Cayman Chemical Company,Inc.
入驻年限:4 年
- 联系人:
Kristina Whitfield
- 所在地区:
美国
- 业务范围:
试剂、抗体、细胞库 / 细胞培养、ELISA 试剂盒
- 经营模式:
生产厂商
推荐产品
公司新闻/正文
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ for the Rapid Screening of Protein-Lipid Interactions
人阅读 发布时间:2023-10-13 12:03
Our new Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are a simple tool for the rapid identification of protein-lipid interactions. Researchers can screen a protein of interest against 22 biologically relevant lipids in one assay in a single day at a lower price compared with existing commercial options.
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are Designed to Help Researchers:
-
Identify one or more lipids interacting with a protein of interest
-
Assess a protein's relative lipid-binding specificity
-
Identify protein candidates for in-depth lipid-binding analysis
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™: A New Tool to Study Protein-Lipid Interactions
Interactions between proteins and lipids have diverse and complex roles in various biological processes, ranging from the structure, function, and dynamics of biological membranes to host-pathogen interactions, metabolism, trafficking and localization, and cell signaling.1-3 As with more hydrophilic ligands, many proteins have lipid-binding sites and can specifically interact with lipids, which can modify the structure, conformation, and assembly of proteins to influence their recruitment, localization, and activation.1,4,5 Protein-lipid interactions have only been characterized for a small number of proteins, and there are likely many more lipid-binding proteins to be discovered.1
A better understanding of the important roles of lipids in modulating protein function through the identification of new lipid-protein interactions would be useful in the pursuit of new therapeutic avenues.
Workflow Overview
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are used to identify potential interactions between a target protein and 22 different lipids arrayed as a preconfigured panel using a protein-lipid overlay assay. The workflow is similar in many ways to a Western blot. The assay is simple to perform, low cost, and can be completed in a single day.
In brief, Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are blocked with blocking buffer and incubated with the purified protein of interest. Antibodies directed against the native protein or an appropriate affinity tag are added, followed by a secondary antibody carrying a reporter enzyme to allow detection using chemiluminescent, fluorescent, or chromogenic substrates. The assay results are visualized with standard imaging equipment based on the chosen detection reagent. The full protocol is provided with the product information (PDF).
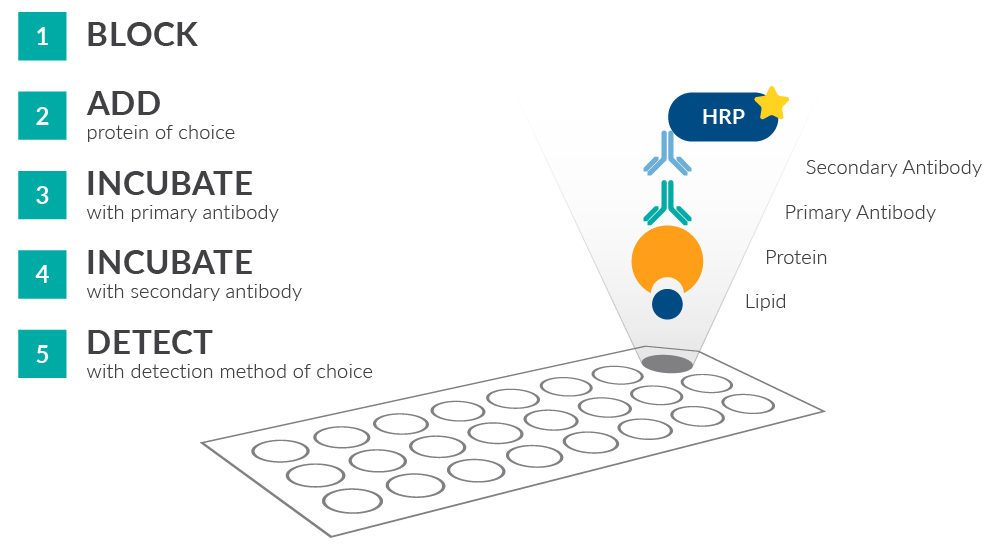
Figure 1. Overview of Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ workflow. Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are compatible with detection using native proteins or epitope-tagged proteins in conjunction with primary or secondary antibody reporters. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is shown above as an example, which in this case requires the final addition of an HRP substrate and its conversion to a product visualized at the appropriate wavelength. The full protocol is provided with the product information (PDF).
Capture a Protein-Lipid Interaction Profile with Cayman LipiDOT Strips™
Each Cayman LipiDOT Strip™ is spotted with 22 biologically relevant lipids and includes two blank (blue) spots for adding positive and negative controls. They are arranged in a 3 x 8 grid on a 3.175 cm x 6 cm supported nitrocellulose membrane.

