) [MIM:176730]: An autosomal dominant condition characterized by elevated levels of serum proinsulin-like material. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent, 2 (IDDM2) [MIM:125852]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical fetaures are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These derangements result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal (PNDM) [MIM:606176]: A rare form of diabetes distinct from childhood-onset autoimmune diabetes mellitus type 1. It is characterized by insulin-requiring hyperglycemia that is diagnosed within the first months of life. Permanent neonatal diabetes requires lifelong therapy. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 10 (MODY10) [MIM:613370]: A form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. |
| Similarity : Belongs to the insulin family. |
| Database links : UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: P01315.2 pig |
胰岛素(Isulin)是胰岛细胞分泌的一种激素,可以降低血糖浓度。此抗体和人胰岛素反应,并与大多数哺乳类动物的胰岛素有交叉反应,主要用于胰岛细胞瘤的功能性研究。 |
| Anti-HCV-NS1 丙型肝炎病毒-NS1抗体 |
| Anti-HCV-NS3 丙型肝炎病毒-NS3抗体 |
| Anti-HCV-NS4a 丙型肝炎病毒-NS4a抗体 |
| Anti-HDL-R(High Density Lipoprotein Receptor) 高密度脂蛋白受体抗体 |
| Anti-Heamachrome 血红素抗体 |
| Anti-HEV 戊型肝炎病毒抗体 |
| Anti-HGF(hepatocyte growth factor) 肝细胞生长因子抗体 |
| Anti-HGV(Hepatitis G vivus) 庚型肝炎病毒抗体 |
| Anti-HHV4/EBV(Human herpesvirus 4 type 2/epstein-barr virus ) 人类疱疹病毒4抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF K2/vIL-6(Human herpesvirus 8) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF50(Human herpesvirus 8 type P) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF50(Human herpesvirus 8 type P) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF50(Human herpesvirus 8 type P) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF50(Human herpesvirus 8 type P) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
| Anti-HHV8/ORF K2(Human herpesvirus 8 type P) 人类疱疹病毒8抗体 |
风险提示:丁香通仅作为第三方平台,为商家信息发布提供平台空间。用户咨询产品时请注意保护个人信息及财产安全,合理判断,谨慎选购商品,商家和用户对交易行为负责。对于医疗器械类产品,请先查证核实企业经营资质和医疗器械产品注册证情况。
 文献和实验
文献和实验指仅对一种抗原决定基的纯粹的抗体。这类抗体不可能通过将抗原 胞的 Hybridoma,在试管内制成了纯粹的单克隆抗体。用某种抗原使动物产生免疫感应,对应于抗原之不同部分可制成各种不同的抗体复合体。然而,因为一个产生抗体的细胞,只能产生一种抗体,所以骨髓肿瘤细胞与产生抗体细胞间的细胞杂种,可形成边产生抗体边增殖的 hybridoma,将每个杂种细胞进行克隆(无性繁殖系)培养,则一个克隆的细胞群只由单种类产生同一抗体的细胞所组成,这样得到的就是单克隆抗体。此抗体在测定
1975年Kohler和Milstein发现将小鼠骨髓瘤细胞与和绵羊红细胞免疫的小鼠脾细胞进行融合,形成的杂交瘤细胞既可产生抗体,又可无性繁殖,从而创立了单克隆抗体杂交瘤技术。这一技术上的突破使血清学的研究进入了一个高度精确的新纪元。 免疫细胞化学的 技术关键之一是制备特异性强、亲合力大、滴度高的特异性抗体,由于每种抗原都有几个抗原决定簇,用它免疫动物将产生对各个决定簇的抗体,即多克隆抗体。单克隆抗体则是由一个产生抗体的细胞与一个骨髓瘤细胞融合而形成的杂交廇细胞经无性繁殖而来
以单克隆抗体为基础的免疫治疗 第1代单抗诞生于1975年,来源于小鼠的B细胞杂交瘤,称为鼠源单抗。但人的免疫系统会识针对此类识别单抗产生人抗鼠抗体,将其清除出体外而限制了它的应用。随后研制了人源化单抗,并于1988年进行了第1次商业性的临床试验。人源化单抗与鼠源单抗相比,具有以下的优点:特异性较强;不易发生过敏反应及免疫复合性疾病;在人体内维持的时间较长;可制备用于人的抗独特型抗体。制备人源化单抗可以采用人―鼠杂交瘤技术、人―人杂交瘤技术、EB病毒转化技术、EB病毒转化