Figure 2. Protein-lipid interactions are identified using Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ - PIPs Plus (Item No. 38924). GST-tagged PtdIns-(4,5)-P2 binding protein was used in this experiment.
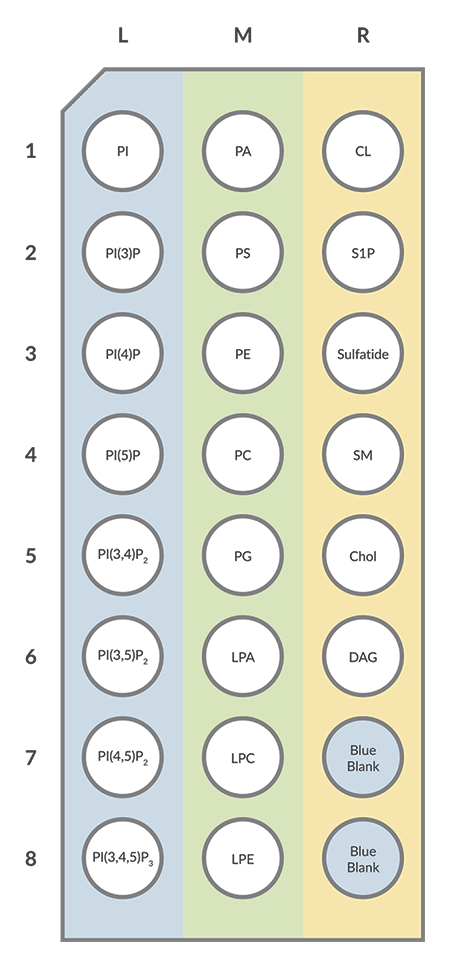
Figure 3. Location of lipids on Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ - PIPs Plus.
Phosphatidylinositol, PI ● Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, PI(3)P ● Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, PI(4)P ● Phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate, PI(5)P ● Phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate, PI(3,4)P2● Phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate, PI(3,5)P2 ● Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, PI(4,5)P2 ● Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate, PI(3,4,5)P3) ● Phosphatidic Acid, PA ● Phosphatidylserine, PS ● Phosphatidylethanolamine, PE ● Phosphatidylcholine, PC ● Phosphatidylglycerol, PG ● Sphingomyelin, SM ● 3-Sulfogalactosylceramide, Sulfatide ● Cardiolipin, CL ● Cholesterol, Chol ● Lysophosphatidic Acid, LPA ● Lysophosphatidylethanolamine, LPE ● Lysophosphatidylcholine, LPC ● Sphingosine-1-phosphate, S1P ● Diacylglycerol, DAG ● Blue Blank (Xylene Cyanol FF)
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ Feature Lipids with Diverse Biological Roles
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are carefully formulated with lipids that have diverse biological roles. Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ - PIPs Plus (Item No. 38924) is Cayman's first introduction in this new product group. It includes biologically relevant lipids, most of them components of cellular membranes. As such, several phospholipids and cholesterol are represented, as well as diglycerides and some sphingolipids.
Membrane phospholipids are well known for their role as the main component of membranes where they form the lipid bilayer due to their amphipathic character.6-9 Alongside cholesterol (chol), a major sterol component of mammalian cell membranes that interacts with membrane phospholipids, lipids interact with proteins to influence their behavior.
Phosphatidylinositol (PI, also known in the literature as PtdIns) is a class of membrane phospholipid that can be phosphorylated at different positions of the inositol ring to produce a variety of phosphatidylinositol (also known as phosphoinositide) phosphates (PIPs), a family of membrane lipids that act as crucial lipid signaling molecules.10 PIPs participate in many cellular responses by functioning as location markers, analogous to biochemical ZIP codes, organizing cellular proteins to particular sites and directing their activities through specific protein-lipid interactions. PIPs can also act as precursors for other second messengers, as, in the case of PIP2, IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG) through hydrolysis by phospholipase C. DAG molecules act as second messengers and recruit protein kinase C (PKC), a key enzyme family with roles in many signal pathways, to cell membranes.
Other membrane lipids can also be transformed into lipid signaling molecules that control a number of downstream responses such as cell migration, proliferation, and survival.11,12 Lysoglycerophospholipids, including lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), or lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) are formed by the PLA2-catalyzed hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids. The bioactive sphingolipid sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is structurally similar to LPA and can also be produced at membranes by hydrolysis of sphingomyelin (SM), which results in the release of the amino alcohol sphingosine, which can then be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase to yield S1P.
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ - PIPs Plus also include the membrane lipids sulfatide and cardiolipin (CL). Sulfatide is a sulfated glycosphingolipid that has a prominent role in the nervous system. It is abundant in the myelin sheath, a lipid-rich extension of the plasma membrane that protects axons and assists the transmission of electrical impulses between neurons.14 CL is a phospholipid and a major lipid component of the inner mitochondrial membrane with roles in bioenergetics and mitochondrial dynamics.15
Why Cayman LipiDOT Strips™
Cayman has made high-quality lipids available to the scientific research community for over 40 years. We offer an extensive selection of biologically relevant lipids that is supported by experienced scientists with state-of-the-art analytical equipment. View our Lipid Resource Center to explore more.
High-purity lipids are the backbone of Cayman LipiDOT Strips™. Our lipid experts make certain that lipids are carefully handled at every step to avoid lipid oxidation and are fully solubilized. We take these steps to ensure our assays are reliable and perform as expected.
Most lipids on the Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are available as an individual component for purchase. These tools are invaluable for complementary methods to Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ such as liposome co-sedimentation and co-floatation assays.9,13

Positive Control Proteins Are Also Available
Known lipid-binding proteins can be used as positive controls when incubated with a separate Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ performed in parallel or can be spotted on the blue blank spots within a single Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ experiment.
Proteins that may be useful as positive controls include:
Additional Resources
Custom Protein & Antibody Services
For proteins and antibodies that are not available commercially, custom solutions are available from Cayman. Cayman offers comprehensive recombinant protein production services that include multiple expression platforms, epitope tags, purification, and characterization services. Cayman also offers full service custom antibody production services, including antigen design and synthesis, antibody production, characterization, validation, and application-specific testing.
Structural Biology Tools for Confirmation
Cayman LipiDOT Strips™ are intended to be used as a first-pass for the rapid screening of protein-lipid interactions. Confirmation of protein-lipid interactions relies heavily on biophysical characterization and structural biology techniques.1
Our structural biology experts offer protein crystallization services and structure determination by X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM. We offer several biophysical characterization methods, including surface plasmon resonance (SPR), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and X-ray crystallography to further characterize protein-lipid interactions.
You May Also Be Interested In

References
1. Sych, T., Levental, K.R., and Sezgin, E. Lipid-protein interactions in plasma membrane organization and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 51, 135-156 (2022).
2. Corradi, V., Mendez-Villuendas, E., Ingόlfsson, H.I., et al. Lipid-protein interactions are unique fingerprints for membrane proteins. ACS Cent. Sci. 4(6), 709-717 (2018).
3. Zhao, H. and Lappalainen, P. A simple guide to biochemical approaches for analyzing protein-lipid interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 23(15), 2823-2830 (2012).
4. Bogdanov, M., Mileykovskaya, E., and Dowhan, W. Lipids in the assembly of membrane proteins and organization of protein supercomplexes: Implications for lipid-linked disorders. Subcell. Biochem. 49, 197-239 (2008).
5. Dowler, S., Kular, G., and Alessi, D.R. Protein lipid overlay assay. Sci. STKE 129, pI6 (2002).
6. Escribá, P.V., González-Ros, J.M., Goñi, F.M., et al. Membranes: A meeting point for lipids, proteins and therapies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12(3), 829-875 (2008).
7. Casares, D., Escribá, P.V., and Rossellό, C.A. Membrane lipid composition: Effect on membrane and organelle structure, function and compartmentalization and therapeutic avenues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20(9), 2167 (2019).
8. van Meer, G., Voelker, D.R., and Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9(2), 112-124 (2009).
9. Saliba, A-E., Vonkova, I., and Gavin, A.-C. The systematic analysis of protein-lipid interactions comes of age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16(12), 753-761 (2015).
10. Dickson, E.J. and Hille, B. Understanding phosphoinositides: Rare, dynamic, and essential membrane phospholipids. Biochem. J. 476(1), 1-23 (2019).
11. Kano, K., Aoki, J., and Hla, T. Lysophospholipid mediators in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol.17, 459-483 (2022).
12. zu Heringdorf, D.M. and Jakobs, K.H. Lysophospholipid receptors: Signalling, pharmacology and regulation by lysophospholipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1768(4), 923-940 (2007).
13. Senju, Y., Lappalainen, P., and Zhao, H. Liposome co-sedimentation and co-floatation assays to study lipid-protein interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2251, 195-204 (2021).
14. Barnes-Vélez, J.A., Aksoy Yasar F.B., and Hu, J. Myelin lipid metabolism and its role in myelination and myelin maintenance. Innovation (Camb). 4(1):100360 (2022).
15. Falabella, M., Vernon, H.J., Hanna, M.G., et al. Cardiolipin, mitochondria, and neurological disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 32(4):224-237 (2021).










